* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1930s – The Rise of Hitler and Nazism in Germany
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
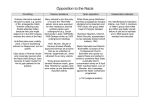
History of Canada 1930s – The Rise of Hitler and Nazism in Germany Germany had lost WW1. The Treaty of Versailles brought peace, but the Treaty also forced many concessions on Germany. The concessions included (1) paying reparation for war damages, (2) giving up land and colonies, (3) reducing its armed forces and (4) taking blame for WW1. Under these strict conditions, Nazism became a political force and eventually a totalitarian regime in Germany. There were a number of factors that led to the rise of Nazism? Why did so many Germans turn to Hitler and Nazism? ? ? ? ? ? ? Read the notes that follow this information (http://fcweb.limestone.on.ca/~stridef) and refer to your textbook In your notebook, make a chart similar to the one below From your research, identify the reasons why many Germans turned to Hitler and Nazism. Note: One reason, the Treaty of Versailles, is provided Provide examples, proof or rationale for each reason. Complete the table Also use Internet research to complete the second table about the role of other nations during this period AND answer the three questions about the idea of isolationism and Canada. Reason for rise in Nazism in Germany Treaty of Versailles Example, Proof or Rationale Grade 10 History of Canada Unit 3 Lesson 1 WORLD EVENTS LEADING TO WORLD WAR 2 How could Hitler and the Nazi Party have gained so much power so quickly? Country Rationale USA and Canada Britain France Russia Japan Italy Germany 1. Why policy of Isolationism a good policy? Explain 2. Why policy of Appeasement a good policy? Explain 3. Could Canada have played a different role? Grade 10 History of Canada Unit 3 Lesson 1 Answer Sheet WORLD EVENTS LEADING TO WORLD WAR 2 How could Hitler and the Nazi Party have gained so much power so quickly? USA and Canada ? Separated…and protected…by two oceans, and thus policy of isolationism ? Desire not to become involved in politics of other countries ? Needed to solve domestic problems of the Great Depression Britain ? Involved in own affairs of rebuilding empire ? Wary of Communist Russia ? Had world largest and most powerful navy – confident they were safe ? Tried to avoid war by signing Munich Agreement with Germany restricting German expansion – called Appeasement France ? Involved in own affairs of reconstructing country ? Wary of Communist Russia ? No desire to enter into another war ? Tried to avoid war by signing Munich Agreement with Germany restricting German expansion – called Appeasement Italy ? Formed an alliance with Germany ? Sought to expand powers (e.g., invaded Eastern Africa and Albania) Japan ? Formed an alliance with Germany ? Planned its own conquest for domination of Asia ? Invaded Chinese province of Manchuria in 1931, and by 1937 controlled all of China Russia ? Rebuilding after bloody Communist Revolution ? Building up a powerful army ? Under Stalin, intending to spread Communist form of government worldwide ? Signed non-aggression pact with Germany Germany ? Used Self-Determination” section within Treaty of Versailles affirming that people in different regions of Europe had the right to determine the form of government under which they would live to German benefit (e.g., claimed part of Czechoslovakia saying Germans living there want German government). Building armed forces secretly in Germany and Austria Grade 10 History of Canada - Unit 3 Lesson 1 NAZISM – HITLER’s RISE ? Hitler fought in WW1. He was a dispatch runner. He was wounded twice and survived a gas attack. For his service, he earned First and Second Class Iron Cross medals. ? The Treaty of Versailles humiliated Hitler. He also felt Germany was being corrupted by Jews and Communists. ? In 1919, he joined the German Workers Party, and by 1921, he became its self-imposed Chairman. He renamed the Party as the National Socialist German Workers Party (Nazi). The Nazi had 3,000 members. ? Hitler introduced his 25-point program that included the Final Solution for Jews (exclusion from society, ghettos, annihilate). ? In 1923, Hitler tried to stage a coup to overthrow the German government. Called the Beer Hall Putsch, the coup ended with 19 dead, many wounded and Hitler jailed for five years. The attempted coup was not a failure because it raised the profile of a political nobody. ? Hitler became more politically active. By 1933, he had been elected Chancellor of Germany with a majority of the seats in the German Parliament. NOTE: 63% of Germans did not vote for Hitler. They failed to vote with a unified voice against the Nazi. ? Almost immediately, Hitler enacted the Enabling Law. The law gave the Government the power for four years to enact laws without the input of the Parliament and deviate from the German Constitution. ? One week later, the Nazi passed the Temporary Law for the Coordination of the States and the Reich. Under this law, states were required to conform to the German Parliament. Hitler installed a Nazi Party member as the leader of each state. ? Police forces were combined to form the SS a nd the Gestapo. Soon afterwards, Germany became a police state. ? In 1933, Germany withdrew from the League of Nations. ? In 1934, Hitler began a campaign to purge Germany of his political foes. ? In 1934, the German Reich President died. Hitler abolished the title and declared himself Fuhrer. All troops were required to swear an oath of allegiance to Hitler…not to the country. ? After the “invited conquest of Austria”, Hitler looked at the Sudentenland of Czechoslovakia. Hitler noted that many people of German descent lived in this area, and that they wanted to be part of Germany. The Czechs were ready to fight, but the world was not. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain and French Premier Dadodian agreed to the German occupation of Sudentenland at the Munich Conference. By March 1939, Germany controlled, by force, all of Czechoslovakia. ? In August 1939, Germany signed a Non-Aggression Pact with the Soviet Union. In the pact, these two nations would not fight each other and they would divide Poland . Hitler could now concentrate his political efforts on his western border. ? In September 1939, Hitler demanded the Polish Corridor awarded to Poland in the Treaty of Versailles be returned to Germany. Poland refused. Germany invaded Poland using a new strategy of warfare called blitzkrieg or lightning warfare. It involved the rapid deployment of troops supported by air attacks on important military sites (e.g., supply depots, air fields). ? On 3 September 1939, Britain under Winston Churchill declared war. Two days later France declared war. Canada followed soon afterwards. ? For the next year, nothing happened, and Hitler readied his troops on his western border. Grade 10 History of Canada Unit 3 Lesson 1 WORLD EVENTS LEADING TO WORLD WAR 2 1933 ? Hitler is elected leader of Germany. Hitler is also the leader of the Nazi Party. ? Germany and Japan leave the League of Nations 1935 ? Hitler tears up the Treaty of Versailles and begins a massive build up of Germany’s army. Britain is too busy trying to rebuild its empire after WW1 to become involved. 1936 ? Spanish Civil War starts. The Spanish Army by Franco and its Nationalist supporters try to overthrow the Spanish Government. The Government is Republican, but they are portrayed as Communists. Russia supports the Republicans, while Germany and Italy help the Nationalists. Most other international powers do not get directly involved, but most countries fear the Communists and covertly back Franco’s Nationalists. ? German troops enter the Rhineland, an area of land between France and Germany. After WW1, France claimed the Rhineland and its rich natural resources. 1937 ? Guernica, Spain is bombed without warning by German planes. Guernica is a non-military target in Republican territory. The bombing kills over 2000 people. Pablo Picasso paints the picture Guernica to protest the bombing. 1938 ? Germany negotiates the Munich Agreement with France and Britain. Under the Agreement, Germany can claim part of Czechoslovakia as German land. ? Germany invades Austria by invitation of the Austrian leader. Germany is now the most powerful country in Europe. ? Germans attack Jews all over Germany. Thousands of Jewish shops are ransacked. The event is called Kristallnacht – “The Night of Broken Glass”. 1939 ? Germany invades all of Czechoslovakia ? Germany and Russia sign a Non-Aggression Pact and agree to divide Poland ? On 1 September 1939, Germany invades Poland. On 3 September 1939, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill declares war.