* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to DNS in Windows Server 2008
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Games for Windows – Live wikipedia , lookup
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Security Essentials wikipedia , lookup
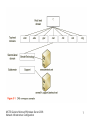
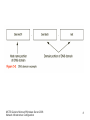
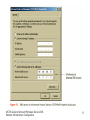
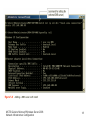
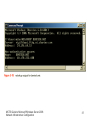
MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration Chapter 5 Introduction to DNS in Windows Server 2008 Objectives • Discuss the basics of the Domain Name System (DNS) and its terminology • Configure DNS clients • Install a standard DNS server on Windows Server 2008 • Create standard DNS zones MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 2 Domain Name System • Primary function is to translate human-readable host names • Assists the flow of e-mail – Provides mail exchanger records that tell a Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server where to send an e-mail message • Supported on the Internet by thousands of distributed servers, or DNS servers MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 3 Domain Name System (continued) • Activity 5-1: Resetting Network Adapters and Disabling DHCP • Time Required: 20 minutes • Objective: Reset the network adapters on lab servers MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 4 DNS Terminology • • • • • • • DNS namespace DNS domain Fully qualified domain name Hosts Host name DNS record DNS zone MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 5 DNS Terminology (continued) • DNS namespace – Organized into the following domains: root domain (.), top-level domain (TLD), second-level domain, and subdomain • DNS domain – The portion of the namespace to the right of the host name • Fully qualified domain names – The entire name for a specific host that needs to have a DNS record created MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 6 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 7 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 8 DNS Terminology (continued) • Activity 5-2: Using Whois • Time Required: 5 minutes • Objective: Research domain names MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 9 DNS Terminology (continued) • Hosts – A computer on the Internet that provides a specific resource • Host name – Name given to a computer, or host, to make connecting to it easier • DNS zone – Collection of connected nodes served by an authoritative DNS name server • DNS records – DNS uses records to provide the information it stores in its database MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 10 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 11 DNS Terminology (continued) • Activity 5-4: Resolving DNS Records with NSLookup • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Query a DNS server with nslookup MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 12 DNS Queries in Windows Server 2008 • Iterative query – A DNS client requests the best answer that its DNS server can provide • Recursive queries – Queries where the client requires an answer from its DNS server MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 13 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 14 Configuring DNS Clients • DNS clients – Often referred to as DNS resolvers • Windows Server 2008 – Uses the DNS Client service to perform DNS queries on behalf of the client MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 15 DNS Client Settings • DNS servers – For a client to resolve DNS queries, it needs to know which server to contact – First DNS server in the list is called the preferred DNS server • DNS suffix – DNS domain appended to all unqualified name queries, or a query that contains only a host name MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 16 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 17 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 18 DNS Client Settings (continued) • Activity 5-5: Adding an Alternate DNS server • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Add an alternate DNS server MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 19 DNS Client Settings (continued) • Activity 5-6: Adding a Domain Suffix to IP Properties • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Configure a client with an additional DNS suffix MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 20 DNS Client Settings (continued) • Activity 5-7: Creating a Full Computer Name • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Change the computer name MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 21 Dynamic Updates • Windows Server 2008 – Supports dynamic updates with both standard and Active Directory Domain Services–integrated domains • Dynamic updates – Sometimes referred to as DDNS MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 22 Installing DNS in Windows Server 2008 • DNS – A role that can be installed on Windows Server 2008 Full and Server Core versions – Often combined with other services such as DHCP MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 23 Installing Cache-Only DNS Servers • Cache-only DNS server – Server that has the DNS role installed – Does not hold a DNS zone so it is not authoritative for any DNS zones – Does not maintain any DNS records MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 24 Installing Cache-only DNS Servers (continued) • Activity 5-8: Installing DNS on MSN-SRV-0XX • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Install the DNS Server role MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 25 Installing Cache-only DNS Servers (continued) • Root hints – Provide IP address pointers to top-level DNS servers – When configured, a DNS server can perform queries when it receives domain name requests for zones in which it is not authoritative – Provide referral answers to queries in a DNS server’s quest to resolve an unknown domain name request • Forwarders – Servers used to resolve names MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 26 DNS Zones • Zones – Building blocks for creating your DNS infrastructure • DNS zones – Classified in three ways • The information they store • Where they are stored • Their read/write status – Fall into two categories • Standard and Active Directory MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 27 Standard Zones • zone.dns – Used to store DNS records – Found in the %systemroot%\system32\DNS folder • Berkeley Internet Name Domain (BIND) – Industry standard of DNS servers on the Internet and networks running DNS on UNIX/Linux systems MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 28 Standard DNS Zone Types • Primary DNS zone – The zone that is authoritative for a specific domain and its name records • Secondary DNS zone – Read-only version of the DNS records for a zone • Stub zone – Read-only copy of a zone that obtains its resource records from the name servers that are authoritative for a particular zone MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 29 Standard DNS Zone Types (continued) • Activity 5-9: Installing a Primary DNS Zone for bentech.local • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Create a primary DNS zone MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 30 Standard DNS Zone Types (continued) • Activity 5-10: Installing a Secondary DNS Zone on MSN-SC-0XX • Time Required: 15 minutes • Objective: Install DNS on Server Core MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 31 Direction of DNS Zones • Forward lookup DNS zones – Allow a DNS client to resolve an FQDN to an IP address • Reverse lookup DNS zone – Maps IP addresses to host names MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 32 Direction of DNS Zones (continued) • Activity 5-11: Creating a Reverse Lookup Zone • Time Required: 15 minutes • Objective: Create a reverse lookup zone MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 33 DNS Resource Records • Information in a DNS record – Owner, Time-to-Live (TTL) – Class, Type – Resource Record Data (RDATA) • Start of Authority (SOA) – Record is the starting point for information related to a zone • Name server (NS) record – Identifies a DNS server that is authoritative for a zone MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 34 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 35 DNS Resource Records (continued) • Host (A) record – Provides host name–to–IP address resolution for DNS clients • Host (AAAA) Records for IPv6 – Records map a host name to an IPv6 address • Mail exchanger (MX) record – Specifies the server that is responsible for handling e-mail • Alias records – Used to create an alias for a specific host MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 36 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 37 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 38 DNS Resource Records (continued) • Pointer records – Resolves IP address to host names for DNS clients • Service locator records – Provides the following information • Location of services it needs • Network protocol needed to access the previously mentioned services • Domain services it provides MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 39 DNS Resource Records (continued) • Activity 5-12: Creating DNS Records in the DNS Console • Time Required: 10 minutes • Objective: Create DNS records MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 40 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 41 Standard DNS Zone Transfers • Master server – Provides updated DNS record information to secondary servers • Slave server – Gets its updates from the master zone transfer partner specified on the Zone Transfer tab in DNS • Zone transfers from the master to the secondary server come in two varieties – Incremental zone transfers (IXFRs) – Full zone transfers (AXFRs) MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 42 MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 43 Summary • DNS – Responsible for providing name resolution for clients on public and private networks • Core functionality of DNS – To provide host name–to–IP address resolution, or forward lookups • Standard zones classifications – Primary, secondary, and stub zones • DNS – Uses many types of records to store information in its zones MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 44 Summary (continued) • Installing the DNS role can be done through the GUI using Server Manager • DNS console – The main GUI tool responsible for managing DNS – Allows you to add, delete, and modify all aspects of DNS MCTS Guide to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Network Infrastructure Configuration 45