* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Computer Science 447 Advanced Topics in Artificial Intelligence
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
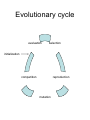
Natural Computation: computational models inspired by nature Dr. Daniel Tauritz Department of Computer Science University of Missouri-Rolla CS347 Lecture May 2003 What is Natural Computation? “Characteristic for man-designed computing inspired by nature is the metaphorical use of concepts, principles and mechanisms underlying natural systems” Quoted from the Leiden Center for Natural Computing The Bioinformatics link • Both straddle the fields of Computer Science & Biology • Bioinformatics’ computational demands are often ill-suited for conventional computational models • Natural Computation offers solutions capable of dealing with extremely large data sets, high dimensionality, complex pattern recognition, and sophisticated classification The Artificial Intelligence Link • Classic (symbolic) AI: game play, diagnostic expert systems, etc. • “True” intelligence eludes classic AI • Nature has produced “true” intelligence • Hopefully nature inspired computational models can achieve “true intelligence” too! Nature’s way of computing • Slow symbolic steps, but extremely parallel (resulting in weak numeric performance, but strong pattern recognition and classification capabilities) • High computational error rates, but very fault-tolerant (good at fuzzy logic) • Imperfect memory, but strong ability to learn/adapt (on the individual and/or population level) Nature inspired models • • • • Quantum Computing DNA/Molecular Computing Artificial Life Swarm Intelligence - Ant Colony Optimization - Particle Swarm Optimization • Artificial Immune Systems (Computational Immunology) • Artificial Neural Networks (Connectionism) • Evolutionary Computation • Quantum Computing based on quantum physics, exploits quantum parallelism; aims at non-traditional hardware that would allow quantum effects to take place • DNA/Molecular Computing based on paradigms from molecular biology; aims at alternatives for silicon hardware by implementing algorithms in biological hardware (bioware), e.g., using DNA molecules and enzymes • Artificial Life - attempts to model living biological systems through complex algorithms (examples: stem cell simulation, computational epidemics, gene regulatory system simulation, stock market simulation, predatorprey studies, etc.) Swarm Intelligence • Ant Colony Optimization – population based optimization technique inspired by the behavior of ant colonies • Particle Swarm Optimization – population based optimization technique inspired by social behavior of bird flocking or fish schooling • Artificial Immune Systems (Computational Immunology) • Artificial Neural Networks (Connectionism) Evolution • • • • • • • Individuals Population Environment Fitness Selection - selective pressure Reproduction Competition – survival of the fittest Heredity • Asexual versus sexual reproduction • Genes • Loci • Alleles • Genotype versus phenotype • Genetic operators: replication, recombination, mutation Evolutionary Computation • Solving “difficult” problems • Search spaces: representation & size • Evaluation of trial solutions: fitness function • Exploration versus exploitation • Selective pressure rate • Premature convergence Environment Problem (search space) Fitness Fitness function Population Set Individual Datastructure Genes Elements Alleles Datatype Evolutionary cycle evaluation selection initialization competition reproduction mutation Pros • General purpose: minimal knowledge required • Ability to solve “difficult” problems • Solution availability • Robustness Cons • Fitness function and genetic operators often not obvious • Premature convergence • Computationally intensive • Difficult parameter optimization Evolving versus learning • In EC learning occurs at the population level instead of at the individual level • In nature evolution and learning are combined • Darwinian evolution evolves the blue print of a learning system • Baldwin effect: phenotypic plasticity (e.g., learning [local search]) • Lamarckian evolution involves direct inheritance of characteristics acquired by individuals during their lifetime Natural Computation Courses Fall 2003 • CS378/Eng.Mg.378/El.Eng.368 Introduction to Neural Networks & Applications Dr. Dagli – Eng.Mg. • CS401 Introduction to Evolutionary Computation Dr. Tauritz - CS