* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Terms - HULK SCIENCE
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
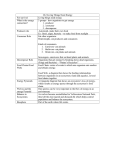
Vocabulary: Ecosystems & Plants 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Terms Anther Petals Pistil or Carpel Sepals Stamens 6. Pollen / Pollination 7. 8. 9. Stigma Style Ovary 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Ovule Fertilization Seed Fruit Germinate Flower Pollinators Filamant Angiosperm Gymnosperm Photosynthesis 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Chlorophyll Glucose Autotroph Heterotroph Respiration 26. Cellular Respiration 27. Cuticle 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. Definition (Male) Part that makes and holds the pollen Colorful part of the flower that attracts pollinators (Female) Entire female part of the flower Leaves protecting the bud (Male) Entire male part of the flower Yellow to orange grains that carry male DNA (Female) Receives pollen for fertilization (it is sticky) (Female) Holds pollen tube (Female) Holds ovules (eggs) (Female) Eggs (has female DNA) The process of pollen joining with an ovule to form a seed An ovule becomes a seed after fertilization After fertilization the ovary ripens into a fruit The process where a seed is transformed into a plant The entire reproductive part of an angiosperm Organisms like bees that spread pollen (Male) A long hair-like structure that holds the anther Plants that have a flower Plants that do not have a flower The process where plants use sunlight energy to change carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen The green pigment in leaves that reacts to sunlight Sugar for living organisms An organism that makes its own food (producer or plant) An organism that must eat its food (humans) The process where oxygen is used to release the energy in glucose (this is a chemical reaction. Respiration in living cells The protective waxy coating on leaves (keeps water from evaporating) Guard Cells Special cells that open and close the stomata Stomata Openings in the leaves that allow water and oxygen to escape the leaf. Transpiration The process a plant uses to bring water from roots to leaf tips. It begins with evaporation from the stomata. Tropism A plant turns as a response to something in the environment Ecosystem A group of interacting organisms and their environment Abiotic Factors Nonliving physical or chemical parts of an ecosystem EXAMPLE: rocks, sand, water, soil, climate 34. Biotic factor Living parts of an ecosystem EXAMPLE: plants, animals, microbes 35. Food Chain 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. A series of organisms each dependent on the next as a source of food EXAMPLE: eagle eats snake, eats bird, eats worm Food Web A system of connected food chains. A group of food chains in the same ecosystem Decomposer An organism of decay (eats dead stuff) Consumer An organism that gets (eats) energy from other organisms EXAMPLE: Tiger eats a student Producer Organisms such as green plants that produce food for other organisms Niche The purpose of a living thing in an environment EXAMPLE: A bee’s job is to pollinate Limiting Factor A factor in an environment that prevents or limits the growth of organisms. Example: a water shortage limits many animals Tolerance 43. Species 44. Biome 45. Habitat -A group of organisms with the same genetic make-up -A group of organisms with similar traits and characteristics -A group of organisms that can breed and produce offspring a large region with plants, life forms, and climate unique to that area: EXAMPLE: desert, rain forest, A particular organism’s environment (where it lives) EXAMPLE: turtle in a pond 46. Stimulus 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. Transfer Predator Prey Scavenger Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Dormancy 55. community 56. population An animal that hunts other animals for food The animal being hunted: ( An animal that eats already dead stuff (vultures, crows) Eats plants Eats animals Eats both plants and animals