* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
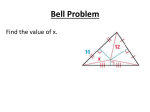
LESSON 5.3 Answers for the lesson “Use Angle Bisectors of Triangles” Skill Practice 16. No; you do not know that the perpendicular segment bisects the angle. 1. bisector 2. Perpendicular bisectors bisect line segments while angle bisectors bisect angles; both divide the segment or angle into two equal parts, and both have special points of intersection. 3. 208 4. 12 5. 9 6. Yes; BAD > CAD, } DB > } AB and } DC > } AC so by the Angle Bisector Theorem DB 5 DC. 7. No; you do not know that BAD > CAD. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved. 8. No; you do not know that } DB > } AB or } DC > } AC. 9. No; you don’t know that ]›, or } HG > } HF, } HF > EF ]›. } HG > EG 17. Yes; x 5 7 using the Angle Bisector Theorem. 18. B 19. 9 20. 8 21. GD is not the perpendicular }. The same distance from G to CE is true about GF; the distance from G to each side of the triangle is the same. 22. T is not the incenter of nUWY. Sample answer: } UZ > } ZY, } } } } WX > XY, and UV > VW 23. C 24. 6 25. 0.5 26. They all have the same length; Concurrency of Angle Bisectors of a Triangle Theorem. Sample: B 10. Yes; Converse of Angle Bisector Theorem 11. No; you don’t know that ]›. ]› or } } HF > EF HG > EG 12. 5 13. 4 14. 8 A C 15. No; the segments with length x and 3 are not perpendicular to their respective rays. Geometry Answer Transparencies for Checking Homework 146 27. Sample answer: Since nABC 30. AAS; HL; is a right triangle, its area is B 1 2 }(AB + AC). The area of nABC is also the sum of the areas of nABD, nADC, and nDBC. D A This sum is C 1 2 1 2 1 2 }x(AB) 1 }x(AC) 1 }x(BC), or 1 2 }x(AC 1 AB 1 BC). Setting B D A 1 2 }(AB + AC) equal to 1 }x(AC 1 AB 1 BC) and solving 2 C 31. a. Equilateral; 3; the angle bisector would also be the perpendicular bisector. AB + AC Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved. for x gives x 5 }} . AC 1 AB 1 BC b. Scalene; 6; each angle Problem Solving bisector would be different than the corresponding perpendicular bisector. 28. No; G is on the angle bisector of LBR. 29. At the incenter of the pond; A 32. Angle bisector; more; no; the diameter of the inscribed circle is greater than 5 inches. 33. Perpendicular bisectors; (10, 10); I 100 yd; about 628 yd; y B C P(10, 20) T(2, 4) N(16, 2) 5 2 x Geometry Answer Transparencies for Checking Homework 147 34. Statements (Reasons) 1. BAC is bisected by } AD, } } } } DB > AB, DC > AC. (Given) 2. BAD > CAD (Definition of angle bisector) 3. DBA and DCA are right angles. (Definition of perpendicular lines) 6. nABD > nACD (HL) 7. BAD > CAD (Corr. parts s are >.) of > n ]› bisects ABC. 8. AD (Definiton of angle bisector) 36. Statements (Reasons) 4. DBA > DCA (Right Angles Congruence Theorem) } bisects CAB, 1. nABC, AD }, } bisects CBA, DE } >AB BD }, DG } > CA }. (Given) } > BC DF 6. nABD > nACD 2. DGC, DFC, DFB, and DEB are right angles. (Def. of perpendicular lines) } > DA } (Reflexive Property 5. DA of Segment Congruence) 7. } DB > } DC Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved. 5. } AD > } AD (Reflexive Property of Segment Congruence) 8. DB 5 DC (AAS) (Corr. parts s are >.) of > n (Definition of congruent segments) 35. Statements (Reasons) 1. BAC with D in its interior, } DB > } AB, } DC > } AC, DB 5 DC. (Given) 2. ABD and ACD are right angles. (Definition of perpendicular lines) 3. nABD and nACD are right triangles. (Definition of right triangle) 4. } BD > } CD (Definition of congruent segments) 3. nCGD, nCFD, nBED, and nBFD are right triangles. (Definition of right triangle) BD > } BD, } CD > } CD 4. } (Reflexive Property of Segment Congruence) 5. EBD > FBD (Definition of angle bisector) 6. The angle bisector of ACB passes through point D, the incenter of nABC. (Definition of incenter) 7. GCD > FCD (Definition of angle bisector) 8. nCGD > nCFD, nDEB > nDFB (AAS) Geometry Answer Transparencies for Checking Homework 148 36. (cont.) 9. } DG > } DF, } DE > } DF s are >.) (Corr. parts of > n 10. } DG > } DE > } DF Mixed Review of Problem Solving 1. Sample answer: The park would be located outside of the county. (Transitive Property of Segment Congruence) Elk County 37. a. Use the Concurrency of Angle Bisectors of Triangle Theorem; if you move the circle to any other spot it will extend into the walkway. Q Elm County Z Deer County X Y Bear County R Forest County I 2. a. incenter; angle bisectors Q R Q R Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved. P b. HL c. 3.9 cm; (AE)2 1 (EG)2 5 P P b. Yes; the incenter will allow the largest tent possible. 38. Sample answer: Construct three circles exterior to the triangle, each one tangent to one side of the triangle and the other two lines. The centers of the circles are the three points. (GA)2 or 72 1 (EG)2 5 82 ‹]› 3. AC ; y 5 2x 1 9; the y-intercepts are 26, 4, and 9. The slope of the line with 9 as the y-intercept is 21 so the equation of that line is y 5 21x 1 9. y H(6, 8) A(4, 5) B(8, 6) 2 22 J(10, 4) G(2, 2) C(6, 3) x Geometry Answer Transparencies for Checking Homework 149 4. 9 ft; 9 5. a. 262 ft b. 840 ft2 Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved. 6. Equilateral triangle } i PR } 7. QPR, STU, TUR; ST } a transversal, so QPR with QP and QST are corresponding } i UT } a trans} with ST angles. PQ versal, so QST and STU are } i PR } alternate interior angles. ST } a transversal, so STU with TU and TUR are alternate interior angles and QST > TUR by the Transitive Property. Geometry Answer Transparencies for Checking Homework 150