* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tectonic plates
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
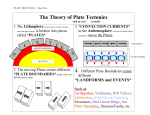
Review for Test Chapter 1 Plate Tectonics Georgia Performance Standard S6E5: Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. a. Compare and contrast the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. c. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. Essential Questions 1. What are the different layers of the Earth? 2. What properties describe each layer? 3. How was the continental drift theory developed? 4. What evidence exists for plate movement from the sea floor? 5. How did scientists develop the theory of plate tectonics? 1. Earth’s inner core and outer core are both: a) b) c) d) Parts of the molten asthenosphere Parts of the earth’s rigid lithosphere Completely solid spheres Made up of hot metals 1. Earth’s inner core and outer core are both: a) Parts of the molten asthenosphere b) Parts of the earth’s rigid lithosphere c) Completely solid spheres d) Made up of hot metals 2. How do Earth’s crust and mantle differ? a) The crust is much thinner and less dense than the mantle. b) The crust is much thinner and denser than the mantle. c) The mantle is much thicker and less dense than the crust. d) The mantle is much thinner and denser than the crust. 2. How do Earth’s crust and mantle differ? a) The crust is much thinner and less dense than the mantle. b) The crust is much thinner and denser than the mantle. c) The mantle is much thicker and less dense than the crust. d) The mantle is much thinner and denser than the crust. 3. Tectonic plates make up Earth’s a) Inner core b) Outer core c) Lithosphere d) asthenoshpere 3. Tectonic plates make up the Earth’s a) Inner core b) Outer core c) Lithosphere d) Asthenosphere 4. Most tectonic plates are made of a) Continental crust and oceanic crust b) The crust and the very top of the mantle c) Parts of the earth’s lithosphere and asthenosphere d) The rigid, upper mantle and part of the asthenosphere 4. Most tectonic plates are made of a) Continental crust and oceanic crust b) The crust and the very top of the mantle c) Parts of the earth’s lithosphere and asthenosphere d) The rigid, upper mantle and part of the asthenosphere 5. The mantle a) Is the Earth’s thickest layer b) Is the Earth’s thinnest layer c) Is less dense near the crust and more dense near the core d) Both a and c 5. The mantle a) Is the Earth’s thickest layer b) Is the Earth’s thinnest layer c) Is less dense near the crust and more dense near the core d) Both a and c 6. Which layer of the Earth is a thin layer of cool rock and surrounds the Earth somewhat like a shell? a) Mantle b) Inner core c) Outer core d) crust 6. Which layer of the Earth is a thin layer of cool rock and surrounds the Earth somewhat like a shell? a) Mantle b) Inner core c) Outer core d) crust 7. The lithosphere is made up of the following: a) The mantle and inner core b) The crust and all of the mantle c) The crust and the very top of the mantle d) None of the above 7. The lithosphere is made up of the following: a) The mantle and inner core b) The crust and all of the mantle c) The crust and the very top of the mantle d) None of the above 8. Why did many scientists reject Wegenar’s continental drift hypothesis? a) He could not explain how the continents moved b) The geology of the continents did not support the hypothesis c) Fossil evidence never showed that the continents were joined d) The climates of the continents have remained the same 8. Why did many scientists reject Wegenar’s continental drift hypothesis? a) He could not explain how the continents moved b) The geology of the continents did not support the hypothesis c) Fossil evidence never showed that the continents were joined d) The climates of the continents have remained the same 9. What was a super continent that existed about 200 million years ago? a) b) c) d) Ridge rush Pangaea Asian plate mass Biggie Continent 9. What was a super continent that existed about 200 million years ago? a) Ridge rush b) Pangaea c) Asian plate mass d) Biggie Continent 10. What is the transfer of heat by the movement of a material? a) Tectonic plates b) Earthquake c) Convection d) Divergent boundary 10. What is the transfer of heat by the movement of a material? a) Tectonic plates b) Earthquake c) Convection d) Divergent boundary 11. The lithosphere is broken into many large and small slabs of rock called a) b) c) d) mid-ocean ridges Convection current Tectonic plates Ridge rushes 11. The lithosphere is broken into many large and small slabs of rock called a) mid-ocean ridges b) Convection current c) Tectonic plates d) Ridge rushes 12. Geologists combined their knowledge of Earth’s plates, the sea floor, and the asthenosphere to develop the a) b) c) d) Pangaea Theory of plate tectonics mid-ocean ridges None of the above 12. Geologists combined their knowledge of Earth’s plates, the sea floor, and the asthenosphere to develop the a) Pangaea b) Theory of plate tectonics c) mid-ocean ridges d) None of the above 13. In the asthenosphere heated rock constantly rises, cools, sinks, and is heated again. This motion that transfers heat in a material is called a) Convection current b) Ridge rush c) Theory of plate tectonics d) convection 13. In the asthenosphere heated rock constantly rises, cools, sinks, and is heated again. This motion that transfers heat in a material is called a) Convection current b) Ridge rush c) Theory of plate tectonics d) convection 14. Huge underwater mountain ridges are called: a) b) c) d) Tectonic plates Convection currents mid-ocean ridges Ridge rushes 14. Huge underwater mountain ridges are called: a) Tectonic plates b) Convection currents c) mid-ocean ridges d) Ridge rushes 15. The lithosphere sits on top of the ______________________. a) Inner core b) Outer core c) Asthenosphere d) crust 15. The lithosphere sits on top of the ______________________. a) Inner core b) Outer core c) Asthenosphere d) crust 16. A ______________________ is when material from mid-ocean ridges pushes the plates. a) Tectonic plate b) Convection current c) Mantle d) Ridge rush 16. A ______________________ is when material from mid-ocean ridges pushes the plates. a) Tectonic plate b) Convection current c) Mantle d) Ridge rush Know the layers! 17.An enormous gap that forms when new crust cools and moves apart is called a ______________________. a) b) c) d) Rift valley Convergent boundary Magnetic reversal Hot spot 17.An enormous gap that forms when new crust cools and moves apart is called a ______________________. a) b) c) d) Rift valley Convergent boundary Magnetic reversal Hot spot 18.A __________________ occurs whenever two plates move toward each other. a) b) c) d) Divergent boundary Convergent boundary Magnetic reversal Hot spot 18.A __________________ occurs whenever two plates move toward each other. a) b) c) d) Divergent boundary Convergent boundary Magnetic reversal Hot spot 19.A __________________ can be used to track some plate movements because it stays in about the same place while the tectonic plate above it keeps moving. a) b) c) d) Rift valley Magnetic reversal Pangaea Hot spot 19.A __________________ can be used to track some plate movements because it stays in about the same place while the tectonic plate above it keeps moving. a) b) c) d) Rift valley Magnetic reversal Pangaea Hot spot 20.Plates move horizontally past each other along a ______________ . a) b) c) d) Convergent boundary Transform boundary Divergent boundary Magnetic reversal 20.Plates move horizontally past each other along a ______________ . a) b) c) d) Convergent boundary Transform boundary Divergent boundary Magnetic reversal 21.A spreading center is a __________________________ on the ocean floor. a) b) c) d) Convergent boundary Transform boundary Divergent boundary Magnetic reversal 21.A spreading center is a __________________________ on the ocean floor. a) b) c) d) Convergent boundary Transform boundary Divergent boundary Magnetic reversal 22.Patterns of _________________ recorded in ocean-floor rocks provide evidence of plate movement. a) b) c) d) Hot spots Magnetic reversals Pangaea None of the above 22.Patterns of _________________ recorded in ocean-floor rocks provide evidence of plate movement. a) b) c) d) Hot spots Magnetic reversals Pangaea None of the above 23.Subduction occurs a) Along a transform boundary on the ocean b) When two oceanic plates pull apart c) When two continental plates converge d) When an oceanic plate and another plate converge 23.Subduction occurs a) Along a transform boundary on the ocean b) When two oceanic plates pull apart c) When two continental plates converge d) When an oceanic plate and another plate converge 24.What happens during a continentalcontinental collision? a) Folded mountain belts form b) One plate sinks below the other plate c) Mountains with volcanic peaks form d) Island arcs form parallel to a trench 24.What happens during a continentalcontinental collision? a) Folded mountain belts form b) One plate sinks below the other plate c) Mountains with volcanic peaks form d) Island arcs form parallel to a trench 25.Island arcs, like the islands of Japan, form when two a) Oceanic plates scrape past each other b) Continental plates scrape past each other c) Oceanic plates converge d) Continental plates converge 25.Island arcs, like the islands of Japan, form when two a)Oceanic plates scrape past each other b)Continental plates scrape past each other c)Oceanic plates converge d)Continental plates converge 26.Crust is neither destroyed nor formed along a) b) c) d) Convergent boundaries Transform boundaries Oceanic-oceanic boundaries Oceanic-continental boundaries 26.Crust is neither destroyed nor formed along a) b) c) d) Convergent boundaries Transform boundaries Oceanic-oceanic boundaries Oceanic-continental boundaries