* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 215: Physics for Engineers Part I
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
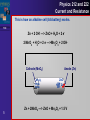
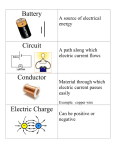
Physics 212 and 222 Current and Resistance TOC Current Batteries Basic Circuit Elements 1 Physics 212 and 222 Current and Resistance •Current is a measure of the movement of charge TOC 2 Physics 212 and 222 Current and Resistance TOC Current is defined as the amount of charge that passes through a surface in a given amount of time. Q I t The units of current are amps Q The direction of the current is opposite to the flow of electrons. It may be thought of as the flow of positive charge. 3 Current always flows from higher potential to lower potential. Physics 212 and 222 Current and Resistance TOC A battery uses chemical reactions to cause a potential difference between the terminals + - The maximum value of the potential difference of a battery is called its voltage In a circuit diagram we draw it like this V + 4 - Physics 212 and 222 Current and Resistance This is how an alkaline cell (AA battery) works. TOC Zn + 2 OH- —> ZnO + H2O + 2 e2 MnO2 + H2O + 2 e- —>Mn2O3 + 2 OH- Cathode (MnO2) Mn2O3 MnO2 MnO2 5 Anode (Zn) ZnO OH HOH O 2 - Zn Zn + 2MnO2 —> ZnO + Mn2O3 + 1.5 V Physics 212 and 222 Current and Resistance Current is defined as the amount of charge that passes through a surface in a given amount of time TOC Q I t The units of current are amps (A) The direction of current is opposite to the flow of electrons The current may be though of as the flow of positive charge Current always flows from higher potential to lower potential In other words, current flows from the positive terminal of the battery through the circuit to the negative terminal V In a circuit diagram we draw it like this 6 + I - Physics 212 and 222 Current and Resistance TOC The following circuit elements and their symbolic representation are the ones most commonly found in circuits. Name Battery Symbol - + V Resistor Capacitor Inductor V R Ω F C H L Switch S 7 Units Physics 212 and 222 Current and Resistance TOC Current Batteries Basic Circuit Elements 8