* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AVOP-ELEKTRO-SMI-010
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
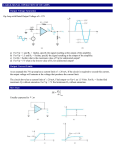
Tutorial: Mechanic - electrician Topic: Basics of electrical engineering the 2nd. year Measurement of current and voltage Prepared by: Ing. Jiří Smílek Projekt Anglicky v odborných předmětech, CZ.1.07/1.3.09/04.0002 je spolufinancován Evropským sociálním fondem a státním rozpočtem České republiky. Change AC and DC current and voltage: Resistance - joined in series a) rheostat - large current consumption b) potentiometer – small current consumption Change AC current and voltage: • Transformer – more economical than resistance • used transformer – Autotransformer Used method: Deflection method - voltage is measured by Ammeters to show the value of the measured current deflection or figure. Involvement of the measuring device: Ammeters are connected in series to the measured circuit Properties of the meter: • Power consumption is negligible - Ammeter does not affect the circuit, • Internal impedance (resistance) - infinitely small, at least significantly smaller than the impedance through which the current is measured. • does not have a rise in voltage drop across the A- meter Magnification range ammeter: • Shunt • constant device • kA = n x range/number of scale intervals • Measuring transformer current– MTP - only AC • nominal secondary voltage MTP I2 = 5 A (1A – for energy - billing metering) • transfer MTP pP = I1/ I2= I1/ 5 • Constant device with MTP kp = kA pP Magnification range of the ammeter: Calculation of the shunt • voltage on the A-meter - RA and shunt Rb is the same • Substituting according to Ohm's law • Expression RP after adjustment • We designate for the number, how many times we want to extend the range of the ammeter, the letter n • passes through the shunt a current (n - 1) times larger than the ammeter and the shunt must have a resistance (n - 1) times smaller than the resistance of the voltmeter. Used method: Deflection method - the voltage is measured by voltmeters showing the value of the measured voltage deviation or figure. Involvement of the measuring device: Voltmeters are connected in parallel to the measured circuit Properties of the measuring device: • Power consumption is negligible - a voltmeter does not have an affect on the circuit being measured,, • Internal impedance (resistance) - infinitely large - at least substantially larger than the impedance at which the voltage is measured. Magnification range of the voltmeter: • Series resistance - series a) connection via terminals - one series b) more series c) by using the ranges • Constant device • kU = n x range/ number of scale intervals • Measuring transformer voltage– MTN - only AC • nominal secondary voltage MTN U2 = 100 V • transfer MTU pN = U1/ U2= U1/ 100 • Constant device with MTN kp = kV pN Magnification range of the voltmeter: Calculation of series • Current in the circuit RP - RV is the same • Substituting according to Ohm's law or • Expression of RP after adjustment • If we need the range of the voltmeter to increase n-times, it must have a ballast resistor (n - 1) times larger, Name the ways of changing the current and voltage AC and DC circuit measurements ◦ current ◦ voltage - Describe the method of measuring current and voltage Draw and write the name of the methods involved in the measuring device for measuring current and voltage ◦ current ◦ voltage List and describe the characteristics of measuring devices for measuring voltage and current ◦ voltage ◦ current - Derive equations for a ballast device to enlarge the measuring range of the device voltage ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Derive equations for a ballast device for increasing the extent of current meter ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Mužík, J. Management ve vzdělávání dospělých. Praha: EUROLEX BOHEMIA, 2000. ISBN 80-7361-269-7. Operační program Vzdělávání pro konkurenceschopnost, ESF 2007 – 2013. Dostupné na: http://www.msmt.cz/eu/provadeci-dokument-k-op-vzdelavani-prokonkurenceschopnost Učebnice Elektrická měření – Ing. Pavel Vylegala, SŠE Ostrava, 2006 Učebnice Elektrické měření – SNTL, 1981 Elektrotechnika - Laboratorní cvičení pro bakalářské studium - Doc. Ing. Miloš Hammer, CSc.