* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroiditis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Thyroid disease
Historical information:
• Galen (1543) - first described the anatomy of the thyroid
•
•
•
•
•
•
gland.
Wharton (1656) - called iron "Thyroid".
King (1836) - studied the role of the glands in the
endocrine organs.
Baumann (1896) - have in particular the exchange of
iodine in the thyroid gland.
OV Nikolaev (1951) - made an enormous contribution to
the study of thyroid disease and suggested an operation
- strumectomy subtotal.
SA Masumov - identify and examine the endemic foci in
Ўzbekistane and suggested measures for prevention of
this disease.
Greater role in the study of thyroid disease in our
country have MS Astrov, R. Islambek, E. X. Turakulov.
The anatomical structure of the
thyroid gland
•
• 1-hyoid muscle schito-
2-share pyramid of
thyroid, 3-upper thyroid
artery, 4 left-hand share
the thyroid gland, 5isthmus of thyroid
gland, 6-lower thyroid
Vienna, 7 trachea, 8lower thyroid artery, 9
unpaired thyroidVienna, 10 right lobe of
thyroid gland, thyroid
Top 11 Vienna, 12
thyroid cartilage, 13 is
the upper laryngeal
artery, a 14-hyoid.
Weight cancer - 25-40g. Blood flow through the gland-150 ml /
sec
Schematic representation of the
structure of the thyroid
•
Hormones produced by the thyroid
gland
тироксин
тетрайодтиронин (Т4)
трийодтиронин (Тз)
Iodinated
Iodine does not contain
тиреколь
тиреокальцитонин
Research Methods
• Complaint, history, physical
•
•
•
•
•
•
examination, palpation,
Ultrasound
The study of blood hormones
Radioisotope scan
CT,
magnetic resonance imaging.
Biopsy, morphological study.
Palpation of the thyroid gland can be done
in two ways:
with the patient sitting with his
back to the doctor, with a
slightly tilted his head forward
and down. In this position, the
neck muscles relax and the
iron becomes more accessible
to study. The four fingers of
each hand are placed on iron
and include your thumbs
behind your neck.
with the patient standing
face to the doctor. In this
case, four fingers of each
hand cover the neck, back,
and thumbs of both hands
make palpation of the
thyroid gland. During
palpation of the prostate
patients are asked to make
swallowing movements,
which helps identify the
mobility of the cancer and
the nature of a hyperplastic
process (diffuse, nodular,
mixed crop)
.
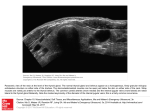
Thyroid scintiscan
Increased accumulation of radioiodine for diffuse
(left) and hub (right), toxic goiter
Fine-needle biopsy technique of thyroid
Classification of Thyroid Disease
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Congenital thyroid
Injuries thyroid
Inflammatory diseases of the thyroid:
- Thyroiditis (Hashimoto's struma)
- Strumity (Riedel struma).
Endemic goiter:
- Diffuse
- Hub
- Mixed
Sporadic goiter:
- Diffuse
- Hub
- Mixed
Graves 'Disease (Graves' disease, thyrotoxicosis)
Toxic adenoma (nodular toxic goiter)
Tumors of the thyroid gland:
- Benign tumor
- Cancer
Clinical manifestations of thyroid diseases
are caused by either excess
(hyperthyroidism) or under-production
(hypothyroidism), thyroid hormones, or
excessive production of calcitonin and
prostaglandins, as well as symptoms of
compression of the tissues and organs of the
neck enlarged thyroid gland without
violations hormone production
(euthyroidism).
Hyperthyroidism - thyroid disease, characterized by increased production of
thyroid hormones T4 and T3.
Hyperthyroidism - a clinical syndrome caused by long-term increase in the
concentration of secreted thyroid gland thyroid hormones in the blood and
tissues.
Hyperthyroidism in 60-80% of cases due to diffuse toxic goiter, is also being
developed in the body is an excess of thyroid hormone preparations and
preparations containing iodine (iodine-Basedow), toxic adenoma (Plummer's
disease), autoimmune thyroiditis, increased tissue sensitivity to thyroid
hormones, in infants born to mothers with hyperthyroidism.
Ocular symptoms of
hyperthyroidism
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Дельримпля
Штельвага
Грефе
Кохера
Мебиуса
Мелихова
Еллинека
Розенбаха
Зенгера
Дальмеди
Severity of hyperthyroidism
Mild form of hyperthyroidism - expressed mild conditions neurasthenia (fatigue,
irritability, tearfulness, and resentment). Against the background of a slight increase
in thyroid, labile pulse - from 80 to 100 per minute, a weak hand tremor. There
may be a slight weight loss. Reduced ability to work in the afternoon. Basal
metabolism does not exceed 30%. .
Thyrotoxicosis moderate - marked impairment of function of the central nervous
system (mild anxiety, irritability, tearfulness). The pulse rate of 100-120 per minute,
increased pulse pressure, increased heart with heart failure, I grade on Lang. A
significant reduction in body weight against the background of relatively high
power, reduced capacity for work during the day. Basal metabolism increased to
60%.
Severe form of hyperthyroidism - along with disorders of the nervous
system, characteristic of thyrotoxicosis of moderate severity, develop
sudden muscle weakness, severe dysfunction of the cardiovascular system,
degenerative disorders of the parenchymatous organs. Tachycardia can be
up to 120-140 beats per minute, often accompanied by atrial fibrillation,
heart failure, II-III degree of Lang. The main exchange of 60% or more,
with significantly increased feeding, body weight is significantly reduced.
Ability to work is lost.
Complications of hyperthyroidism.
Extremely serious complication of hyperthyroidism is
thyrotoxic crisis (hyperthyroid coma, Basedow coma), which
may develop thyrotoxicosis of moderate severity. Provoking
crisis factors are inadequate compensation of hyperthyroidism
for a long time, surgery on the thyroid gland, the accession of
any medical condition. Top of thyrotoxic crisis is characterized
by fever, agitation, changing adynamia, symptoms of
dehydration due to vomiting and diarrhea, a sharp drop in
blood pressure until he lost consciousness.
Treatment of thyrotoxicosis.
Specific treatment of hyperthyroidism is the
appointment of anti-thyroid, radionuclides, or
conducting surgery. Treatment of
thyrotoxicosis in nodular toxic goiter or mixed
and toxic adenoma operative.
Treatment of thyrotoxic crisis should be
comprehensive.
Surgeon treatment
Indications for surgical treatment:
• Allergies to drugs iodine
• toxic goiter of moderate and severe
forms of
• nodular toxic goiter (thyrotoxic
adenoma)
• large goiter, compressing organs of
the neck, regardless of the severity
of
• Mixed crop
Complications
• Intraoperative:
• Bleeding
• Damage to the
Postoperative:
thyrotoxic crisis
recurrent nerve
parathyroid
• Pneumathemia
tetany
• Damage to the
parathyroid glands traheomalyatsiya
• acute asphyxia
hypothyroidism
aphonia
Surgeon treatment
• By O. Nikolaev - subtotal subfascial
strumectomy.
• Methods Drachinskoy, Brady.
• Enucleation
• The method of Mikulicz
Hypothyroidism - a clinical syndrome caused by
decreased thyroid function (decreased production of
hormones T4 and T3).
Classification of hypothyroidism
Distinguish primary and secondary hypothyroidism.
In primary hypothyroidism decrease in production of
thyroid hormones associated with the pathological
process in the most iron.
Secondary hypothyroidism is caused by a pathological
process in the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
The pathogenesis of hypothyroidism is defined by a decrease
in biosynthesis and secretion in the blood of iodinated
thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
and the inhibition of all types of metabolism.
Hypothyroidism reduces oxygen consumption, heat
production and heat transfer, protein synthesis is disturbed,
the body accumulate products of protein decomposition.
Inhibited the metabolism of brain tissue, decreasing the
biosynthesis of many hormones. In the skin, subcutaneous
tissue, organs and tissues accumulated mucinous material,
which, holding the water, cause the development of a
peculiar mucosal edema. In severe hypothyroidism mucinous
fluid accumulates in the pericardial cavity, pleural and
abdominal cavities.
Conservative treatment
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
1. Small doses of iodine, lugol, seaweed.
2. Merkazolil
3. Beta-blockers
4. Cardiac glycosides
5. Methyluracil
6. Detoxification and stimulation of diuresis.
7. Restorative: anabolic steroids, and vitamins.
8. Blood transfusion, substituting drugs, transfusion of
plasma and protein drugs.
8. Physical therapy techniques - electrosleep, galvanic
collar, HBO.
9. Radioactive iodine (J131) (in the individual dose)
Malformations of the thyroid gland.
Aplasia (absence) of the thyroid gland is rare, due to
violation of differentiation of the embryonic rudiment of
thyroid tissue is found in early childhood on the basis of the
clinical picture of severe congenital hypothyroidism.
Congenital hypoplasia of the thyroid gland develops as a
result of iodine deficiency in the mother, clinically cretinism
and delayed physical development of children.
The main type of treatment of both pathologies - a lifelong
hormone replacement therapy. Offset of the rudiment of
thyroid gland in the mediastinum leads to the development
of retrosternal goiter or tumor. The source of their
formation may also be dystopic in the wall of the trachea,
pharynx, myocardium, pericardium foci of thyroid tissue
Damage to the thyroid gland
Damage to the thyroid gland are extremely
rare, usually they are combined with injuries to
other organs of the neck. Typically, damage to
the open, accompanied by profuse bleeding,
requiring emergency surgery. Closed injury
observed in the compression of the neck (for
example, a gin with suicidal attempt), manifest
the formation of a hematoma.
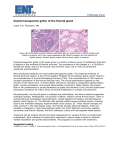
Autoimmune (Hashimoto's disease
limfomatozny) thyroiditis - an autoimmune
disease, which is the most common of all
diseases of the thyroid. Its prevalence in
children ranges from 0.1 to 1.2% and from
6 to 10% among women older than 60
years. In the general population for every
10-30 adult females have a case of
autoimmune thyroiditis.
Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's disease lymphocytic) should be divided
into:
[Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis (the most frequent clinical form - enlarged
thyroid gland diffuse II or II-III degree, usually without violating the function
of the gland, may experience mild manifestations of hyperthyroidism or
hypothyroidism);
[Hypertrophic form of autoimmune thyroiditis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis or
(thyroid dense, diffuse, its function is not broken, but more frequent moderate
disturbances of its function - hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism)
[Atrophic form of autoimmune thyroiditis (thyroid gland has never been larger
or had noted a mild increase in thyroid cancer, and at the time of the survey
volume of the thyroid gland does not enlarged, functional - hypothyroidism).
The etiology and pathogenesis.
The immune system produces antibodies
against its own thyroid gland. It was
found that this disease revealed
antibodies to thyroglobulin and thyroid
peroxidase to (microsomal antigen).
Hashimoto's thyroiditis tends to occur in
the form of family forms of the disease.
Antitiroid titer antibodies in autoimmune
thyroiditis depend on the activity of the
autoimmune process and may decline with
increasing duration of disease.
The clinical picture in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis
During the first years of complaints and symptoms of the disease are usually
absent. Thyroiditis with clinical hyperthyroidism, usually occurs in the first few
years of the disease, is temporary in nature and in the future, as the
destruction and reduction of functioning thyroid tissue it is replaced at some
time eutirozom, and then - hypothyroidism. In the hypertrophic form of
autoimmune thyroiditis thyroid gland is enlarged, with atrophic form of the size
of a normal or even reduced
The main complaints
patients are associated with an increase in thyroid cancer: a feeling of
difficulty swallowing, difficulty breathing, often a little pain in the thyroid gland.
Increase its symmetrical, iron, usually solid consistency at palpation and
defined "irregularity" - varying the density and elasticity of the surface
"nodularity"
In the hypertrophic form of
autoimmune thyroiditis and severe
compression of the phenomenon of
mediastinal enlarged thyroid gland,
surgery is recommended. Surgery is
also indicated in cases where the
long-existing moderate increase in
thyroid gland begins to progress
rapidly in volume (size).
Subacute thyroiditis
- An inflammatory disease of the
thyroid gland, probably of viral
etiology, as described in de Kervenom
1904. The disease can be acute,
chronic or recurrent. Subacute
thyroiditis occurs 3-6 times more often
in women aged 20-50 years.
Subacute thyroiditis preceding the development of the following symptoms:
malaise, weakness, fatigue, muscle aches, mild fever, impaired function of the
gastrointestinal tract. These states are considered "influenza virus" infection.
Typically, the development of subacute thyroiditis begins after recovery (after a few
weeks or months) from the previous viral infection. We describe the cases of the
disease after infection caused by adenovirus, coxsackie virus, after mumps,
influenza.
Subacute thyroiditis is characterized by a moderate increase in thyroid gland and
mild inflammatory reaction, which involved the capsule gland. The site of
inflammation is usually limited and localized in a fraction of thyroid gland or in the
isthmus. Very rarely, the inflammation can capture an entire share of the thyroid
gland
The clinical picture
One of the main symptoms - pain in the thyroid gland, aggravated by
swallowing, sometimes radiating to the ear. The increased share of the
thyroid gland, but most of its limited area of tenderness. Lymph nodes were
not enlarged. These symptoms are often accompanied by fever up to
subfebrile, but sometimes up to 38-39 degrees. With more than 50% of
patients in this stage of developing moderate effects of hyperthyroidism,
which is associated with excess release of thyroid hormones from thyroid
follicles undergoing destruction. Duration of acute illness of several weeks to
1-2 months., Subacute - 3-6 months. At the end of the disease may be
transient phenomens of hypothyroidism. Even after seemingly permanent
cure for the disease can recur.
SCA - thyroid hyperplasia
Endemic goiter
Iodine deficiency,
Imbalance of trace elements,
Strumogens factors
Sporadic goiter
Psychological stress,
Infection of the mouth,
Failure to comply with the
sanitary - hygiene,
Classification of the degree of thyroid
enlargement on OV Nikolaeva
• On stage - the iron is not visible and not palpable;
• Grade I - the iron is not visible, but the neck can be felt and seen in
•
•
•
•
swallowing;
Grade II - during swallowing is visible and well-palpable thyroid
gland, but the shape of the neck is not changed;
Grade III - iron visible to the eye when viewed, alters the contour of
the neck, giving it the appearance of a "thick neck";
IV degree - pronounced goiter, which violates the configuration of
the neck;
V degree - increased iron is enormous, which is often accompanied
by compression of the esophagus, trachea, in violation of
swallowing and breathing.
On the functional state of goiter can be:
a) hyperthyroid - increased thyroid function;
b) euthyroid - thyroid function is not compromised;
c) hypothyroid - thyroid function is reduced
Nodular
goiter
Mixed crop
The clinical picture
For large scale crop
may squeeze the organs
of the neck and cause
difficulty in swallowing,
a feeling of pressure in
the neck, with the crop,
as a rule will be evident
on examination.
Endemic goitre - diffuse thyroid enlargement due to
lack of intake of iodine.
The conventional view of the pathogenesis of goiter is
reduced to that lack of iodine in the environment or any
defects in its metabolism are responsible for reducing
the concentration of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) in
the blood, which is the mechanism of feedback
increases the production of pituitary thyroid stimulating
hormone (TSH). TSH activates the activity of existing
thyrocytes and, most importantly, increasing their
number increases the production of thyroid hormones
and thereby restores normal levels of T3 and T4, that is,
homeostasis is maintained at the cost of stress
regulatory mechanisms
Diagnosis of endemic goiter
At present the most accurate method of determining the size
of the thyroid gland is an ultrasound. By international
standards when using ultrasound in adults (aged 18), goiter
is diagnosed when the amount of cancer in women greater
than 18 ml in men - 25 ml. To determine the thyroid volume
measured by ultrasonography in three sizes each beat
cancer and then calculated.
Treatment of endemic goiter
For children and adolescents using drugs at a daily dose of
iodine 200 mcg, for example, "Potassium iodide 200 BerlinChemie" for adults - higher doses - 300-400 mg / day.
Prevention of goitre
Total:
The use of a population of
iodized salt,
Compliance with sanitary
standards,
Reducing stress,
Balanced diet.
Individual
Small doses of iodine and
antistrumin
Toxic goiter
Goiter Graves (synonym: Basedow's
disease, Graves' disease, thyrotoxic
diffuse goiter, a disease Parry Flajani
disease) - a disease of autoimmune
nature, which is based on genetically
based defect in the immune system, in
which cells produce antibodies that can
exert a stimulating effect on the thyroid
gland.
Disease in women occurs 5 times more likely than males and
can develop at any age.
The clinical picture
On examination, the patient attention is drawn to the clinical
manifestations of hyperthyroidism, palpitations, trembling
body, excessive sweating, emotional lability. Feature of the
tachycardia is its stable nature, it does not depend on the
position of the body prior to sleep, a long period of dormancy.
Patients complain of progressive weight loss with increased
appetite, enlarged thyroid gland, sometimes - in loose stools,
appearance of darker skin pigmentation.
Diagnosis is established on the basis of
characteristic clinical and biochemical data,
radiobiological and immunochemical studies. In the
presence of diffuse toxic goiter even capture high
radionuclide thyroid iodine or technetium (or
identification of individual sections of the capture of
high radionuclide scans to - "Hot Sites" at the hub
or diffusely nodular toxic goiter), increased gland goiter, determined visually or with ultrasound High
concentrations in the blood of thyroid hormones
and thyroglobulin and low thyroid hormone, the
presence of antibodies to thyroglobulin and
microsomal fraction thyrocytes, endocrine
ophthalmopathy certainly indicate hyperthyroidism.
Treatment of diffuse toxic goiter.
Treatment of diffuse toxic goiter may be operative and
conservative.
Absolute indications for surgery are allergic reactions, or
steady decline in white blood cells, recorded in the
conservative treatment, the large size of goitre
(enlarged thyroid gland above the level III), breach of
heart rate by type of atrial fibrillation with symptoms of
cardiovascular disease.
The operation is performed when a state medical
compensation because otherwise, in the early
postoperative period may develop thyrotoxic crisis.
Nodular goiter - a collective clinical concept combines all of the thyroid gland
formation with different morphological characteristics. The term "node" in
clinical practice, education is meant by the thyroid gland of any size, having
a capsule, determined by palpation or with ultrasound. The value of palpable
node is usually greater than 1.0 cm using the method of ultrasound can
identify sites and smaller sizes.
Endemic nodular goiter - is at the heart of iodine
deficiency.
Solitary node - the only education in the thyroid gland
Multinodular goiter - Multiple encapsulated education
in the thyroid gland does not welded together
Conglomerate nodular goiter - a few sites in the
thyroid gland, welded together
True cyst - the cavity containing the liquid
Diffusely nodular goiter - node (s) in the presence of
diffuse thyroid enlargement
Pathogenesis and causes of
Nodules in the thyroid gland are very common
thyroid disease. It is known that about 10% of the
world's population have some kind of focal lesions of
the thyroid. Since the concept of nodular goiter is a
collective pathogenesis of this disease is caused by
various reasons in each case depending on the
morphological form of nodules.
The clinical picture
Most often, patients with nodes in
the thyroid gland does not impose
any complaints. Sometimes there is a
feeling of discomfort in the neck, a
feeling of pressure in the neck.
Treatment of nodular / multinodular goiter
Treatment of this disease may be two main
types:
1. Conservative
Indications for early medical treatment are:
lack of proven patient cancer or a benign
tumor in the thyroid gland, the size of the
site at least 2-3 cm
2. Operational
Indications for surgical treatment:
- Thyroid cancer, suspicion of cancer in nodular goiter
- Follicular thyroid adenoma
- Host more than 2.5-3cm
- Patients with a negative trend over the period of conservative treatment
- The presence of multinodular toxic goiter
- The presence of cysts over 3cm
- The presence of thyroid adenoma
- Retrosternal nodular goiter
Thyrotoxic adenoma (Plummer's disease) - a condition
accompanied by high levels of thyroid hormones in the blood
caused by excessive functioning adenomas (adenomas or
rarely several) of the thyroid.
The disease is 3-5 times more common in
women of any age (with a slight predominance
of age 40-60 years), especially those living in
the territories in terms of iodine deficiency
(endemic goiter area.) Often toxic adenoma
occurs in children.
Pathogenesis and causes of
Thyrotoxic adenoma, usually of small size (about 2-2.5 cm in
diameter). The peculiarity of the functional activity of
thyrotoxic adenoma that secretes excessive She thyroid
hormones autonomously, ie regardless of the secretion of
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). The mechanism by
which adenoma acquires such autonomy is not fully
understood. Recent studies have shown that the ability of
adenomas to increased functional activity associated with
mutation of the receptor for TSH. The ability of individual
sites (nodes) to acquire an autonomous thyroid function is
associated with non-genetic and genetic mechanisms. It is
recognized that the development of thyrotoxic adenoma and
autonomous activity required 3-8 years.
The clinical picture in thyrotoxic adenoma identical to that
which is characteristic of diffuse toxic goiter (weight loss,
shortness of breath, palpitations, poor tolerance of heat),
except for more severe symptoms of cardiovascular and
myopathy. In some cases, older women are the main
complaints of palpitations and irregular heart - sinus
tachycardia or atrial fibrillation, shortness of breath, severe
muscle weakness, chained to the bed sleepy. Ocular
symptoms of hyperthyroidism may occur, but eye disease
in this disease is never found.
In a study of one of the lateral lobes of thyroid gland is
palpable node, the rest of the gland is usually not
palpable.
Diagnosing thyrotoxic adenoma
Laboratory studies often confirm a significant increase in
serum T3 in moderately elevated or normal maintenance
T4. Thyroid stimulating antibodies in patients with
thyrotoxic adenoma is not detected. Diagnosis of
radioactive iodine, especially thyroid scan, can help
identify areas strongly absorbing radioactive iodine ("hot
site"). Absorption by other parts of the thyroid may be
dramatically reduced or completely absent in connection
with the suppression of TSH secretion by the pituitary
gland.
Treatment of thyrotoxic adenoma surgery. If there is a severe form of
hyperthyroidism in the preoperative period for the elimination of the
latter is used tireos toxic therapy. In some cases (in patients aged over
40 years) preferred treatment with radioactive iodine.