* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
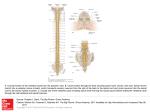
Direct and indirect motor pathways to the spinal cord. In the lateral view of the human brain; numbered areas are functional areas identified by Brodmann. The transverse section of the spinal cord shows three functional areas. The dorsal horn contains the sensory neurons of the spinal cord; the intermediate zone contains interneurons; and the motor nuclei zone contains the motor neurons that innervate the muscles. A. The corticospinal tract, also called the pyramidal tract, originates in a vast region around the central sulcus that includes the parietal lobe and the posterior part of the frontal lobe (areas 4 and 6). Area 4, the primary motor cortex, is the only area of motor cortex that directly connects with spinal motor neurons. Area 6 comprises various subareas, most of which send fibers to interneurons the intermediate zone of the spinal cord. The parietal lobe sends Source: Cognitive Functions of the Premotor Systems, Principles of Neural in Science, Fifth Editon fibers to the dorsal horns. Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available B. Indirect pathways to spinal motor neurons originate in 10, area2017 4 and area 6 and terminate in medial and lateral areas of the brain stem. The main at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May components Copyright of the medial pathways are the reticulospinal, medial and lateral vestibulospinal, and tectospinal tracts; they descend in the ventral column © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved and terminate in the ventromedial area of the spinal gray matter. The main lateral pathway is the rubrospinal tract, which originates in the magnocellular