* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modeling Financial Crises: A Schematic Approach
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Economic bubble wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
Currency War of 2009–11 wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Currency war wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
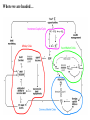
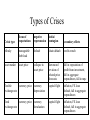
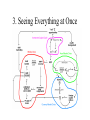
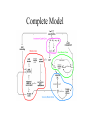
Modeling Financial Crises: A Schematic Approach John T. Harvey Professor of Economics Texas Christian University Book Idea: A Post Keynesian Analysis of Exchange Rates in the PostBretton Woods Era Revised Book Idea: Currencies and Capital Flows: A Post Keynesian Analysis of Exchange Rate Determination Currencies, Capital Flows, and Crises: A Post Keynesian Analysis of Exchange Rate Determination Mexican Financial Crisis: 1994 Asian Financial Crisis: 1997 •Minsky crises (debt default) •Currency crises (catastrophic depreciation/devaluation) •Asset-market crises (catastrophic depreciation) Goals of Paper 1. Show that all financial crises are manifestations of the same phenomenon 2. Highlight an often overlooked factor 3. Model the economy in a way that allows us to see “everything” at once 4. Compare the model to various historical incidents Where we are headed… 1. All financial crises are manifestations of the same phenomenon the development of increasingly optimistic forecasts alongside economic forces that cannot justify those expectations Stages of Crisis: shock => negative repercussions => contagion Types of Crises focus of expectations negative repercussion initial contagion secondary effects Minsky manageable debt load default chain default credit crunch asset market asset price collapse in asset price downward revision of related price forecasts fall in expectation of profit from investment, fall in aggregate expenditures, fall in mpc flexible currency price currency exchange rate depreciation capital flight inflation, FX loan default, fall in aggregate expenditures fixed currency price currency exchange rate devaluation capital flight inflation, FX loan default, fall in aggregate expenditures Crisis type 2. An overlooked factor The Investment-Capital Cycle 3. Seeing Everything at Once Minsky Crisis Asset-Market Crisis Currency-Market Crisis Complete Model Conclusions The root cause of financial crisis is the initially gradual and eventually rapid separation of expected returns from what the real economy can actually generate. Ultimately, evidence of the relative under performance of the nonfinancial sector will become known. Shock, negative repercussions, and contagion result. Depending on the magnitude, the economic impact can be significant and even catastrophic. This phenomenon is, given the current structure of market economies throughout the world, systemic. It does not require “crony capitalism,” unique events, or government “interference” with the market mechanism–it is, in fact, the market mechanism itself that causes this outcome.