* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study guide for Late Middle Ages
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 11th century wikipedia , lookup
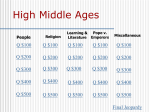
Study guide for Middle Ages 1. Who was Charlemagne? King of the Franks who was crowned Holy Roman Emperor Conquered and controlled most land in Western Europe since the Roman Empire Emphasized Christianity and Education 2. What is feudalism? It was the political and social system of the Middle Ages Started with the need for protection after the Roman Empire [central government] fell apart It provided stability by creating a rigid class system Power based on land ownership Characterized by the exchange of land for military service/loyalty o Vassal receives land in exchange for service 3. What was manoralism? It was the economic system of the Middle Ages It was based on farming [agriculture] The manor was self-sufficient Serfs worked the land in exchange for protection 4. What is the role of a knight? They were the warrior class Similar to samurai in Japan 5. What was the role of the Church in the Middle Ages? Church was a unifying institution Church collected a tax called a tithe [10% of income] 6. What were the Crusades? A series of religious wars fought between Christians and Muslims from the late 1000s to the mid-1200s Called for by Pope Urban II 7. What was the goal of the crusaders? To regain control of the Holy Land (Palestine/Jerusalem) from the Muslims 8. What were the causes for the Crusades? Free Holy Land from Muslim control Pope wanted to increase his power Nobles wanted to gain wealth and land Chance for adventure Serfs wanted to escape feudal manor 9. What happened during the first Crusade? Christians were successful in controlling the Holy Land Christian captured city of Jerusalem and massacred Muslim and Jewish inhabitants 10. What happened during the last (fourth) Crusade? Christians were diverted from their attempt to regain Jerusalem and knights began attacking the city of Constantinople [fighting other Christians] 11. What were some of the major results of the Crusades? Increased trade between Europe and Middle East- Europeans wanted goods from East o Led to growth of towns and cities Encouragement of learning o Cultural diffusion Hatred between different religious groups Feudal kings gained power Feudal system weakens 12. How did the development of towns and cities change Western Europe in the later Middle Ages? Rise in Middle Class [burghers] New ways of doing business- Commercial Revolution Guilds were created [organization of skilled workers] 13. What new farming techniques were introduced? Three- field system- farmers grew crops on 2/3 of land and allowed 1/3 to lay fallow o Farmers could grow more food and feed more people o More food leads to population growth 14. Which countries fought during the Hundred Years War? England and France fought for land in France and over the throne of France 15. Who did Joan of Arc say was speaking to her? Joan said that God spoke to her through his angels 16. What did Joan of Arc want to do? Joan wanted to lead the French Army against the English in order to have Charles VII crowned King of France 17. What was the result of the trial of Joan of Arc? Joan was accused of being a witch and of heresy [breaking church laws] She was burned at the stake 18. What was the bubonic plague? A highly contagious disease spread by the fleas that lived on rats 19. Where did the plague come from? The outbreak began in China and spread into Europe through increased trade 20. How did people react to the plague? People abandoned families and homes People despaired People turned to magic and witchcraft 21. How did it affect the population of Europe? One in three people died (1/3 of population of Europe) 35 million Chinese died 22. How did it affect the economy? Farm and industrial production declined Labor shortage led to workers demanding higher wages Peasant revolts took place Global trade was disrupted Feudal system broke down 23. How did England develop as a nation-state? William the Conqueror of Normandy won the Battle of Hastings in 1066 He developed the Domesday Book to keep track of population for taxation Henry II established common laws and set up a trial by jury system King John was forced to signed the Magna Carta in 1215 o Limited the power of the king [monarch] o Established concept that king is not above the law, but must obey it