* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Deserts
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
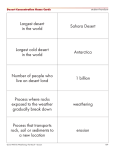
Deserts JERICA RODE AND TARA BANFIELD What is a desert? Less than 50 cm/year Occupies 20% of the land surface of the Earth Four types Hot and dry Semiarid Coastal Cold Where are they located? Deserts General Characteristics: Soil Lithosols Stone or mineral soil Evaporated water leaves deposits of salt Shrubbery and animals add nutrients General Characteristics: Plants Plant hair helps to reduce evaporation Produce small leaves in response to rainfall Some remain as seeds and only germinate during wet periods Ephemerals Hot and Dry Desert Annual temperature: 20-25°C Annual rainfall: 1.5 – 28 cm/year Plants Small, thick, and covered in cuticles Open their stomata at night Animals include species that are able to burrow Semiarid Desert Summer Temperature: 21-27°C Annual rainfall: 2 - 4 cm/year Plants Spiny for protection Some are glossy to reflect radiation Animals Avoid direct sunlight Coastal Desert Average temperature: 13-24°C Average rainfall: 8-13 cm/year Plants Some plants form ridges/grooves to hold water Thick fleshy leaves/stems to store water Animals Some are able to speed up their life cycle in ideal conditions Cold Desert Long, cold winters and warmer summers Annual temperature: -2 - 4°C Annual precipitation: 15- 26cm Plants are scattered Animals burrow