* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homework 2
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
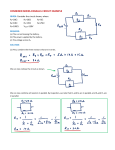
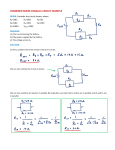
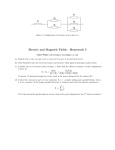
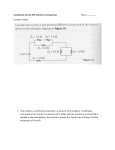
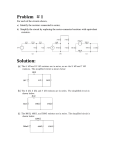
ECE 252 Introduction to Electrical Engineering Lesson 2. Resistors in Series and Parallel Homework Version S17 Homework partner name: _______________________Homework partner name: ________________________ Please note: You don’t need delta-wye transformation for this assignment. 1. Quickies a) Engineers define current as the flow of ( electrons, protons, negative charges, positive charges ). b) Some of the resistors in the circuit below ( are in parallel, are in series, are neither in series nor in parallel ). Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 2. R1 = 9 Ω, R2 = 24 Ω, R3 = 12 Ω, R4 = 5 Ω. Find the resistance between X and Y. The answer is an integer. RXY = Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 3. R1 = 38 Ω, R2 = 22 Ω, R3 = 15 Ω, R4 = 12 Ω. Find the resistance between C and D. The answer is an integer. RCD = Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 4. R1 = 84 Ω, R2 = 160 Ω, R3 = 240 Ω, R4 = 90 Ω. Find the resistance between E and F. The answer is an integer. REF = Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 5. R1 = 15 Ω, R2 = 4 Ω, R3 = 60 Ω, R4 = 14 Ω, R5 = 20 Ω, R6 = 30 Ω, R7 = 25 Ω, R8 = 75 Ω. Find the resistance between A and B. The answer is an integer. RAB = Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 6. a) Using exactly five 24 Ω resistors and no other resistors, design and sketch a circuit with a resistance of exactly 28 Ω. All five resistors must be significant parts of the circuit. b) Combine resistors in series and parallel to prove that your circuit has the correct resistance. Note: Don’t spend more than ½ hour on this problem. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 7. E is 40 V. R1 is 100 kΩ and has a tolerance of 20%. R2 is 50 kΩ and has a tolerance of 10%. What is the maximum possible voltage for Vout? What is the minimum possible voltage for Vout? Max Vout = Min Vout = Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ 8. E = 18V. R1 = 9 MΩ. R2 = 1 MΩ. A student uses a voltage divider in hopes of converting 18 V to 2 V, using the circuit shown. When the student connects a cheap volt-ohm meter (VOM) to Vout, she gets just 1.75 V. Explain why the voltage is lower than expected. Note: This problem has nothing to do with tolerance (the resistor values are correct), or temperature. Furthermore, the VOM does not have an accuracy problem. Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________ BONUS (no partial credit). What is the color code for a 91 kΩ resistor with a tolerance of 5% and 4 color bands? Signatures: ________________________________________________________________________