* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 6 :Water Quality and Management
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Purified water wikipedia , lookup
Sewage treatment wikipedia , lookup
Water purification wikipedia , lookup
Water testing wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation wikipedia , lookup
Portable water purification wikipedia , lookup
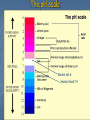
Topic 6 :Water Quality and Management Dissolved in Water Hard water contains dissolved minerals like calcium, lime, fluoride, and magnesium that often form scaly deposits on faucets and tiles as water evaporates and leaves behind the minerals. These deposits can be removed by solvents like CLR Soft water has less calcium and magnesium in it. Water softeners are added to make it soft Oxygen, CO2, sediments, phosphate, nitrogen, sulfur, and some other chemicals can be found dissolved in water. Bad stuff in water… Toxic substances are materials added to the environment that harms it or other organisms. (ex) PCB – used in making electronics DDT – used as pesticide CFC – used in fridgerants a/c, destroys O3 Sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NO) are released into the air from burning fossil fuels. They come down in raindrops as acid rain. Over time, the build up of these acids in the water and soil decrease the pH (level of acidity) affecting organisms’ lifecycles, reproduction, cells, developement The pH scale Normal rain 6 Human blood 7.4 Bioindicators The health of the environment can be evaluated by looking at bioindicator species sensitive to changes in the environment. (ex) insect larvae, northern leopard frog, salamanders, fish, clams, snails, algae Changes to their development and lifecycles give us indication of problems, pollutants Contaminants in the environment can make their way into the food chain and affect top predators like humans through bioaccumulation Purifying Water To make water potable (safe for drinking), it has to go through water treatment. See diagram on page 463 WATER INTAKE FROM RIVER LIME, ALUM, CHARCOAL ADDED TO WATER AT TREAMENT PLANT TO REMOVE DIRT AND SEDIMENTS. WATER PUMPED THROUGH SAND AND GRAVEL TO FILTER OUT FURTHER PARTICLES CHLORINE AND OZONE ADDED TO KILL ANY BACTERIA LEFT. FLUORIDE ADDED Sewage Sewage is the waste from homes, businesses, industries. Basically what goes down toilets and sinks and drains. What happens to sewage? SEWAGE IS PUMPED TO SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT SEWAGE IS FILTERED TO REMOVE LARGER PARTICLES. CHEMICALS ADDED TO KILL BACTERIA, REMOVE SMELL, AND SMALLER PARTICLES THE “CLEANED” WATER IS NOW CALLED EFFLUENT AND PUMPED BACK INTO THE RIVER A gorgeous garden on Phi Phi island Thailand….but what was that smell???? Oh…… In rural areas with no access to sewage treatment, sewage is collected in septic tanks for trucks to collect New Sources of Water As fresh water supplies dwindle, we look to the sea for more water to desalinate Giant distillation stations separates the salt from the water. Water can also be put through reverse osmosis. Pressure pushes water through membrane Purified water Semipermeable membrane