* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning About Earth`s Geography - Hewlett
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Diver navigation wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Celestial navigation wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
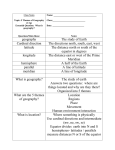
* What is the geography of the earth? * * Geography is the study of particular places on earth and their characteristics. * This includes landforms, water features, weather patterns, as well as plant, animal and human life. * An environment includes land and water, as well as weather patterns and all plants and animals that live in a place. * Only 30% of the earth is covered by land, from huge continents to small islands. * Landforms include: hills, mountains, isthmus, peninsula and island * Water covers 70% of the earth * Oceans and seas are the largest bodies of water; however the oceans are really just one large body of water that flows around the world * Water is also found within land masses in the form of rivers and lakes. * Many kinds of plants grow on earth * Each environment has its own unique plant life * The natural plant life of a region is called its vegetation. * The easiest way to locate any place on earth is to use the imaginary lines shown on most maps and globes. * The lines that run east to west are called lines of latitude. * The lines that run north to south are called longitude. * Lines of latitude run east to west, however they measure the distance in * * * * degrees north or south from the equator. A degree is a unit of measurement that describes the distance between lines of latitude and lines of longitude. The symbol for degree is , just like a degree of temperature. The equator is the starting line for measuring latitude. On any map, the line marking the equator is labeled 0 meaning zero degrees latitude. The line above the equator is labeled 30 N or 30 degrees north; the line below the equator is marked 30 S or 30 degrees south. There are 90 degrees of latitude between the equator and the north pole and 90 degrees of latitude between the equator and the south pole. * Math connection: Lines of latitude are also known as parallels. Parallels are lines that run in the same direction and are always the same distance apart. They never meet or cross. * Lines of longitude run from the north pole to the south pole. * These lines measure distance in degrees east and west of the line of longitude we call the prime meridian. * The prime meridian is marked 0 or zero degrees longitude. The lines west of the prime meridian are measured in degrees from 1 to 179 west. * The line at 180 is called the International Date Line. It is in fact directly opposite on the globe from the prime meridian. * Longitude measurements are also used to evaluate time. Each advance of 15 of longitude represents about one hour’s time in terms of measurement by the sun. * Latitude and longitude is used in GPS and is the primary coordinate system for navigation on the planet. * These lines form an imaginary grid over the earth to allow us to determine the exact location of a place. Geography, the Superpower Links with other places Location Shape of the land Water features Climate What is Geography ? Human Interaction Soils and natural resources Animal Life Vegetation GEOGRAPHY – THE SUPERPOWER It influences everything and everyone. Humans try to control it and use its power. The Five Themes of Geography 1. Location How do I get there? Exact location - latitude and longitude Relative location - What is it near? 2. Place What's it like to live there? Describe the physical features - mountains, deserts, forest, rivers. Describe the cultural features - most people are ______. 3. Interaction How do people relate to the land? Are there farms up the hillside? 4. Movement How are people, goods and ideas moved into and out of this place? How do people get from here to there - by donkey, car, or bullet train? 5. Regions Geographers invent regions. They carve the world into physical regions - the Rocky Mountains. They carve the world into cultural regions - the corn belt, the rust belt, the sun belt. FOCUS: How has geography affected humans and what changes have we made to master it?