* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download statistics undergraduate courses
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
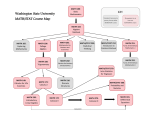
STATISTICS UNDERGRADUATE COURSES STAT 201 Introduction to Statistics (2-2-3) Descriptive statistics: measures of location, dispersion, and skewness. Probability. Random variables. Normal and Binomial probability distributions. Sampling distribution of the mean. Estimation. Testing hypotheses. Regression and correlation. Applications using statistical packages. Note: Not to be taken for credit with Stat 319 or ISE 205 Prerequisite: MATH 102 STAT 211 Statistics for Business I (3-0-3) Data description: Frequency table, histogram, measures of central tendency, scatter diagram and correlation. Probability theory; sampling; probability distributions; point and confidence interval estimation; application for managerial decision. A statistical package will be used. Note: Not open for credit to Statistics or Mathematics Majors, Not to be taken for credit with ISE 205, STAT 201 and STAT 319. Prerequisite: MATH 131, MATH 132 STAT 212 Statistics for Business II (3-0-3) Hypothesis testing for means and variances; index numbers and time series; simple linear progression and correlation analysis; multiple regression analysis; the chi-squared and F distributions and their applications. A statistical package will be used. Note: Not open for credit to Statistics or Mathematics Majors, Not to be taken for credit with ISE 205, STAT 201 and STAT 319. Prerequisite: STAT 211 STAT 213 Statistical Methods for Actuaries (2-2-3) Descriptive Statistics: Frequency table; histogram, measure of central tendency and variability, scatter diagram and correlation. Probability theory; sampling techniques; probability distributions; estimation; hypothesis testing for means and variances; index number and introductory time series analyses; simple linear regression and correlation analysis; multiple regression analysis; the chi-squared and F distributions and their applications; application for financial decisions; application using statistical packages. Note: Not to be taken for credit with STAT 201, STAT 211, STAT 212, or STAT 319. Prerequisite: MATH 102 STAT 301 Introduction to Probability Theory (3-0-3) Basic classical models of probability. Set functions. Axiomatic definition of probability. Conditional probability and Bayes’ theorem. Random variables and their types. Distributions, moments, and moment generating functions. Special discrete and continuous distributions. Random vectors and their distributions. Marginal and conditional distributions. Independent random variables. Functions of random variables. Sums of independent random variables. Weak law of large numbers and the central limit theorem. Prerequisite: MATH 201, STAT 201 or STAT 212 or STAT 213 or STAT 319 STAT 302 Statistical Inference (3-0-3) Random sampling and the sampling distributions: t, chi-square, and F. Order Statistics. Methods of estimation: maximum likelihood and moments. Properties of a good estimator: unbiasedness, consistency, efficiency, sufficiency, and approximate normality. Testing of simple hypotheses, the Neyman-Pearson lemma. Testing composite hypotheses, uniformly most powerful and likelihood ratio tests. Bayesian Statistics. Prerequisite: STAT 301 STAT 310 Regression Analysis (3-0-3) Simple linear regression: The least squares method, parameter estimation, confidence intervals, tests of hypotheses and model adequacy checking. Multiple linear regression, including estimation of parameters, confidence intervals, tests of hypotheses and prediction. Model adequacy checking and multicollinearity. Polynomial regression. Variable selection and model building. Prerequisite: STAT 201 or STAT 212 or STAT 213 or STAT 319 STAT 319 Probability and Statistics for Engineers and Scientist (2-3-3) Presentation and interpretation of data, elementary probability concepts, random variables and probability distributions, binomial, Poisson, exponential, Weibull, normal and lognormal random variables. Estimation, tests of hypotheses for the one sample problem. Simple and multiple linear regression, application to engineering problems. The lab session will be devoted to problem solving using statistics software. Note: Not open for credit to Statistics or Mathematics Majors, Cannot be taken for credit with ISE 205 or STAT 201. Prerequisite: MATH 102 STAT 320 Statistical Quality Control (3-0-3) How control charts work. Control chart methods for attributes and variables. Process-control chart techniques. Process-capability analysis. Acceptance-sampling by attributes and variables. Note: Not to be taken for credit with ISE 320 Prerequisite: STAT 201 or STAT 212 or STAT 213 or STAT 319 STAT 325 Non Parametric Statistical Methods (3-0-3) One sample problem, the sign, and Wilcoxon signed rank tests. Two-Sample problem, Wilcoxon rank sum and Mann-Whitney tests. Kruskal-Wallis test for one-way layout. Friedman test for randomized block design. Run test for randomness. Goodness of fit tests. Prerequisite: STAT 201 or Consent of the Instructor STAT 342 Applied Statistics (3-0-3) Review for descriptive statistics, estimation, and testing hypotheses. Simple linear regression. One way analysis of variance. Multiple regression. Randomized block designs. Factorial experiments. Random and mixed effect models. Note: Not to be taken for credit with STAT 310 and/or STAT 430 Prerequisite: STAT 201 or STAT 212 or STAT 213 or STAT 319 STAT 355 Demographic Methods (3-0-3) Scope of demography. Vital events. Demographic survey. History of world population and distribution. Demographic transition. Fertility and its measures. Mortality and its measures. Direct and indirect standardization. The life table. Construction of a life table. Stationary population. Stable population. Migration. Theories of migration. Consequences of migration. Population estimates and projections. Prerequisite: STAT 201 or STAT 212 or STAT 213 or STAT 319 STAT 361 Operational Research I (3-0-3) Problem solving and decision making. Linear programming: formulation, the graphical method, the simplex method, sensitivity analysis, and duality. Transportation and assignment problem. Integer programming. Project scheduling PERT/CPM. Note: Not to be taken for credit with ISE 303 Prerequisite: STAT 201 or STAT 212 or STAT 213 or STAT 319 STAT 365 Data Collection and Sampling Methods (3-0-3) Concept of data collection. Sample surveys, finite and infinite populations, execution and analysis of samples. Basic sampling designs: simple, stratified, systematic, cluster, two-stage cluster. Methods of estimation of population means, proportions, totals, sizes, variances, standard errors, ratio, and regression. Prerequisite: STAT 201 or consent of the Instructor STAT 375 Categorial Data Analysis (3-0-3) 2x2 contingency tables, two-way contingency tables, three-way and higher dimensional contingency tables. Loglinear models for contingency tables. Logistic regression. Building and applying loglinear models. Prerequisite: STAT 201 or STAT 212 or STAT 213 or STAT 319 STAT 399 Summer Training (0-0-2) Students are required to spend one summer working in industry prior to the term in which they expect to graduate. Students are required to submit a report and make a presentation on their summer training experience and the knowledge gained. Prerequisite: ENGL 214, Junior Standing, Approval of the Department STAT 415 Stochastic Processes (3-0-3) Basic classes of Stochastic processes. Poisson and renewal processes with applications in simple queuing systems. Discrete and continuous time Markov chains. Birth-Death and Yule processes. Branching models of population growth and physical processes. Prerequisite: STAT 301 STAT 416 Stochastic Processes for Actuaries (3-0-3) Basic classes of Stochastic processes. Poisson (regular, compound, compound surplus, and non-homogenous) and renewal processes with applications in simple queuing systems and actuarial science. Discrete and continuous time Markov chains. Birth-Death and Yule processes. Branching models of population growth processes. Actuarial risk models; simulation. Arithmetic and geometric Brownian motions, and applications of these processes such as in computation of resident fees for continuing care retirement communities, and pricing of financial instruments. Note: Not to be taken for credit with STAT 415 Prerequisite: STAT 301 STAT 430 Experimental Design (3-0-3) Importance of statistical design of experiments. Single-factor and multifactor analysis of variance. Factorial designs. Randomized blocks. Nested designs. Latin squares. Confounding and 2-level fractional factorials. Analysis of covariance. Prerequisite: STAT 302 STAT 435 Linear Models (3-0-3) Review of multiple regression. The general linear model. Quadratic forms. Gauss- Markov theorem. Multivariate normal distribution. Computational aspects. Full rank models. Models not of full rank. Computer applications. Prerequisite: STAT 310 STAT 440 Multivariate Analysis (3-0-3) Introduction to multivariate analysis. Multivariate normal distribution theory. Distribution of the sum of product matrix. Inference about the parameters of the multivariate normal distribution. Comparison of means. Linear models. Principal components. Factor analysis. Classification and discrimination techniques. Prerequisite: STAT 310 STAT 460 Time Series (3-0-3) Examples of simple time series. Stationary time series and autocorrelation. Autoregressive moving average processes. Modeling and forecasting with ARMA processes. Maximum likelihood and least squares estimator. Nonstationary time series. Prerequisite: STAT 310 STAT 461 Operational Research II (3-0-3) Inventory models. Waiting line models. Decision Analysis. Multicriteria decision problem. Markov process. Dynamic programming. Calculus-based Procedures. Note: Not to be taken for credit with ISE 421 Prerequisite: STAT 301, STAT 361 STAT 470 Senior Project in Statistics (1-3-2) This course is designed to draw upon various components of the undergraduate curriculum. The project could be in the area of data analysis, sampling survey, experimental design, regression analysis, multivariate data analysis, time series and etc. A report is essential for course completion. Prerequisite: Senior Standing STAT 475 Statistical Models for Life time Data (3-0-3) Life tables, graph and related procedures. Single samples: complete or Type II censored data and Type I censored data for Exponential, Weibull, Gamma and other distributions. Parametric regression for Exponential, Weibull and Gamma distributions. Distributions- free methods for proportional hazard and related regression models. Prerequisite: STAT 302, STAT 310 STAT 499 Topics in Statistics (3-0-3) Variable contents. Open for senior students interested in studying an advanced topic in statistics with a departmental faculty member. Prerequisite: Senior standing, Permission of the Department Chairman upon Recommendation of the Instructor.