* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SCIENCE 10 – Power Supply Conduction Insulation
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Electrical connector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
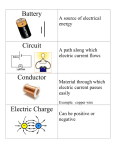
Technological World Electrical Function An electrical function is the role that a component plays in the control or transformation of electric current. Power Supply Power supply is the electrical function performed by any component that can generate or provide an electric current in a circuit. Battery Electrical Outlet Photovoltaic Cell Batteries Batteries transform the energy from a chemical reaction into electrical energy. Advantages: Portability Disadvantages: Must be replaced after a certain amount of time Can contaminate the environment if not disposed of properly Applications: mp3 players, watches, remote controls Electrical Outlet When the prongs of an electric plug enters an outlet, contact is made with parts permanently connected to an electrical network. Advantages: Stable & long-lasting power supply Hydro-electricity creates very little greenhouse gas Disadvantages: Appliances cannot be moved far from the wall outlet Appliances stop working in the event of a power shortage Applications: TVs, Fridges, Computers Photovoltaic Cell Photovoltaic (solar) cells generate an electric current when exposed to light. Advantages: Can power equipment in isolated areas without access to power grids. Can also power portable or mobile devices Do not cause greenhouse gas emissions Disadvantages: Their operation depends on sunny conditions. Very expensive Applications: Solar homes, solar cars, calculators Conduction Conduction is the electrical function performed by any component that can transmit electric current from one part of a circuit to another. Electricity is primarily conducted through wiring – usually copper. Components other than wires can also act as conductors. Ex: two pieces of metal that come into contact Ex: the human body Printed Circuits A printed circuit is an electrical circuit printed on a solid support called a circuit board. Printed circuits have replaced copper wires for the purposes of conduction in smaller electronic devices such as cell phones and MP3 players. A printed circuit is usually a plastic board 1mm thick covered in a thin layer of copper. The circuit board is then etched and finally all the excess copper is removed leaving only the electrical circuit printed on the board. Insulation Insulation is the electrical function performed by any component that prevents an electric current from flowing. Insulators are poor conductors so they prevent electrons from leaving wires. Plastics & ceramics make for good insulators. Protection Protection is the electrical function performed by any component that can automatically cut current flow in the event of a power surge. If a short circuit or electrical overload occurs, in order to avoid serious accidents like fires or shocks and to avoid damaging plugged in appliances, protective devices such as fuses or breakers can be connected to the electrical circuits. Fuses The electric current crosses the fuse through a conductive filament. If the current intensity exceeds a certain level, the filament melts and breaks, preventing the current from flowing through the fuse. The fuse then needs to be replaced. Breakers In some breakers, the current passes through a bimetallic strip. Other breakers use an electromagnetic mechanism. When the current intensity exceeds a certain level, the strip becomes hot, it bends, and the connection is interrupted. In order to restore circuit operation, the breaker switch must be switched back. The breaker does NOT need to be replaced. Resistance A resistor is a component designed to limit the flow of electrons through an electrical circuit. A resistor acts like a small-diameter pipe in a water supply system. Even if a large volume of water is present, the water flow will be restricted by the size of the small pipe. Resistors function in a similar way, by hindering the flow of electrons through a circuit. Resistance Electrical resistance is expressed in ohms – represented by the Greek letter omega [Ω] Ex: Resistor ‘A’ has an electrical resistance of 2500Ω. Resistance Resistance is usually indicated with a color code. The color of the first band corresponds to the first digit. The color of the second band corresponds to the second digit. The color of the third band corresponds to the multiplier. The color of the fourth band corresponds to the tolerance. THE COLOR CODE FOR ELECTRICAL RESISTORS: DIGIT MULTIPLIER TOLERANCE COLOR 0 1 ± 20% BLACK 1 101 2 102 3 103 4 104 5 105 6 106 7 107 8 108 9 109 Gold ± 5% BROWN RED ORANGE YELLOW GREEN BLUE VIOLET GREY WHITE GOLD Silver ± 10% SILVER Resistance