* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Use Angle bisectors of triangles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
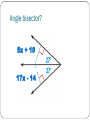
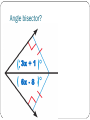
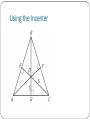
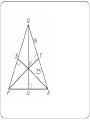
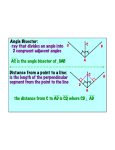
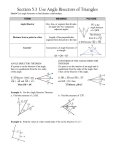
Use Angle bisectors of triangles Ch 5.3 In this section… We will use the properties of an angle bisector to solve for missing side lengths. That can’t be the only thing we need What is an angle bisector? to learn about angle bisectors! An angle bisector is a line or ray that divides an angle in half. The distance from the angle bisector to each of the sides of the angle are congruent and perpendicular to the sides of the angles. Angle Bisector? Angle Bisector? Angle bisector? 5x + 10 17x - 14 Angle bisector? 3x + 1 6x - 8 Page 313 #2 - 17 Point of Concurrency The angle bisectors will always intersect at a point called the incenter. If you draw perpendicular lines from that point to the sides of the triangle, then those segments are congruent. Perpendicular? Congruent? Sounds like some Using the Incenter stuffwill to me! potential ProblemsPythagorean that involve Theorem the incenter require you to at some point set some values equal to each other. Because the incenter deals with perpendicular lines, that does open up the possibility of using the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for missing sides and then set values equal. Using the Incenter Using the incenter Page 314, #19 - 25