* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Egypt
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Animal mummy wikipedia , lookup
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian pyramid construction techniques wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta Stone wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Women in ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
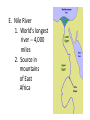
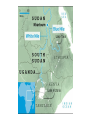
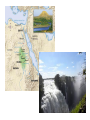
Ancient Egypt ANCIENT EGYPT I. Geography and location A. NE Africa 1. Southeast of ancient Greece and ancient Italy B. Mediterranean Sea -- to the north C. Red Sea – to the east D. Deserts called “red land” 1. Spread out on both sides of the river a. Western Desert – most of the Sahara b. Eastern Desert – smaller 2. Useless for farming 3. Offered protection from foreign attack E. Nile River 1. World’s longest river -- 4,000 miles 2. Source in mountains of East Africa 3. Forms S shape 1,000 miles long just north of where the Blue Nile and White Nile meet 4. Forms six cataracts or rock filled rapids a. The first cataract forms the southern border of ancient Egypt 5. Nile Delta – a triangular plain at the mouth of the Nile River 6. Flowed north and emptied into the Mediterranean Sea 7. Flooded annually providing rich farmland a. Grain 1.) Wheat 2.) Barley 3.) Flax 8. Provided transportation a. Traveled the Nile in small boats made from papyrus steered with oars and poles b. Worked well for short trips 9. Drinking water, bathing, and recreation II. Government A. Type of government system was a monarchy—rule by one B. Title for ruler 1. Kings 2. Pharaohs (after united) – people considered pharaohs living gods on earth C. Famous rulers 1. Hatshepsut—the world’s first woman ruler greatly increased Egypt’s wealth through trade. 2. Menes--united Upper and Lower Egypt and combined the red crown of Upper Egypt with the white crown of Lower Egypt forming the double crown. D. Three Kingdoms 1. Old Kingdom (2700BCE—2200BCE) a. “The Pyramid Age” b. Pyramids were used as burial tombs for pharaohs during this time. 2. Middle Kingdom (2100BCE) a. Egypt’s Golden Age b. Trade, arts, literature flourished c. Strong armies defended Egypt d. Pharaohs buried in hidden tombs 3. New Kingdom (1500BCE—1000BCE) a. Egypt expanded its borders through military conquest, became a world power b. Pharaohs buried in the Valley of the Kings E. Social Pyramid 1. Pharaoh at the top 2. Vizier—reported to the Pharaoh and was judge of the high court 3. Nobles, priests, doctors, engineers 4. Scribes 5. Artisans – craftsmen 6. Farmers, soldiers, tomb builders 7. Slaves III. Religion A. The ancient Egyptians were polytheistic or believed in many gods 1. Amon Ra (Re) or Ra--main god; sun god a. Human form b. Falcon head crowned with a sun disk and cobra c. Often shown holding the Ankh, the key of life 2. Anubis--god of mummification a. Head of a jackal b. Tail of a lion c. Body of a man 3. Osiris--god of the dead 4. Isis--wife of Osiris B. Monotheism – a belief in one God 1. Aten – the sun god a. Creator of the world b. Affected the world through his active presence 2. Practiced only for a brief time under King Akhenaten a. Upon his death, the Egyptians reverted back to worshipping their former gods C. Believed in an afterlife—belongings were buried with kings and pharaohs; they would need them in the next world D. Mummification—the process of preparing the dead for burial E. All most all homes had cats 1. They were thought to have magical powers a.) It was believed that cats were able to protect homes and children. 2. Hurting a cat was a serious crime. a.) A person could be sentenced to death for killing a cat. IV. Art and architecture A. Pyramids—burial tombs for kings and pharaohs 1. Contained burial chamber with treasure 2. Smaller rooms served as burial places for family members and servants B. Great Sphinx—lion’s body with the head of a pharaoh 1. The Great Sphinx faces the sunrise and guards the pyramid tombs C. Obelisk – vertical stone column topped with a pyramid 1. Monument with names written on them 2. Ancient Egyptians believed if their name was not written down by the time of their death then they disappeared forever D. Temples—Abu Simbel 1. 180 feet long 2. 90 feet high 3. Decorated with 60 feet high statues of Ramses II E. King Tut’s death mask 1. Made of gold, inlaid colored glass, and semiprecious stones F. Pottery – Used for cooking, storing food, and holding water 1. Used pottery to reflect their creativity a. Made from coiled clay and later from a pottery wheel b. Color was added c. Designs were scratched on the surface V. Law A. Pharaoh’s had absolute power, or complete control over their people B. Whatever the pharaoh decided became law. 1. He decided when the fields would be planted 2. He demanded crops from the workers at harvest time VI. Writing A. Hieroglyphics--picture symbols written on walls of tombs 1. Could be written in any direction: right to left, left to right, top to bottom, or bottom to top 2. Had to look like art B. Hieratic 1. Faster than hieroglyphics 2. Written by scribes on papyrus paper for record keeping C. Book of the Dead—instructions for preparing the dead D. Rosetta Stone– (discovered near Rosetta, Egypt) 1. Before the discovery of the Rosetta Stone, no one knew the meaning of the Egyptian hieroglyphics . 2. The stone contained same story in hieroglyphics, Demonic, and Greek 3. Since scholars could read Demonic and Greek they could figure out the meaning of the hieroglyphics 4. Once scholars had translated more of the writing on the stone, they used it as a basis to work on other Egyptian hieroglyphs. 5. The Rosetta Stone became the ‘key’ to unlocking the door to the messages and writings found in so many areas of Egypt.