* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DETERMINATION OF SELF, Mutual inductnces
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Power dividers and directional couplers wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
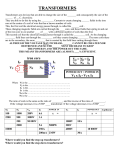
DETERMINATION OF SELF, MUTUAL INDUCTNCES AND COEFFICIENT OF COUPLING AIM To determine the self-inductance, mutual inductance and coefficient of coupling of the given 1- transformer. APPARATUS:S. No Name of the apparatus Range Type Quantity 1 Single phase transformer 230V / 115V, 3KVA - 01No 2 1- auto transformer 230V / 0-270V,10A, Induction 01No 3 Ammeter (0-2) A MI 01 No 4 Voltmeter (0-600) / (0-300) V MI 01No 5 Ammeter (0-2) A MC 01No 6 Connecting wires - - Required number 7 Voltmeter 0-1V MC 01No PRECAUTIONS: 1. Ensure the minimum position of autotransformer during power on and off. 2. Set the ammeter pointer at zero position. 3. Take the readings without parallax error. 4. Avoid loose connections. Circuit for finding ‘ M’ Value:- Circuit for self inductance (L1):- Circuit for self inductance (L2):- Theory:A voltage is induced in a coil when there is a time rate of charge of current through it. The inductance parameter L, is defined in terms of the voltage across it and the time rate of change of current through it V(t) = Where V(t) is the voltage across the coil. I(t) is the current through the coil,L is the inductance of the coil,Strictly speaking, this definition is of self-inductance and this is considered as a circuit element with a pair of terminals. Where as circuit element “mutual inductor” does not exist mutual inductance is a property associated with two or more coils or inductors which are in close proximity and the presence of common magnetic flux which links the coils. A transformer is such a device whose operation is based on mutual inductance. The two coils, or circuits are said to be inductively coupled, because of this property they are called “ coupled elements “ , are coupled circuits and the induced voltage or emf is called voltage (or) emf of mutual induction and is given by V2(t) = volts. Where V2 is the voltage induced in coil L2 And M1 is the co-efficient of proportionality and is called the co-efficient of mutual inductance or simple mutual inductance. The amount of coupling b/wn the inductively coupled coils is expressed in terms of the co-efficient of coupling which is defined as K= where M= mutual inductance b/wn the coils, L1 = self inductance of first coil, L2 = self inductance of second coil. Co-efficient of coupling is always less than unity, and has a maximum value of 1(or100%). This case, for which K=1 is called perfect coupling when the entire flux of one coil links the other. The greater the co-efficient of coupling b/wn the two coils, the greater the mutual inductance between them, and vice-versa. It can be expressed as the fraction of the magnetic flux produced by the current in one coil that links the other coil. The co-efficient of coupling k is a non magnetic number and is independent of the reference directions of the currents in the coils. If the two coils are a great distance apart in space, and K is also very small. For iron core coupled circuits, the value of K may be as high as 0.999, for air-core coupled ckts, K varied between 0.4 to 0.8. Circuit for RDC1: Circuit for RDC2:- Procedure:To find Z1: Apply rated voltage (V1) i.e 115 to primary winding and note down corresponding ammeter reading. Then find out Z given . We use auto transformer to vary voltage. To find Z2: Apply rated voltage i.e 230 to primary winding and note down corresponding ammeter reading. Then find out Z2 using the formula . To find Rdc1: Apply low voltage to primary winding i.e 115 V and note down corresponding ammeter readings. Then find Rdc given by and from this Rac1 = 1.0 Rdc. To find Rdc2 : Apply a low voltage to primary i.e 230V winding and note down corresponding ammeter readings. Then find Rdc2 given by and from this Rac2 = 1.6 Rdc2. To find M : Apply voltage of primary winding till the voltmeter in secondary reads 115V and note down corresponding ammeter reading in primary. To find Z1:- S.No V1 (Volts) I1 (amp) Z1 V1 Ω I1 V2 (Volts) I2 (amp) Z2 V2 Ω I2 V (Volts) I (amp) V1 (Volts) I1 (amp) R1 V1 Ω I1 V2 (Volts) I2 (amp) R2 V2 Ω I2 1 To find Z2:- S.No 1 To find M :S.No M=V/I 1 To find Rdc1:S.No 1 To find Rdc2 :- S.No 1 Calculations:XL1 = = XL2 = = XL1 = 2 fL1 L1 = XL2 = 2 fL2 L2 = Co-efficient of coupling K= Where M = = = Result:- Review Questions:1. Derive an expression for Mutual coupling coefficient. 2. Explain series aiding & series opposing in coupled circuit. 3. Explain parallel aiding& parallel opposing in a coupled Circuit 4. Two coupled coils with self-inductance L1 and L2 have 500 turns And 1000 turns respectively. The coefficient of coupling between Them is 0.8.The portion of flux that links both the coils when a current Of 5A flows through coil is 0.9 wb.Find the values of L1 and L2. CONCLUSION: The coefficient of coupling, K of the given 1- iron cored transformer is less than unity.