* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Exam 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
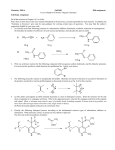
NOTE: PLEASE NOTE THAT THIS PRACTICE TEST IS ONLY MEANT TO GIVE YOU AN IDEA OF THE TYPES OF QUESTIONS THAT I WILL ASK. REMEMBER, THE NUMBER AND NATURE OF THE TOPICS I COVER IN A PARTICULAR YEAR VARIES BASED ON TIME AND NUMEROUS OTHER FACTORS. AS AN EXAMPLE, I SEE THAT THERE IS VERY LITTLE FROM CH 7, OSMOSIS, ETC! 1. a) (8 pts.) Provide the functional group names for the groups indicated. Functional group names are listed on the right and may be used (i) once, (ii) more than once, or (iii) not at all. Make sure you consider the entire group. Thyroxine A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. L. alcohol aldehyde alkene alkyne aromatic amide amine ester ether carboxylic acid ketone b) (2 pts.) In the structure of Thyroxine above, put a star on the chiral carbon atom(s). 2. (3 pts.) Which of the following pairs of compounds are cis-trans isomers? a) and b) and c) d) HC ≡ C-CH3 and CH3-C ≡ CH and R e) 3. and (3 pts.) Which of the following is NOT typical of most organic compounds? a) high melting point b) poor solubility in water c) low boiling point d) covalent bonding e) high flammability 4. (8 pts.) For each of the following solutions, indicate if the [OH-] concentration is greater than, less than, or equal to the [H3O+] concentration. a) acidic solution c) pH = 9 d) [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-6 M d) [H3O] = 1.0 x 10-8 M 5. greater than greater than greater than greater than less than less than less than less than (4 pts.) Pictured in the enclosed box below is one enantiomer of valine, an amino acid used by nature in synthesizing proteins. Which of the molecules on the right is the same enantiomer? CO2H H NH2 CH3 6. equal to equal to equal to equal to CO2H H2N H CH3 CH3 H CH3 NH2 CO2H H2N H CO2H O || (3 pts.) The common name of the compound CH3-C-OH is: a) butanoic acid. b) propanoic acid. c) propionic acid. d) acetic acid. e) butyric acid. R 7. (25 pts. total – 5 pts. each) For each reaction shown, (i) predict the major organic product(s) produced AND (ii) write the IUPAC name for the product molecule(s) that you determine. OH | CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2 CH3 | CH2=C-CH2-CH-CH3 | Cl [O] Pt + H2 CH3 O | || CH3-CH-CH2-C-O-CH2CH3 Η+ + OH | CH3-CH-CH-CH3 | CH3 H2O H+, ∆ O [O] + + 2Ag 2Ag(s) + H Cl R 8. (3 pts.) Alkenes and alkynes are called unsaturated compounds because a) they have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon in the compound. b) they have fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than alkanes. c) they have more hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than alkanes. d) they have more carbon atoms than alkanes. e) they have fewer carbon atoms than alkanes. 9. (3 pts.) A 10.0 mL of 0.121 M HCl is neutralized by 17.1 mL of KOH solution. The molarity of the KOH solution is a) 0.207 M b) 0.4141 M c) 0.0708 M d) 0.428 M e) 0.142 M 10. (4 pts.) Rank the following compounds (that have similar mass) in order of decreasing solubility in water: 3-pentanol (C5H11O), hexane (C6H14), 1-pentanal (C5H10O), and butanoic acid (C4H8O2). Most soluble 11. → Least soluble (3 pts.) Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidized because a) there are no oxygen atoms to remove from the alcohol carbon. b) there are no hydrogen atoms attached to the alcohol carbon. c) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no oxygen can be added to it. d) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no hydrogen can be added to it. e) the alcohol carbon is too electronegative to have hydrogen removed from it. R 12. (5 pts.) No matter how long you heat up the molecule shown below in the presence of an acid, it does not dehydrate. Based on your knowledge of dehydration reactions, briefly explain why a reaction does not occur for this molecule. OH 13. (3 pts.) What is(are) the product(s) of the complete combustion of any hydrocarbon? a) CO only b) CO2 only c) CO + H2O d) CO2 + H2O e) H2O only 14. (4 pts.) Draw the condensed structural formula of 4,5-dimethyl-1-hexyne. 15. (4 pts.) Consider the following acid/base reaction: HCl (g) + H2O (l) Cl- (aq) + H3O+ (aq) a) Is HCl a strong acid or a weak acid? b) What is the conjugate base of the acid HCl? R 16. (5 pts.) Glycerol (1,2,3-propanetriol) has a boiling point of 290 °C, while that of 1pentanol boils at 138 °C. Discuss the factors that contribute to the observed boiling points of each of these molecules, and then explain why glycerol has a higher boiling point than that of 1-pentanol. 17. (3 pts.) Which of the following pairs of compounds are constitutional (structural) isomers? a) CH2 - CH2 | | CH2 - CH2 and CH3 - CH - CH3 | CH3 b) CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH3 and CH3 - CH2 - CH3 c) CH3 CH3 | | CH2 – CH–CH3 and d) CH3 CH3 | | CH3 -C – C - CH3 | | CH3 CH3 18. and CH2-CH3 | CH3 - CH2 - CH - CH3 CH3 CH3 | | CH3 - CH – CH- CH2-CH2-CH3 (3 pts.) Which of the following statements concerning aromatic compounds is NOT true? a) A benzene ring can be represented by a hexagon with a circle inside of it. b) Aromatic rings are very stable. c) Benzene has conjugated pi bonds that are spread over the entire ring of C atoms. d) Aromatic rings undergo the same reactions as alkenes. 19. (4 pts.) A compound with the formula C4H8O has the following properties: (i) it can be made from 2-methyl-1-propanol and (ii) it oxidizes easily to give a carboxylic acid. What is the condensed structure of this compound? R