* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Pumping Heart
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
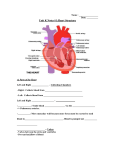
The Pumping Heart • The heart is enclosed in a double-walled sac called the pericardium. • The functions of the pericardium are: 1. Protects the heart 2. Anchors the heart • The heart is divided into 4 chambers. 1. Right Atria (top) 2. Left Atria (top) 3. Right Ventricle (bottom) 4. Left Ventricle (bottom) • The beating and rhythm of the heart are controlled by the sinoatrial node, which is sometimes called the pacemaker of the heart. .The SA node is a small mass of tissue in the upper wall of the right atrium. .The heart of a healthy adult at rest beats about 70 times a minute. • The heart has two muscular pumps that operate side by side. 1. Pulmonary Circulation The pulmonary pump is on the right side. It receives blood from the body and circulates it to the lungs. • 2. Systemic Circulation The systemic pump is located on the left side of the body. It receives blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body. • Pulmonary arteries take blood away from the heart. • Pulmonary veins take blood to the heart. • The "lubb" sound is produced when the atrioventricular valves in the heart close. These valves are between the atria and ventricles • . The "dupp" sound is created when the semilunar valve closes. These valves are located between the aorta and pulmonary artery. These valves are at the top of the heart and lead to the arteries that carry blood to either the lungs or the body. The "lubb" is the first heart sound and softer. The "dupp" sound is shorter and louder than the "lubb" sound. This is because the cusps of the semilunar valves are more rigid than the atrioventricular valves (mitral and tricuspid). • An abnormal heart sound is called a murmur. • Murmurs are caused by backflow of blood through a damaged valve or flow of blood through an abnormally narrowed valve. • Blood with waste products (deoxygenated blood) returns to the right atrium thorugh the superior and inferior vena cavae. • This blood is dull red because it has little oxygen in it. When the atrium contracts, the blood moves through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. When the ventricle contracts, blood is pumped through a valve to the pulmonary arteries and then to the lungs, where it releases carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen. • When oxygen enters the blood from the alveoli, the oxygen binds to the hemoglobin and the blood turns bright red. • The blood returns through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium. It then moves through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle. • The left ventricle pumps the blood into the aorta (the heart’s major artery) and the aorta branches off into the rest of the body. • No other muscle in the human body has the strength and endurance of the heart muscle. • The heart is 1/200 of the bodies weight but requires 1/29 of the body’s blood to function because it has a very high metabolic rate. • The coronary arteries supply the nutrients necessary to keep the heart beating. • If these arteries become blocked, a heart attack may occur. • Because the blood remains confined in the blood vessels, humans are said to have a closed circulatory system. • Creatures like insects, have an open circulatory system . Insects blood is sucked into the heart through small holes in its sides and pumped out through holes in the front. • Insects have no true blood vessels and their blood is mainly used to remove wastes, but not for oxygenation. • Heart Problems A number of things can affect the heart and its functioning: Smoking Air pollution Stress Lack of exercise Advanced aging may result in hardening of the arteries. Congestive heart failure occurs when the pumping ability of the heart is insufficient to circulate the blood throughout the body. Congenital heart defects account for a large percentage of infant deaths.