* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
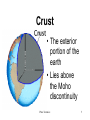
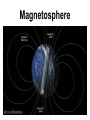
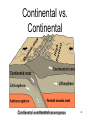
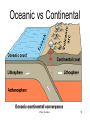
The Earths’ Interior Plate Tectonics 1 Earth Facts Plate Tectonics 2 Don’t copy this slide Happy the man whose lot it is to know the secrets of the earth. He hastens not to work his fellows' hurt by unjust deeds, but with rapt admiration contemplate immortal Nature's ageless harmony, and how and when her order came to be. Such spirits have no place for thoughts of shame. - Euripides (484-406 B.C.) Plate Tectonics 3 Inside the Earth Plate Tectonics 4 Crust • The exterior portion of the earth • Lies above the Moho discontinuity Plate Tectonics 5 Crust • 3 types of solid rock – igneous, sedimentary, & metamorphic • Oxygen & silicon • Oceanic crust 8 km thick: basalt • Continental crust 32km thick: granite & basalt Plate Tectonics 6 Don’t Copy • • • • • • • • • • Elements in the Crust Oxygen Silicon Aluminum Iron Calcium Sodium Potassium Magnesium Titanium Hydrogen Plate Tectonics 46.6% 27.72% 8.13% 5.00% 3.63% 2.83% 2.59% 2.09% 0.40% 0.14% 7 Mantle • Layer between the crust and the core • Silicon, oxygen, iron & magnesium • 870°-2200°c • 2900 km thick Plate Tectonics 8 Lithosphere • Thin outer shell of the earth • Consisting of the crust and the rigid upper mantle Plate Tectonics 9 Lithosphere • Rigid layer • Broken up into 7 major lithospheric plates Plate Tectonics 10 Plate Tectonics 11 Asthenosphere • Zone of the mantle beneath the lithosphere • Consists of slowly flowing solid rock • Plasticity: when solid rock flows Plate Tectonics 12 Plate Tectonics 13 Moho • The Mohorovicic discontinuity • Croatian scientist found increased speed of seismic waves • Boundary between the mantle and the earth’s crust • Reveals increase in density Plate Tectonics 14 Seismic Waves Plate Tectonics 15 Shadow Zones • Location on the earth’s surface where no seismic waves or only P waves can be detected. Plate Tectonics 16 Core • Central portion of earth • Below the mantle • Depth of about 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) • Consisting of iron and nickel • Liquid outer core and a solid inner core Plate Tectonics 17 Magnetosphere Plate Tectonics 18 Magnetosphere • Region of space that is affected by the Earth’s magnetic field Plate Tectonics 19 The Dynamic Earth Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics 20 Theory of Continental Drift • 1900’s Alfred Wegener proposed that the earth used to be one giant landmass that split to form today’s continents Plate Tectonics 21 Continental Drift • Pangaea • Panthalassa –“all lands” –a single landmass –origin of all the continents –“all seas” –giant ocean that must have surrounded Pangaea. Plate Tectonics 22 Wegener's Evidence for Continental Drift • The shape of continents suggests they once fit together –Noticed first in 1858 as soon as good maps were being made Plate Tectonics 23 Wegener's Evidence for Continental Drift • Fossils – The glossopterus flora and fauna are now found in widely separated continents in the southern Hemisphere. Plate Tectonics 24 Fossil Evidence • Fossils support Wegener’s theory • • • • Glossopteris Mesosaurus Lystrosaurus Cynognathus Plate Tectonics 25 Wegener's Evidence for Continental Drift • Paleoclimate evidence • Distribution of Paleozoic –Coral reefs –Coal beds –Deserts • 250-300 million years ago Plate Tectonics 26 Wegener's Evidence for Continental Drift • Rock types and mountain ranges can be traced across now widely separated continents. Plate Tectonics 27 Rock Evidence • Glacial deposits • Folded mountains • Coal deposits Plate Tectonics 28 Wegener's Evidence for Continental Drift • Evidence of ancient glaciers in all of the southern continents • Do you think all of this satisfied the critics? Plate Tectonics 29 Plate Tectonics 30 Where is the Force? • What makes the plates move? • The answer is on the ocean floor Plate Tectonics 31 Mid-ocean Ridge • System of undersea mountain ranges • Wind around the earth • 65,000 km • Ocean rocks much younger than continental rocks Plate Tectonics 32 Mid-Atlantic Ridge • Undersea mountain range • Steep, narrow valley down the center Plate Tectonics 33 Seafloor Spreading • Movement of the ocean floor away from either side of a mid-ocean ridge • Caused by convection currents Plate Tectonics 34 Seafloor Spreading Plate Tectonics 35 Convection Cells Plate Tectonics 36 Uneven heating causes movement in fluids Plate Tectonics 37 Paleomagnetism of the Ocean Floor • Magnetic fossil record of the alternating magnetic field of the ocean floor. Plate Tectonics 38 Plate Tectonics • Theory that the lithosphere is made up of plates that float on the asthenosphere • Plates possibly moved by convection currents Plate Tectonics 39 Plate Tectonics 40 Plate Tectonics 41 Types of Crust • Oceanic crust –Material that makes up the ocean floor • Continental crust –Material that makes up landmasses Plate Tectonics 42 Divergent Boundary • Formed by two lithospheric plates that are moving apart Plate Tectonics 43 Rift Valley • Steep, narrow valley • Formed as lithospheric plates separate Plate Tectonics 44 Convergent Boundary • Border formed by the collision of two lithospheric plates Plate Tectonics 45 Continental vs. Continental Plate Tectonics 46 Plate Tectonics 47 Plate Tectonics 48 Plate Tectonics 49 Oceanic vs Continental Plate Tectonics 50 Subduction Zone • Region where one lithospheric plate moves under another. Plate Tectonics 51 Ocean Trench • Formed when one oceanic crust is subducted under another oceanic crust Plate Tectonics 52 Oceanic vs Oceanic Plate Tectonics 53 Island arc • Chain of volcanic islands • Formed by subduction at ocean trenches Plate Tectonics 54 Plate Tectonics 55 Transform Fault Boundary • Formed by two lithospheric plates that slide past each other Plate Tectonics 56 Plate Tectonics 57 Theory of Suspect Terrains • – theory that continents are a patchwork of pieces of land that have individual geologic histories Plate Tectonics 58 The earth was made so various, that the mind of solitary man, studious of change and pleased with novelty, might be indulged. - Cowper, English poet Plate Tectonics 59 Plate Tectonics 60 Crust • Asthenosphere –Lithosphere Plate Tectonics 61 Continental Drift • Hypothesis stating that the continents once formed a single landmass • Broke up and drifted to their present location Plate Tectonics 62 The Earths’ Interior Plate Tectonics 63