* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
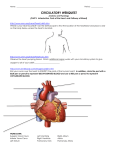
JOSE S. SANTIAGO M.D. The Cardiovascular System Consists of the heart and blood vessels Types of blood vessels Arteries Carry blood away from heart Veins Carry blood toward heart 2 The Cardiovascular System Capillaries Tiny blood vessels Join arterial and venous systems and carry blood to organs 3 The Cardiovascular System Oxygenated blood Oxygen and nutrients Deoxygenated blood Carbon dioxide and waste products 4 Structure of the Heart Heart in fluid-filled sac called pericardium Located in thoracic cavity 5 Structure of the Heart Connected to: Aorta Inferior and superior venae cavae and the pulmonary veins and arteries 6 Structure of the Heart Composed of muscle tissue for powerful contracting action 7 Interior of the Heart Four chambers Right and left atria and right and left ventricles Septum 8 Interior of the Heart Atrioventricular valves Tricuspid and bicuspid or mitral value Attached by chordae tendinea 9 Interior of the Heart Semilunar valves Pulmonary and aortic 10 Structure of the Heart 11 Walls of the Heart Myocardium Thick middle layer Cardiac muscle tissues Endocardium Thin inside layer Epithelial tissue 12 Walls of the Heart Epicardium Outer layer Connective and epithelial tissue 13 Conduction System Heart’s electrical system Sinoatrial node SA node or pacemaker Atrioventricular node AV node Atrioventricular bundle AV bundle or bundle of His 14 Conduction System Right and left bundle branches Purkinje fibers 15 Electrocardiograph Instrument Monitors and produces a written record of electrical activity of the heart 16 Electrocardiograph P waves Atrial contraction QRS waves Ventricular contraction T waves Ventricular recovery 17 Pulse Pulse – pressure wave of blood Monitored at “pressure points” where pulse is easily palpated Blood Pressure Systole Contraction phase Diastole Resting phase One heartbeat is one cycle of systole and diastole 19 Blood Pressure Pulse Feel systole as blood being forced out to arteries Sphygmomanometer Measures pressure during systole and diastole 20 Blood Pressure Systolic pressure First number Highest Diastolic pressure Second number 21 Lowest Blood Pressure Normal range 100/60 to 120/80 Too high Hypertension Too low Hypotension 22 Variations in Blood Pressure Human normal range is variable 1. Normal 100–130 mm Hg systolic 60–80 mm Hg diastolic 2. Hypotension Low systolic (below 90 mm HG) Often associated with illness 3. Hypertension High systolic (above 130 mm HG) Can be dangerous if it is chronic Heart Sounds Sounds made by the closing of valves First heart sound (S1) Atrioventricular vales closing “Lubb” sound Second heart sound (S2) Semilunar valves closing 24 “Dubb” sound Heart Sounds Murmur Blowing sound indicative of abnormal blood flow 25 Blood Vessels Arteries Arterioles Veins Venules Capillaries 26 Circulation Superior and inferior venae cavae Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Pulmonary semilunar valve Pulmonary arteries Lungs 27 Circulation Pulmonary veins Left atrium Bicuspid valve Left ventricle Aortic semilunar valve Aorta Arteries 28 Circulation Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins 29 Circulation All arteries except the pulmonary arteries carry oxygenated blood. All veins except the pulmonary veins carry deoxygenated blood. 30 Circulation Coronary arteries Feed the heart Parallel routes to allow for blockages 31 Circulation Arteries and veins Often named after the organ in which they pass 32 Circulation Arteries and veins Often named after the organ in which they pass 33 Additional Word Parts – Roots Constrict/o to draw together Vasoconstriction-narrowing of the lumen 34 Additional Word Parts – Roots Dilat/o to expand Vasodilation-widening of lumen 35 Roots Angi/o vessel Angiogram-record of blood vessel 36 Roots Aort/o Arteri/o aorta artery 37 Roots Ather/o fatty debris; fatty plaque Atherosclerosis-hardening of arteries due to fat deposit 38 Roots Atri/o -atrium Cardi/o -heart 39 Roots Coron/o- crown Coronary arteryblood supply of the heart 40 Roots Ech/o sound Echocardiogram record of the heart produced by sound waves 41 Roots Embol/o plug Embolism-plug of clotted blood transported to the bloodstream 42 Roots Isch/o -hold back Myocardial ischemia-hold back of blood to the heart muscle 43 Myocardial Infarct -area of tissue that has died due to lack of blood supply to the heart Roots Phleb/o vein Phlebothrombosis -abnormal condition of clots in a vein 45 Roots Rhythm/o- rhythm Arrhythmia-abnormal heart rhythm 46 Roots Thromb/o clot Phlebothrombosis -clot in the vein 47 Roots Valvul/o - valve 48 Roots Varic/o Varicose veins 49 twisted and swollen Roots Vascul/o Vas/o 50 vessel vessel Roots Ven/o vein 51 Roots Ventricul/o- ventricle 52 Suffix -ectasis dilation; dilatation; stretching Angioectasis-dilation of blood vessels 53 Prefixes Brady- slow Bradycardia-heart rate <60 beats/min. 54 Prefixes Tachy- fast Tachycardia-heart rate >100 beats/min 55 Aging Heart muscle stiffens Cannot pump as well Decreased response to demands of exercise Usually functions well under normal stressors 56 Aging Walls of arteries Thicker and less elastic which can lead to hypertension Reduce effects Avoid smoking and excess alcohol Exercise regularly 57 Common Diseases Aneurysm-bulge in the wall of an artery 58 Common Diseases Coronary heart disease (CHD)/ Coronary artery disease (CAD)- narrowing of the coronary artery; progressive disease that increases the risk of myocardial infarct (MI) and sudden death Stable angina- chest pain during exercise or other physical activity; due to small blockage in the coronary artery Unstable angina- chest pain with little or no activity; due to large obstruction in the coronary artery 59 Common Diseases Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)- condition in which fatty deposits build up in the inner linings of the artery walls Symptoms: 1. Claudication- dull, cramping pain in the hips, thighs, calves or buttocks 2. Paresthesia- numbness or tingling in the legs or feet 3. Impotence- inability to have erection in males 4. Paresis- weakness in arms or legs 5. Sores or infections that do not heal 60 Common Diseases Hypertension (HTN)- blood pressure reading that is higher than normal Factors contributing to hypertension: Controllable: 1. Smoking 2. Overweight 3. Lack of exercise 4. Stress 5. Alcohol 61 Common Diseases Factors contributing to hypertension: Uncontrollable: 1. Heredity- family history of hypertension 2. Race- more common in African-Americans 3. Gender- more common among men 4. Age- incidence increases with age 62 Common Diseases Cardiac arrest Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) Stroke Myocardial infarction (MI) Heart attack The blood supply to part of the heart muscle is reduced or stopped. 63 THANK YOU FOR LISTENING!!!