* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Detecting B-Type Natriuretic Peptide to Better Diagnose Congestive
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
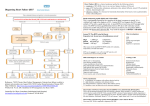
Detecting B-Type Natriuretic Peptide to Better Diagnose Congestive Heart Failure “Where there is stress, there is BNP.” Greenfield High School SMART Team: Tammy Tian, Jordan Tian, Panfua Thao, Robin Sandner, My Nguyen, Guetzie Maya, Elizabeth Konieczny, Amber Inman, Chi Huynh, Marlene Hagen, Hope Gueller, Nick Evers, Brayden Campagna, Tania Alvarez, Jodi Allison Teachers: Julie Fangmann and Martin Volk Mentor: Shama Mirza, Ph.D., Medical College of Wisconsin Abstract There are about 400,000 new cases of congestive heart failure (CHF) every year in the United States. CHF is a disease that interferes with the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently throughout the body. Major symptoms of CHF are fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea, sleeplessness, and swelling of the heart, lungs, and legs. One indicator of CHF is B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP), a hormone released due to stress on heart ventricles. A biologically active BNP molecule consisting of 32 amino acids (BNP-32) results from proteolytic cleavage of the precursor protein (originally 134 amino acids long). While CHF patients have a high concentration of BNP, high levels of BNP are not always due to CHF. BNP32 indirectly regulates sodium and water levels to reduce swelling. Natriuretic peptides, like BNP, do this by causing vasodilation and decreasing levels of certain chemicals that cause swelling. One of the receptors of BNP is Natriuretic Peptide Receptor-C (NPR-C), a clearance receptor found in the heart and other organs. When BNP binds to NPR-C, BNP is removed from the bloodstream and broken down, and swelling in that area reduces. Since CHF patients have a large amount of BNP, the receptors are unable to break down all of it and the swelling remains. Continual stress and swelling can be fatal. A way to measure the level of BNP in vivo could diagnose CHF before it becomes serious. Scientists are currently working on this through quantification of BNP using mass spectrometry (MS)based technology. Congestive Heart Failure Congestive heart Failure (CHF) is a condition where the heart insufficiently pumps oxygen-rich blood. Each year, there are 400,000 new cases in the United States. Some Causes of CHF: •High Blood Pressure ( hypertension) •Long term alcohol abuse •Disorders of the heart valves Symptoms of CHF: •Swelling of heart, lungs and legs •Fatigue •Shortness of breath •Wheezing •Chest Pain •Pneumonia •Nausea •Sleeplessness . The Role of BNP in the Heart 2. Different types of natriuretic peptide hormones (including BNP) are released due to the stress and swelling in the heart. 1. Stress and swelling of the heart (potentially due to CHF). BNP NPR-C 4. Natriuretic Peptide Receptor-C (NPR-C) is a clearance receptor that removes circulating natriuretic peptides (such as BNP). 6. In a CHF heart, BNP levels continue to elevate as the heart produces more than NPR-C can remove. This cycle continues until the stress on the heart is relieved or the heart ultimately fails. 5. In a healthy heart, BNP levels reduce. Swelling and stress on the heart also return to normal levels. Future Research Using Mass Spectrometry to Better Diagnose CHF Mass Spectrometer Inlet Ion Source Sample introduction Generates gas phase ions e.g. MALDI Mass Analyser(s) Separates ions by m/z and fragments ions Detector Computer Counts number of ions for each m/z e.g. electron multiplier •The best current bed-side CHF diagnosis equipment is only 81% accurate. Better methods of detecting BNP levels could help diagnose CHF patients. Instrument control and data acquisition Vacuum Chamber * CHF’s Connection to BNP O •CHF patients have a high amount of stress on their hearts. This stress triggers the release of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) into the bloodstream. * O Light isotope * Heavy isotope *with heavy isotopes •BNP is a protein naturally found in the human body, but CHF patients have a higher concentration of BNP. •A high concentration of BNP is only an indicator of CHF, but does not cause the disease. 3. These hormones signal other molecules to regulate salt and water levels in order to relieve swelling. •A mass spectrometer (MS) is an instrument that can identify and quantify molecules, such as BNP. The quantity of the desired molecule can be identified by adding the same molecule of known concentration, but with a heavy isotope . Multiple Reaction Monitoring BNP (B-Type Natriuretic Peptide) MRM of pdb file: 1YK1 Sources: http://www.medicinenet.com/congestive_heart_failure/article.htm; Images and data from the Mirza lab; pdb file: 1YK1 from He, X.L., Dukkipati, A., and Garcia, K.C.’s Structural determinants of natriuretic peptide receptor specificity and degeneracy. Reference: Hawkridge et al.PNAS 102 (2005) 17442 Ion source Analyzer Q1 Analyzer Q2 (collision cell) Analyzer Q3 Data Signal •One of the MS-based approaches, multiple reaction monitoring, combines several mass spectrometry tests to get a result with the greatest sensitivity and selectivity for measuring BNP. Scientists hope these methods will lead to a better method for early CHF diagnosis. SMART Teams are supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)- National Center for Research Resources-Science Education Partnership Award (NCRR-SEPA), and an NIH CTSA Award to the Medical College of Wisconsin.