* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Standard 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
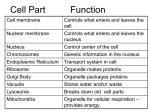
Standard 2 Vocabulary Review Name __________________________________ Match the term on the left with its definition on the right: ____ Activation Energy A. Structure provides extra support and protection for plant cells. ____ Active Transport B. These are cells where the genetic material is contained in membrane-bound nuclei. ____ ATP C. This is a jelly-like material that fills cells. ____ Base Pair Rule D. This is the use of biological processes, organisms, or systems to manufacture products intended to improve the quality of human life. ____ Biotechnology E. This is the main energy storage & transfer molecule in the cell. ____ Cancer F. Cell organelle that stores material. ____ Carbohydrate G. A thin, flexible, semipermeable barrier around all cells which regulates what enters and leaves the cell. ____ Cell H. This is the last part of the cell cycle. Process in which the cytoplasm is divided between the two new daughter cells. ____ Cell Cycle I. These are complex proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy. ____ Cell Division J. The series of events in a eukaryotic cell that involve growth, replication and division. (G1, S, G2) ____ Cell Membrane K. This is the foundation for DNA replication, the rule that states that adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) and that cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). ____ Cell Theory L. Energy stored in chemical bonds of molecules. ____ Cell Wall M. This holds an organism’s hereditary information; in nucleus. ____ Vacuole N. These are cells which have become modified and specialized within an organism. DIFFERENT! ____ Chemical Energy O. This is the result of uncontrolled cell division. Often caused by mutations. ____ Chemical Reaction P. This is the result of fertilization, in the early stages of growth and development. ____ Cytokinesis Q. This is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells that is the production and processing center of proteins & lipids. ____ Cytoplasm R. The process when molecules tend to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. ____ Differentiated S. This is the process of cell reproduction where cell splits into Cells two daughter cells. ____ Diffusion T. This is the process where cells engulf material from outside their cell membranes. ____ DNA U. States that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and cells come from pre-existing cells. ____ Embryo V. This is a compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (1:2:1); it is used by cells to store and release energy. ____ Endocytosis W. This is the energy needed to activate a reaction. ____ Endoplasmic Reticulum X. Structural and functional unit of all living organisms, and are sometimes called the "building blocks of life." ____ Enzyme Y. Process requiring energy for the movement of particles across a cell membrane against the concentration gradient. ____ Eukaryote Z. The changing of substances to other substances by breaking of bonds in reactants & formation of bonds in products. Match the term on the left with its definition on the right: ____ Exocytosis A. This is a process by which substances are transported across cell membranes by means of protein molecules. ____ Facilitated Transport B. This kind of cell has a large central vacuole and a cell wall. ____ Genetic Engineering C. This is the transport of material out of a cell by means of a sac or vesicle that first engulfs the material and then is exported through an opening in the cell membrane. ____ Golgi Apparatus D. A macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, which is used by the body for growth and repair. ____ Homeostasis E. Control center of the cell. ____ Hypertonic F. Organisms consisting of more than one cell, and having differentiated cells that perform specialized functions. ____ Hypotonic G. This is a process in which water moves through a membrane, from an area of high concentration to an area of low conc. ____ Isotonic H. One-celled. ____ Lipid I. Scale used to describe how acidic or basic a solution is. ____ Mitochondria J. These are organisms where the genetic material is not bound by a nucleus. They are usually unicellular. ____ Mitosis K. A non-energy requiring process that moves materials across a cell membrane with the concentration gradient. ____ Multicellular L. When the concentration of solute and solvent are equal on both sides of the membrane. ____ Nucleic Acid M. Specialized structures that perform specific cell functions. ____ Nucleus N. Process of manipulating the DNA code of living organisms. ____ Organelle O. This is an undifferentiated cell whose "job" within the organism is yet to be determined. ____ Osmosis P. Relatively constant internal physical and chemical conditions. ____ Passive Transport Q. A solution that causes a cell to swell because of osmosis. ____ PH R. This organelle serves to process and package lipids and proteins in the cell. ____ Virus S. A macromolecule made up of mainly carbon and hydrogen atoms that is primarily used for long term energy storage. ____ Plant Cell T. A microscopic parasite that infects cells in biological organisms. They reproduce only by invading & controlling cells because they lack cell machinery for self-reproduction. ____ Prokaryote U. The process of nuclear division in cells that produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ____ Protein V. Single strand nucleic acid that plays a role in protein synthesis. ____ Ribosome W. This organelle synthesizes proteins. ____ RNA X. This is a macromolecule that holds cell information in a coded form. Made of sugar, phosphate & nitrogen-containing bases. ____ Stem Cell Y. A solution that causes a cell to shrink because of the high concentration of solute in the solution surrounding the cell. ____ Unicellular Z. An organelle found in most eukaryotic cells described as "cellular power plants", because their primary function is to convert organic materials into energy in the form of ATP