* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14- Mesoderm-paraxial and intermediate
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
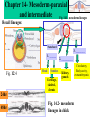
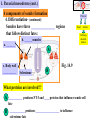
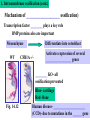
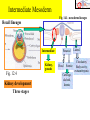
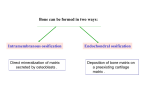
Chapter 14- Mesoderm-paraxial and intermediate Fig. 14.1- mesoderm lineages Recall lineages: Notochord 3. ________ 1. ______ Fig. 12.4 Head Somites Cartilage, skeletal, dermis 2. __________ Kidney, gonads 24hr 48hr Fig. 14.2- mesoderm lineages in chick Circulatory, Body cavity, extraembryonic Chapter 14- Mesoderm-paraxial and intermediate 1. Paraxial mesoderm Fig. 14.3 1. Paraxial Neural tube a. 4 components of somite formation 1. __________________• somites form from ____________ in regular intervals Head Somites Cartilage, skeletal, dermis • total number of somites is __ in chicks, __ in mice Mechanism? Involves the _______ gene _____ gene expression correlates with positioning of somites •This effect is _____________ of all surrounding tissue 2. __________________- mesenchyme is converted to epithelium prior to final somite formation • EM proteins fibronectin and N-cadherin link cells into clustered units 1. Paraxial mesoderm 4 components of somite formation (cont.) 3. ___________________________ •Distinct somites give rise to distinct __________ •Specific ___ gene expression predicts the type of vertebra formed Somites hox5 hox6 hox9 hox10 Fig. 11.40-Mouse somites mapped to vertebrate regions and to specific_____ gene expression Paraxial Head Somite Cartilage, skeletal, dermis 1. Paraxial mesoderm (cont.) 4 components of somite formation (cont.) 4. _____________________- somites form 1) cartilage of ____________ and ribs 2) ___________ of rib cage, limbs and back 3) dermis of the dorsal _________ Paraxial Head Somite Cartilage, skeletal, dermis Sclerotome cells Fig. 14.7 Some somite cells become mesenchymal cells again to form ___________________- these will become _____________ of vertebrae and ribs 1. Paraxial mesoderm (cont.) 4 components of somite formation 4. Differentiation- (continued) Somites have three ________________ regions that follow distinct fates: b. ______ muscles a. _______ Paraxial Head Somite Cartilage, skeletal, dermis A c. Body wall __________ Fig. 14.9 Sclerotome B What proteins are involved?? A ___________ produces NT-3 and ____ proteins that influence somite cell fate B ____________ produces ___________________ to influence sclerotome fate Myogenesis What dictates the muscle phenotype? ______ is a transcription factor that activates transcription factors Myf5 and MyoD Wnt? Pax3 Myf5 + MyoD MyoD binding site Muscle-specific genes Signaling pathway to activate muscle-specific genes (Figure not in text) Introduction of ______ into other cell types converts them to ______ Myoblasts fuse to form ___________ to produce muscle ______ Fig. 14.10 Osteogenesis (Bone development) What dictates the bone development? There are three lineages that produce bone1) ________ (vertebrae/ribs) 2) ________________ (limbs)- Not yet discussed 3) Cranial _____________ (head/face) Osteogenesis occurs by two mechanisms 1) _______________ossification- bone without cartilage precursor 2) _________________ ossification- cartilage converted to bone 1. Intramembrane ossification Mesenchyme ___________cells Differentiate into __________ (bone cell) Cell _____________ Differentiate into _________ (secrete collogenproteoglycan matrix) 1. Intramembrane ossification (cont.) Mechanism of ___________________ ossification) Transcription factor ________ plays a key role BMP proteins also are important Mesenchyme WT _______ CFB1A -/- Differentiate into osteoblast Activates expression of several _________________ genes ________ KO- all ossification prevented Blue- cartilage Red- Bone Fig. 14.12 Human disease- _____________________ (CCD)- due to mutations in the ______ gene 2. Endochondral ossification A Pax B Mesenchyme _______ C E D Proliferation ceases, ______ is modified __________ invade, Chondocytes die A B C D Fig. 14.13 Differentiate into__________ Proliferate and form _____ of bone by producing an EM F Adjacent cells (not chondrocytes) differentiate into __________ to fill in bone E F ______________ - cells which hollow out bones to form cavities • Osteoclasts enter through _____________ • Osteoclasts are likely form blood-lineage ____________ The disease ___________ occurs if too ______ osteoclast activity- bones become brittle The disease ___________ occurs if too ___________ osteoclast activity- bones are not hollowed out enough Intermediate Mesoderm Fig. 14.1- mesoderm lineages Recall lineages Intermediate Fig. 12.4 Kidney development Three stages Kidney, gonads Paraxial Lateral Circulatory, Head Somite Body cavity, extraembryonic Cartilage, skeletal, dermis Kidney development Three stages 1. ________________ arises from intermediate mesoderm just ventral to anterior somites and migrates toward tail 2. _________________ cells induce mesenchyme to form ______________(tubules) Pronephros Nephric Duct 3. Pronephric tubules degenerate, but a new set of _____________ tubules are formed (approx 30 in humans) further down Fig. 14.18 Kidney development Three stages Pronephros Stage 3. (cont.) The ________________produces: a. ______________ stem cells b. __________ carrying tubes (In some mammals) The ______________tubules are formed from mesenchyme, which induces ____________ buds (these become ureters that transport urine from _______________) Nephric Duct Fig. 14.18 Ureteric bud and metanephrogenic mesenchyme interact to become the kidney- called _______________________ Mechanism of ______________________ 1. __________________ mesenchyme (MM) formed 2. MM secretes GDNF and ____ to induce ___________________ formation Fig. 14.19 3. Ureteric bud secretes ____ and _____ to prevent _________ of MM 4. Ureteric bud secretes _____ to induce mesenchyme cells to aggregate and become ___________ 5. MM induces __________ of ureteric bud 6. _______________ and growth of the ureteric bud.