* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document 51144
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
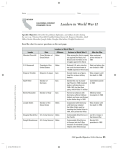
Causes of WWII 1. Problems in Europe from World War I. - - - World wide Depression Germany’s high World War I debt (remember Treaty of Versailles and reparations) High inflation – the value of money goes down over time. Massive unemployment Causes of WWII 2. Rise of Fascism: a political philosophy in which total power is given to a dictator. – – – Germany Italy Japan • Dictators of these countries became known as the Axis Powers Extreme nationalism and racism Individual freedoms are denied Censorship/ government controls the media Fascism What is it? Use of violence and terror Strong military Government controls the economy 3. Appeasement = giving in to Hitler’s actions to avoid war • The United States and other European countries did not want to get involved in other government’s disputes because of the Great Depression and the legacy of World War I United States Great Britain FDR Joseph Stalin Winston Churchill Truman USSR – United Soviet Socialist Republic Major Leaders of the War Franklin D. Roosevelt (Allied Power) • U.S. President – • • Elected in 1933 during the Great Depression and leads until his death in 1945. Enters war after attack on Pearl Harbor Dies three weeks before the end of the war Major Leaders of the War Harry Truman (Allied Power) • U.S. President after the death of President Roosevelt • Important at the end of the war by dropping atomic bomb and giving aid to worn-torn countries Major Leaders of the War Winston Churchill (Allied Power) • Prime Minister of Great Britain • Strong stand against Hitler • His speeches kept British morale high Major Leaders of the War Joseph Stalin (Allied Power) • Soviet Union (USSR) Dictator • Led communist party • Ruled for 30 years by fear and terror • Helped defeat Nazi Germany “The Big Three” Stalin, Roosevelt, Churchill Germany Japan Hideki Tojo Mussolini Adolf Hitler Hirohito Italy Major Leaders of the War Adolf Hitler (Axis Power) • Fascist dictator of Germany • Leader of the Nazi Party • Rose to power through propaganda • Started the “Third Reich” (Reich = empire in German) • Preached hatred of Jews Major Leaders of the War Benito Mussolini (Axis Power) • Fascist dictator of Italy • Aligned with Hitler • Fired by King of Italy in 1943 but is reinstated days later after Hitler takes control of Italy Major Leaders of the War Hideki Tojo (Axis Power) • Japanese General – leader of the military • Ordered attack on Pearl Harbor • Executed at the end of the war Major Leaders of the War Hirohito • Emperor of Japan • Viewed as a divine figure (God gave him the power to rule) • Japan’s military gained political influence during his rule 1939 - 1945 1. German Invasion of Poland: Sept. 1, 1939 Blitzkrieg -“Lightning War” – swift military offense, usually combining land and air forces • Germany invaded Poland, setting off war in Europe • The Soviet Union also invaded Poland and the Baltic nations • NAZI SOVIET PACT:1939, Germany and Soviet Union signed a pact to invade and control Northern and Eastern European nations. German troops marching into Warsaw, Poland (1939) 2. Germany invaded France and captured Paris (1940) • Italy invades France from the South and Germany takes over from the North – France Surrenders SOME FRENCH OPPOSED THE NAZIS and the Vichy Gov. Examples of groups organizing French resistance from Germany The Free French The Maquis General Charles DeGaulle Now Britain Is All Alone! 3. Battle of Britain (1940) • Germany bombed London. • Massive air strikes between the two countries • Germany was defeated • Also known as: Operation Sea Lion Battle of Britain excerpt: 4. Lend Lease Act – United States gave war supplies to Britain • At the start of the war, the United States remained neutral; however, were closely allied with Great Britain • The United States gave Britain war supplies and old naval warships in return for military bases in Bermuda and the Caribbean Video (4) 5. German Invasion of the Soviet Union • Operation Barbarossa – Hitler’s Biggest Mistake (Hitler breaks his treaty with Stalin) 5. German Invasion of the Soviet Union • Hitler’s biggest mistake because now he is fighting on TWO FRONTS! Operation Barbarossa: June 22, 1941 • 3,000,000 German soldiers. • 3,400 tanks. 6. Japanese Attack on Pearl Harbor (December 7, 1941) Known as: “A date which will live in infamy” Pearl Harbor USS Arizona, Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor from the Cockpit of a Japanese Pilot U.S. Enters World War II • After Japan bombed Pearl Harbor, the US declared war on Japan, so Germany declared war on the US • In response, the US declared war on Germany. Pearl Harbor Memorial • 2,887 Americans Dead! “ I fear all we have done is awaken a sleeping giant and fill him with a terrible resolve.” - Japanese Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto Stalin switches sides & the U.S enters the war. The “Big Three” is now created Winston Churchill, Franklin Roosevelt, Joseph Stalin Video 7. Battle of Midway – June 4-7, 1942 • US Navy destroyed Japan’s naval strength • Japan’s navy never recovered and was on the defensive after this battle. • Turning point of the war in the Pacific Battle of Midway – June 4-7, 1942 Video (11) 8. Battle of Stalingrad (July 1942 - February 1943) • Long battle between Germany and USSR • Deadliest battle of WWII – 1.5 million casualties. • Germany lost • Turning point of the war in Eastern Europe 9. D-Day - Operation Overlord (Allied invasion of Europe – June 6, 1944) Led by General Eisenhower and the allied forces D-Day (June 6, 1944) • Allied troops ferried across the English Channel and sailed from Britain to the beaches of Normandy, France • Germans retreat • Beginning of the end of war in Western Europe • V-E Day: May 8, 1945 Normandy Landing (June 6, 1944) German Prisoners Video (9) Atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki • In 1945, President Truman authorizes the United States to drop the atomic bomb on Japan. • The Manhattan Project – led by Robert Oppenheimer – was responsible for creating the atomic bomb Hiroshima – August 6, 1945 “Little Boy” © 70,000 killed immediately. © 48,000 buildings. destroyed. © 100,000s died of radiation poisoning & cancer later. Nagasaki – August 9, 1945 “Fat Man” © 40,000 killed immediately. © 60,000 injured. © 100,000s died of radiation poisoning & cancer later. Japan Surrenders – August 15, 1945 (V-J Day) Video (11) Japanese A-Bomb Survivors Video Outcomes of World War II 1. After the war, Britain and France were broke 2. Establishment of two major world powers: The United States and the U.S.S.R. 3. War Crime Trials • The Nuremberg War Trials: Crimes Against Humanity • Japanese War Crimes Trials Trial against SS German Officers General Hideki Tojo Those that did not make it to trial… The Führer’s Bunker Cyanide & Pistols Mussolini & His Mistress, Claretta Petacci Are Hung in Milan, 1945 Mr. & Mrs. Hitler 4. Division of Germany • Germany was partitioned (divided) into 2 countries – East and West Germany • East Germany was controlled by the USSR • West Germany was controlled by the USA, Great Britain, and France • Berlin (capital of Germany) was also divided into two 4. Division of Germany • East Germany and East Berlin were communist • West Germany and West Berlin were capitalist 5. United States takes control of Japan • Japan was occupied by American forces • Soon, Japan adapted a democratic government • Later, gained self government and became an economic super power 6. Creation of the United Nations • Improved the League of Nations • Goal: to prevent all future wars The Universal Declaration of Human Rights • Established and adopted by members of the United Nations • Provided a code of conduct for the treatment of people under the protection of their government 7. Marshall Plan • Created by General George Marshall (United States) • A plan to rebuild European countries • Gave money to European democratic countries to rebuild 8. Rapid US Economic Growth • After the war, defense plants switched to producing consumer goods • Americans bought goods on credit • New technology boomed • Women were forced out of factory jobs they gained during the war to make room for men returning from war • Labor Unions gained more power and gave workers higher salaries WW II Casualties: Europe Each symbol indicates 100,000 dead in the appropriate theater of operations WW II Casualties: Asia Each symbol indicates 100,000 dead in the appropriate theater of operations Country Men in war Battle deaths Wounded Australia 1,000,000 26,976 180,864 800,000 280,000 350,117 625,000 8,460 55,5131 40,334 943 4,222 339,760 6,671 21,878 Canada 1,086,3437 42,0427 53,145 China3 17,250,521 1,324,516 1,762,006 Czechoslovakia — 6,6834 8,017 Denmark — 4,339 — 500,000 79,047 50,000 — 201,568 400,000 20,000,000 3,250,0004 7,250,000 Greece — 17,024 47,290 Hungary — 147,435 89,313 India 2,393,891 32,121 64,354 Italy 3,100,000 149,4964 66,716 Japan 9,700,000 1,270,000 140,000 Netherlands 280,000 6,500 2,860 New Zealand 194,000 11,6254 17,000 Norway 75,000 2,000 — Poland — 664,000 530,000 650,0005 350,0006 — 410,056 2,473 — — 6,115,0004 14,012,000 5,896,000 357,1164 369,267 16,112,566 291,557 670,846 3,741,000 305,000 425,000 Austria Belgium Brazil2 Bulgaria Finland France Germany Romania South Africa U.S.S.R. United Kingdom United States Yugoslavia WW II Casualties 1. Civilians only. 2. Army and navy figures. 3. Figures cover period July 7, 1937 to Sept. 2, 1945, and concern only Chinese regular troops. They do not include casualties suffered by guerrillas and local military corps. 4. Deaths from all causes. 5. Against Soviet Russia; 385,847 against Nazi Germany. 6. Against Soviet Russia; 169,822 against Nazi Germany. 7. National Defense Ctr., Canadian Forces Hq., Director of History.