* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data
Flow-based programming wikipedia , lookup
Logic programming wikipedia , lookup
Program optimization wikipedia , lookup
Go (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Falcon (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Functional programming wikipedia , lookup
Programming language wikipedia , lookup
Parallel computing wikipedia , lookup
Object-oriented programming wikipedia , lookup
Stream processing wikipedia , lookup
Abstraction (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
C Sharp (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
C++ Programming:
Program Design Including
Data Structures, Fifth Edition
Chapter 1: An Overview of
Computers and Programming
Languages
Objectives
In this chapter, you will:
• Learn about different types of computers
• Explore the hardware and software components of a
computer system
• Learn about the language of a computer
• Learn about the evolution of programming languages
•
•
•
•
Examine high-level programming languages
Discover what a compiler is and what it does
Examine a C++ program
Explore how a C++ program is processed
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
2
Introduction
• Without software, the computer is useless
• Software developed with programming
languages
– C++ is a programming language
• C++ suited for a wide variety of
programming tasks
• Before programming, it is useful to
understand terminology and computer
components
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
3
A Brief Overview of the History of
Computers
• Early calculation devices
– Abacus, Pascaline
• (only addition and subtraction)
– Leibniz device (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division)
– Babbage machines: difference and analytic engines
– Hollerith machine. Run on electricity and can store data. (IBM)
Hollerith machine
Leibniz device
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
Leibniz device
4
A Brief Overview of the History of
Computers (cont'd.)
• Early computer-like machines
– Mark I. 52 feet long, 50 tons weight, and 750,000 parts
– ENIAC. Electrical Numerical Integrator And Calculator
– Von Neumann architecture. Base for Today computer design:
Arithmetic logic unit, control unit, memory, input/output devices
– UNIVAC. UNIVersal Automatic Computer
– In1956, Transistors and microprocessors invented
UNIVAC
ENIAC
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
Mark I
5
A Brief Overview of the History of
Computers (cont'd.)
• Early computer-like machines
– In 1970, microprocessor, an entire CPU on a single chip, was
invited.
– 1977, first Apple computer was built.
– 1981, IBM introduced its personal computer.
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
6
Elements of a Computer
System
• A computer is an electric device capable of performing
commands. The basic commands that a computer
perform are input (get data), output (display result),
storage, and arithmetic and logic operations.
•
•
•
•
•
•
Hardware
CPU
Main memory
Secondary storage
Input/Output devices
Software
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
7
Hardware
- Major hardware components include:
•
•
•
•
CPU
Main memory: RAM (Random Access Memory)
Input/output devices
Secondary storage
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
8
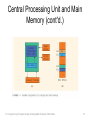
Central Processing Unit and Main
Memory
• Central processing unit
– Brain of the computer
– Most expensive piece of hardware
– Carries out arithmetic and logical operations
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
9
Central Processing Unit and Main
Memory (cont'd.)
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
10
Central Processing Unit and Main
Memory (cont'd.)
• Random access memory
• Directly connected to the CPU
• All programs must be loaded into main memory before
they can be executed
• All data must be brought into main memory before it can
be manipulated
• When computer power is turned off, everything in main
memory is lost
• Main Memory is an ordered sequence of cells. Each cell
has a unique location in Main memory called address of
the cell
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
11
Secondary Storage
• Secondary storage: device that stores
information permanently
• Examples of secondary storage:
– Hard disks
– Flash drives
– Floppy disks
– Zip disks
– CD-ROMs
– Tapes
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
12
Input/Output Devices
• Input devices feed data and programs into
computers
– Keyboard
– Mouse
– Secondary storage
• Output devices display results
– Monitor
– Printer
– Secondary storage
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
13
Software
• Software: programs that do specific tasks
• System programs take control of the
computer, such as an operating system
• Application programs perform a specific
task
– Word processors
– Spreadsheets
– Games
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
14
The Language of a Computer
• Computer use Digital signals: sequences of 0s and 1s
• Machine language: language of a computer which is a
sequence of 0s and 1s
• Binary digit (bit):
– The digit 0 or 1
• Binary code:
– A sequence of 0s and 1s
• Byte:
– A sequence of eight bits
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
15
The Language of a Computer (cont’d.)
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
16
The Language of a Computer
(cont'd.)
• Every letter, number, or special symbol on your keyboard
is encoded as a sequence of bits, each having a unique
representation (Code).
• ASCII (American Standard Code for Information
Interchange)
– 128 characters
– A is encoded as 01000001
– 3 is encoded as 00110011
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
17
The Language of a Computer
(cont'd.)
• EBCDIC
– Used by IBM
– 256 characters
• Unicode
– 65536 characters
– Two bytes are needed to store a character
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
18
The Evolution of Programming
Languages
• Early computers were programmed in machine language
• To calculate wages = rates * hours in machine
language:
100100 010001
//Load
100110 010010
//Multiply
100010 010011
//Store
• Problem: Very difficult to Remember the
Machine language codes for various operations
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
19
The Evolution of Programming
Languages (cont'd.)
• Assembly language instructions are
mnemonic
• Assembler: translates a program written in
assembly language into machine language
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
20
The Evolution of Programming
Languages (cont'd.)
• Using assembly language instructions,
wages = rates * hours can be
written as:
LOAD rate
MULT hour
STOR wages
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
21
The Evolution of Programming
Languages (cont'd.)
• High-level languages closer to natural
languages
• High-level languages include Basic,
FORTRAN, COBOL, Pascal, C, C++, C#, and
Java
• Compiler: translates a program written in a highlevel language machine language
• The equation wages = rate * hours can
be written in C++ as:
wages = rate * hours;
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
22
Processing a C++ Program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "My first C++ program." << endl;
return 0;
}
Sample Run:
My first C++ program.
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
23
Processing a C++ Program
(cont'd.)
• To execute a C++ program:
– Use an editor to create a source program in
C++
– Preprocessor directives begin with # and are
processed by a the preprocessor
– Use the compiler to:
• Check that the program obeys the rules
• Translate into machine language (object program)
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
24
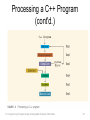
Processing a C++ Program
(cont'd.)
• To execute a C++ program (cont'd.):
– Linker:
• Combines object program with other programs
provided by the SDK to create executable code
– Loader:
• Loads executable program into main memory
– The last step is to execute the program
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
25
Processing a C++ Program
(cont'd.)
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
26
Summary
• Computer: electronic device that can perform
arithmetic and logical operations
• Computer system has hardware and software
• Central processing unit (CPU): brain
• Primary storage (MM) is volatile; secondary
storage (e.g., disk) is permanent
• Operating system monitors the overall activity of
the computer and provides services.
• Various kinds of languages, such as machine
language, assembly, high-level
C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Fifth Edition
27