* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How our Solar System (and Moon) came to be
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
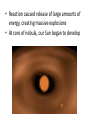
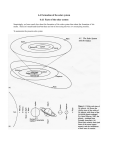
How our Solar System (and Moon) came to be… Learning Objectives • Be able to explain – How our solar system and moon came to be • IRAS launched into orbit 1983 – Direct evidence that solid matter exists around stars – Can cloud particles be early stages in the development of the planets? • Theory emerged: Planets form while star is forming Rotating Nebula Theory • Solar system began as collection of dust and gases (nebula) • This nebula made up of mainly hydrogen and helium gases – Also some solid particles like iron, rock, ice • These particles came from massive explosion of an older star called supernova – Supernova = star in it’s final phase of life, when it explodes it is many time it’s original size – Particles had moved closer together due to gravity • As nebula collapsed, internal pressure and temperature increased and more particles were attracted to nebula • Eventually temperature and pressure in the gas cloud was great enough for a complex reaction to begin • Reaction caused release of large amounts of energy, creating massive explosions • At core of nebula, our Sun began to develop • Early stages of the nebula began to rotate due to gaseous material • The speed of rotation became too great to hold al of matter together at center • Matter spread out from center like pancake • Bulge remained at center forming the Sun • While sun formed, smaller clumps of cooler matter called protoplanets began to appear in outer regions of nebula – Protoplanets condense to form planets of our solar system getting larger as they pick up debris • Likely how gas giants came to be • Sun flared up in a sudden burst of energy – Caused helium and hydrogen into the outer regions – Dense chunks of solid matter left behind • Formation of inner planets Other bodies in Solar System • Asteroids – Rocky object, smaller than a planet that orbits the sun – They orbit the sun between Mars and Jupiter (asteroid belt) – Asteroids often collide and break into pieces called meteoroids – “Falling stars” are meteoroids becoming meteorites as they pass into earth’s atmosphere • Meteors and Meteorites – Meteor – lump of rock or metal that falls from space towards earth’s surface – Meteorite – a meteor that is large enough to survive entry and reach the surface of the earth • Separated into 2 broad groups: stones and irons • Impact of meteorite creates a crater • Comets: – Usually name after their discoverers – Are made of rock dust and icy matter left over from the formation of the solar system – Ancients believed comets to be the soul of a hero or king on its way to heaven or messengers of disasters • Gas pushed out behind nucleus (Tail) • Nucleus (rocky and metallic particles coated with H20, ammonia, methane and CO2 • Come – formed as frozen substances begin to vapourize Formation of our Moon • Moon about 4.5 billion years old…. Similar in age to the Earth • How?? Why?? Big Splash Theory • Large object (size of Mars) collided with Earth • Collision caused high temperatures and pressures – This ended up in materials like iron to become part of Earth’s core • Less dense materials blasted into space – Ended up orbiting around the Earth • Materials began to condense and gravitate into each other through more heat and pressure