* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 31.3 Vertebrates - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
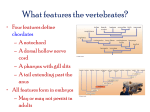
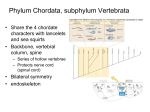
31.3 Vertebrates Vertebrate Intro Have all 4 chordate characteristics at some point of development Embryonic notochord generally replaced by vertebral column Generally a high level of cephalization (brain and nervous system) with complex sense organs Closed circulatory system Vertebrate Intro (cont’d) Jaw evolution allowed for easier predation Strong endoskeleton allows for large terrestrial organisms Complete digestive tract Generally, sexes are separate (not hermaphrodites) Sexual reproduction typical Vertebrate Intro (cont’d) Evolution of amnion (extraembryonic membrane that encloses a fluid filled sac) Some lay shelled eggs Others are placental (e.g. mammals) and development of offspring occurs in female uterus Fishes Evolutionary development: (from least to most evolved) 1. Jawless fishes (superclass Agnatha) a) b) c) d) e) About 63 species Cylindrical Up to 1 meter long Include hagfish and lampreys Some are parasitic Fishes (cont’d) 2. Cartilaginous fishes (class Chondrichthyes) a) About 850 species b) Include rays, sharks and skates c) Have jaws (adapted gill arches – structure that supports gills) d) Skeletons made of cartilage (not bone) e) Well-developed senses make good predators: a) b) c) Ability to sense electric currents in water Have lateral line system that allows them to sense pressure changes in water from movement nearby Keen sense of smell Fishes (cont’d) 3. Bony fishes (class Osteichthyes) a) About 20 000 species b) Most diverse class of all vertebrates c) Types of bony fishes: I. Ray-finned fishes i. Include fish we commonly eat: trout, cod, salmon ii. Have a pair of fins with thin bodies iii. Often have a swim-bladder, which regulates buoyancy iv. Water passes into mouth and out through gill slits: oxygen is absorbs and carbon dioxide given off v. Heart is simple pump with two chambers (one atrium and one ventricle) Fishes (cont’d) II. Lobe-finned fishes i. Evolved into amphibians ii. Had fleshy appendages that were adapted to limbs for terrestrial life iii. Had a lung used for respiration iv. E.g. coelacanth, though extinct 20 000 years ago was discovered off the coasts of Eastern Africa