* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Which Constellation is Which?
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Planetarium wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
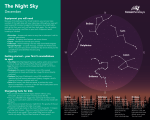
Objective – I can describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky. Constellations You probably know some constellations. The Big Dipper looks like a giant pot with a long handle. Orion is named after a great hunter. You can see his belt, marked by three bright stars. Constellations are imaginary pictures in the sky. The stars look like they are all the same distance away. That’s not true. The stars in the sky are different distances from Earth. Which Constellation is Which? When you look up at the sky, you may see shapes. Ancient stargazers created these shapes. They are the constellations. They are named after people, animals, and things that were important to them You can use a star chart that shows where stars appear in the sky. As the night passes, these shapes seem to move through the sky. It’s Earth that’s moving, not the Sun and stars. It’s rotating on its axis. You can only see the brightest stars with the naked eye. Look at the stars through binoculars or a telescope. Thousands of fainter stars can be seen. You can no longer see the shapes of constellations. ~1~ Objective – I can describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky. Do Constellations Always Look the Same? The Earth revolves around the Sun. This is why you see different constellations through the year. In the summer, we can’t see Orion because it is between the Earth and Sun. It is daylight. Six months later we can see Orion. It is on the side of Earth away from the Sun. People in the Southern Hemisphere see different constellations than people in the Northern Hemisphere. Southern Hemisphere Constellations Northern Hemisphere Constellations ~2~ Objective – I can describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky. Constellations shapes also change. It takes thousands of years for changes to be seen. They will look different in a hundred thousand years. Big Dipper – 100,000 years ago Big Dipper – Today Big Dipper – In 100,000 years How Do Astronomers Use Constellations? Astronomers divide the sky into 88 constellations. Astronomers name objects after their constellation. The Andromeda galaxy and the Orion nebula are examples. Earth sometimes passes through showers of meteors. The showers are named after the constellations from which they seem to fall. The Perseids and the Geminids are two examples. What Are the Constellations of the Zodiac? The Babylonians noticed the Sun’s position in the sky changes through the year. They divided the stars along the Sun’s path into twelve constellations. We call these twelve the constellations of the zodiac. (There are really thirteen!) ~3~ Objective – I can describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky. The constellation Ophiuchus (the Serpent Bearer) is the thirteenth. The Moon and the planets appear to move through the constellations of the Zodiac. Here’s what the Moon might look like travelling through Leo. May 13th May 15th May 17th Look at Saturn. We would say, “Saturn is in Leo.” Over six weeks, Saturn moves through Leo. When you see a planet, you will a couple of things. First, it will be brighter than the stars around it. And, it will not twinkle like the stars around it. Feb 9th Jan 16th Mar 1st ~4~