* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organization of the skeletal system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
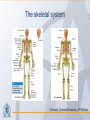
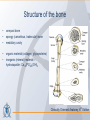
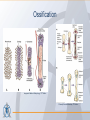
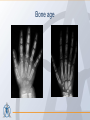
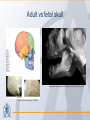
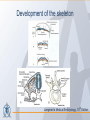
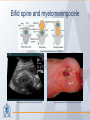
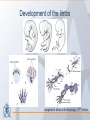
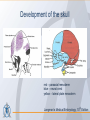
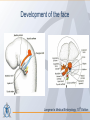
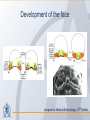
Organization of the skeletal system Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research Medical University of Warsaw Function of the skeleton • • • • • • movement protection haemopoiesis (bone marrow) calcium reservoir hearing moisturizing and warming the inhaled air The skeletal system • axial skeleton – skull – vertebral column – ribs and sternum • appendicular skeleton – skeleton of the girdle – skeleton of the free limb The skeletal system Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th Edition Tissues forming the skeleton • • • • bone cartilage fibrous connective tissue (most of ligaments) elastic connective tissue (ligamenta flava) Structure of the bone • • • compact bone spongy (cancellous, trabecular) bone medullary cavity • • organic material (collagen, glycoproteins) inorganic (mineral) material – hydroxiapatite: Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th Edition Structure of the bone • woven (bundle) bone – fetal bone – rapid remodelling – repair of fractures • lamellar bone – – – – – – osteons (Haversian systems) lamellae osteocytes canaliculi central Haversian canals Volkmann’s canals Gray’s Anatomy, 39th Edition Structure of the bone • periosteum – outer surface of the bone – thick fibrocollagenous layer – tethered to the bone by Sharpey’s fibres – important for repair of fractures • endosteum – – – – inner surface of the bone thinner and more cellular remodelling and repair calcium homeostasis Gray’s Anatomy, 39th Edition Cells of the bone • osteoblasts – derived from osteoprogenitor (stem) cells – synthesis and secretion of organic matrix (osteoid) – role in mineralization of osteoid – osteocalcin, alkaline phosphatase, pyrophosphatase – regulation of bone resorption (osteoclasts activity) – endosteum, periosteum, vascular canals within osteons • osteocytes – major cell type of mature bone – do not divide • osteoclasts – local removal and remodelling of bone – respond to cytokines, parathormon, 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D Bone marrow • red marrow – haemopoietic organ – all bones in fetus and children <5th year – in adults: vertebrae, sternum, ribs, clavicles, scapulae, pelvis, cranial bones, proximal ends of femur and humerus • yellow marrow – blood vessels and adipocytes (fat cells) – may be reactivated when necessary Cartilage • cells (chondroblasts, chondrocytes) • matrix (collagen – type II, proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans – chondroitin sulphate, keratan sulphate) • perichondrium Cartilage • hyaline cartilage – – – – – • homogenous, glassy, bluish opalescent costal, nasal, some laryngeal, tracheobronchial, most articular cartilages cell nests (mostly pairs of cells) surrounded by the matrix poor regenerative capacity prone to calcification in adults fibrocartilage – dense, fasciculated, opaque, white – fibroblasts and small groups of chondrocytes – intervertebral discs, articular discs, glenoid labra, cartilaginous lining of bony grooves, some articular cartilages • elastic cartilage – – – – typical chondrocytes yellow elastic fibers external ear, laryngeal cartilages vibrational functions Ossification • intramembranous – mesenchymal models of bones form during the embryonic period and ossify directly • endochondral – cartilage models of bones form from mesenchyme during the fetal period and ossify subsequently Ossification Langman’s Medical Embryology, 10th Edition Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th Edition Bone age Adult vs fetal skull material of the Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy, MUW Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th Edition Bone formations • • • • • • • • • Capitulum: small, round, articular head Condyle: rounded, knuckle-like articular area, often occurring in pairs Crest: ridge of bone Epicondyle :eminence superior to a condyle Facet: smooth flat area, usually covered with cartilage, where a bone articulates with another bone Foramen: passage through a bone Fossa: hollow or depressed Groove: elongated depression or furrow Head (L. caput): large, round articular end • • • • • • • • • • Line: linear elevation Malleolus: rounded process Notch: indentation at the edge of a bone Protuberance: projection of bone Spine: thorn-like process Spinous process: projecting spine-like part Trochanter: large blunt elevation Trochlea: spool-like articular process or process that acts as a pulley Tubercle: small raised eminence Tuberosity: large rounded elevation Pneumatization Fatu C, Puisoru M, Rotaru M, Truta AM. Ann Anat 2006;188:275-280 Fracture healing Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th Edition Development of the skeleton Langman’s Medical Embryology, 10th Edition Development of the vertebrae Langman’s Medical Embryology, 10th Edition Bifid spine and myelomeningocele Langman’s Medical Embryology, 10th Edition Perinatology and Prenatal Cardiology Clinic, MUW Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy, MUW Development of the limbs Langman’s Medical Embryology, 10th Edition Development of the limbs AER – apical ectodermal ridge Langman’s Medical Embryology, 10th Edition Limb anomalies • meromelia – partial absence of the limb • amelia – complete absence of the limb • phocomelia – rudimentary hands attached to the trunk by small, irregurarly shaped bones • micromelia – all segments present, but short • brachydactyly – shortened digits • syndactyly – fused digits • polydactyly – extra digits • ectrodactyly – absence of digits (usually the thumb) • lobster claw deformity - cleft hand and foot Development of the skull red – paraaxial mesoderm blue – neural crest yellow – lateral plate mesoderm Langman’s Medical Embryology, 10th Edition Development of the skull material of the Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy, MUW Development of the face Langman’s Medical Embryology, 10th Edition Development of the face Langman’s Medical Embryology, 10th Edition Thank you for your attention