* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Jewish Context- Persecution, Rebellion, and
The Invention of the Jewish People wikipedia , lookup
Hamburg Temple disputes wikipedia , lookup
History of the Jews in Gdańsk wikipedia , lookup
Interfaith marriage in Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish religious movements wikipedia , lookup
Index of Jewish history-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Jewish military history wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on religious pluralism wikipedia , lookup
First Jewish–Roman War wikipedia , lookup
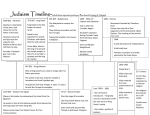
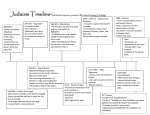
The Jewish Context- Persecution, Rebellion, and Division RELS 3300: Early Christianity Monday, January 23, 2017 Announcements • First blog response due on Wednesday, January 25th by MIDNIGHT (11:59pm)- The Roman Context, Lynch Ch. 3 + Ehrman Ch. 3 • See list on WordPress for Ehrman chapter titles (under “supplementary”) • Paper assignment discussion on Monday, January 30th Where we left off… • Solomon’s political, military, and economic policies caused division with in the kingdom of Israel. • Upon Solomon’s death, the kingdom split into two nations • Israel, in the North • Judea (Judah) in the South After Solomon and the Divided Kingdom • Israel conquered by Assyrians in (approx.) 722 BCE • Judah conquered by Babylonians in 597 BCE • King Nebachudnezzar • Babylonian exile Babylonia, Egypt, Asia Minor • Diaspora • Persia invades, conquers Babylonians in 538 BCE • Cyrus the Great • Jewish people allowed to return, many did not • Rebuilt and rededicated the Temple; the second Temple Under Foreign Rule • Persian rule (520-332 BCE) • Hellenistic rule/ Greek (332-63 BCE) • Roman rule (63 BCE- 395 CE) Hellenistic/Greek Conquest • Alexander the Great • Judea was part of his conquest of Egypt and the Near East • Antiochus IV Epiphanes (175-164 BCE) • Hellenization (171-168 BCE) • • • • Spread of Greek culture and language Overturned the Jewish priesthood Placed statues of Greek gods within the Temple, forced worship Forbade adherence to Jewish Law- no sacrifices, no circumcision, no kosher Discussion Question Why would Antiochus focus primarily on the elimination of Jewish religious practices? • Goal? • Methods? • Effectiveness? Maccabean Rebellion (167-160 BCE; war until 142 BCE) • Refusal to accept forced Hellenization • Mattathias the Hasmonean • Judas Maccabeus “The Hammer” • Establishment of Hasmonean dynasty • Small Jewish kingdom with Jerusalem at the center • Lasted approximately eighty years (142-63 BCE) Hasmonean Dynasty (142-63 BCE) Backlash against Hellenization 1. Separation and sense of superiority intensified 2. Strict observance of Mosaic Law enforced 3. Mutual dislike grows among neighbors and non-Jews 4. Precedence for martyrdom 5. Proliferation of apocalyptic literature This was not a great time; tensions inside and outside Roman Conquest and Rule • General Pompey, conquest of eastern Mediterranean shore, 63BCE • Jewish kingdom left under Jewish rule until 40 BCE • King Herod (“The Great”) • • • • 37-4 BCE Appointed by Roman Senate Hated by Jewish people Known for his building projects Why don’t they like me??? • Romans take direct control of Judea in 6 CE The Second Temple • Rebuilt after Babylonian exile in 516 BCE • Herod did massive renovations to the Temple in 20 BCE • Role of the Temple • • • • Economic center Daily religious rituals Pilgrimage site Strict designation of space (Jews and NonJews) Synagogues • “Houses of prayer” • Served daily religious needs of Jews living outside of Judea • Discussion of law- scribes • Charity, teaching, community Judaism(s)- General Beliefs • One true God • Mosaic Covenant • Observance of Sabbath • Mosaic Law • Dietary restrictions • Temple as holiest place • Willingness to die for religion • throne of Yahweh Judaism(s)- Sects Orthopraxy vs. Orthodoxy • Sadducees • Pharisees • Only the Torah • Aristocratic leaders • Rejected Messianic concepts • Worked closely with Romans • No Revolt • Esenes • Zealots • Josephus • Monastic, secret • Only God as • Adaptable; used oral society king and written law • Separated, • Rebellious; • Working class avoided Temple militant • Story Oriented • Battle between • No Revolt children of light + darkness Judaism(s)- Others • Proselytes • Gentiles that converted to Judaism • “God-Fearers” • Admirers of Judaism, but not converts Discussion Question How do you think class and social status affected belief and practice among the different Jewish sects? Diaspora • Caused by Babylonian exile; migration • Dispersion of Jews outside of Judea • Refers to a state of being, not a place • Jews living outside of Judea; they still consider Judea to be the homeland and themselves to be Jews Diaspora vs. Jerusalem • Jews were given special allowances by the Roman government • Peace was easy to maintain in the Diaspora than in Judea • Jews in Judea wanted direct rule of God, or through Jewish leaders • Tensions and rioting • Pontius Pilate • Caligula Discussion Question Why do you think Roman rule was more easily maintained among the Jewish Diaspora than among Jews in Judea? Jewish Wars- 66-73; 132-135 CE • High taxes and rent • Priests refused to sacrifice in the name of the Emperor • Titus attacks Jerusalem • • • • Five months of seige Captured the city in 70 CE Temple destroyed Triumphal Arch of Titus • 132-135 CE • Second unsuccessful rebellion Triumphal Arch of Titus, built 82 CE Results of Jewish Wars + Unsuccessful Rebellions • Synagogues became centers of Jewish worship • Without the Temple, movement toward text-based religion with strict emphasis on the Law • No converts • Rejection of Hellenization Discussion Question How do you think the failed rebellions between 66-135 CE shaped early Christian ideas? Looking Forward • The Greco-Roman context of the Jesus Movement • Roman social, political, and religious structure • Making connections- how does this all fit together? • The man, the mystery, the messiah(?)