* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANATOMY – Cranial Nerves
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
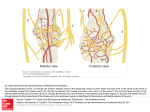
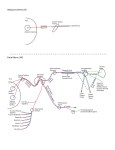
Chiro Essentials Part 1 www.isuperlearn.com ANATOMY – Cranial Nerves 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 EclipseCrossword.com WORD BANK ABDUCENS CILIARY MOTOR PARASYMPATHETIC SPINAL TASTE TRACT TWELVE AMBIGUUS HYPERACUSIS OCULOMOTOR PAROTID STAPEDIUS THALAMUS TRAPEZIUS AWAY LINGUAL OLFACTORY PONS STYLOPHARYNGEUS THIRD TRIGEMINAL BITEMPORAL MANDIBULAR OTIC RIGHT SUBLINGUAL TOWARDS TROCHLEAR 15 Chiro Essentials Part 1 www.isuperlearn.com ANATOMY – Cranial Nerves Across 5. 7. 11. 12. 16. 18. 19. 20. 21. 23. 24. 25. 27. 28. 29. Only muscle innervated by the ninth cranial nerve. Cranial nerve which controls dilation of the pupil. Cranial nerve which is derived from the myelencephalon. Division of the trigeminal nerve which carries the innervation for the muscles of mastication. Hearing complaint associated with facial nerve damage. Location of the lateral geniculate body. Location of the mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve. Nerve to which the submandibular ganglion is attached. Type of nerve fibers which originate from the solitary tract nucleus. Salivary gland which receives parasympathetic innervation from the glossopharyngeal nerve. One of the two muscles innervated by the accessory cranial nerve. Type of hemianopia seen with a large space occupying lesion in the sella turcica. Nucleus which is shared by cranial nerves 9, 10 and 11. Part of the optic pathway that lies between the optic chiasm and the lateral geniculate body. Specialized nerve cells located below the cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone. Down 1. 2. 3. 4. 6. 8. 9. 10. 13. 14. 15. 17. 22. 26. Optic radiation involved in the left homonymous hemianopia. Side of deviation of the uvula with damage to one vagus nerve. Cranial nerve when damaged will produce diplopia on going down stairs. Type of nerve fibers which originate from the nucleus ambiguus. Salivary gland which receives parasympathetic innervation from the facial nerve. Ganglion carrying parasympathetic fibers to the pupil and ciliary body. Type of autonomic fibers originating from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus. Parasympathetic ganglion which is attached to the auriculotemporal branch of CN V3. Nerve which innervates the lateral rectus muscle. Nerve which innervates the tensor veli palatini. Side of deviation of the tongue with damage to one hypoglossal nerve. Part of the 11th cranial nerve which arises from the upper cervical part of the spinal cord. Middle ear muscle innervated by the facial nerve. Cranial nerve which innervates the interior oblique.