* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Rocks are Formed
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary rock wikipedia , lookup
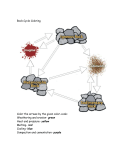
How Rocks are Formed http://magma.nationalgeographic. com/ngexplorer/0605/quickflicks/ Everywhere you look, you see ROCKS. The concrete high-rises are made from limestone. The Cement you walked on this morning – ROCKS The Mountains in the distance - ROCKS Bill Nye - ROCKS http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v3-JZQt1ws http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tBk1mj9 6EX8&feature=related Only show second clip until 2:27 Three Families of ROCKS Scientists group rocks into three major families, based on how they are formed. The three families are: Sedimentary Metamorphic Igneous Igneous Rock Forms when hot magma or lava cools and becomes solid Magma is melted rock found deep below Earth’s crust, where temperatures and pressures are high. Lava is molten rock on Earth’s surface. More Igneous Rock Geologists classify igneous rock based on whether it was formed above or below Earth’s surface. Rock that cooled below (in) Earth’s surface is called intrusive rock. ie Granite. Rock that forms when lava has cooled is called extrusive rock. Volcanic rocks such as pumice are extrusive. The size of the crystal in igneous rocks depends on how quickly the rock cooled. Sedimentary Rocks is made from sediment and/or by chemical reactions Sediment is loose material, such as bits of rocks, minerals, plants and animals. Sediment slowly settles over sediment, forming layers. Sedimentary rocks are usually made in the ocean and lakes where the larger, heavier fragments settle first. Each layer of sediment is squeezed together by the weight above it. The process of squeezing together layers of sedidment is called compaction. Cementation The minerals in some rocks dissolve as water soaks into the rocks. The dissolved minerals form a natural cement that sticks the larger pieces of sediment together. Other sedimentary rocks, such as limestone, are formed in water by a chemical change. The three processes that make sedimentary rocks are: Compaction Cementation Chemical Change Sedimentary Rocks and Fossils Fossils are evidence of once-living organisms. BC contains a wealth of fossils. Sedimentary rocks throughout the province contain fossilized shells, bones, scales, footprints, teeth and leaves. Fossils provide evidence of the environment and the climate in which the animals or plants lived. Scientists know that BC was once covered by tropical forests because tropical plant fossils have been discovered. Yoho Valley The fossils found in Yoho Valley (Eastern BC) are so special that it has been declared a World Heritage Site. It is home to some of the most famous and unusual fossils in the world. Burgess Shell Show Bill Nye at 2min http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4ve7lUy5910 Types of Fossils The remains of plants and dead animals decay and are destroyed quickly. When their remains are protected from bacteria and scavengers their bodies can be fossilized. Actual Remains – very rare – an entire animal or plant can be encased is amber, ice, natural paraffin or tar. Unaltered Hard Parts – Occasionally the unaltered bones of dinosaurs are found Carbonization – In the process, all of the volatile substances decay and leave behind a thin layer of carbon. Both plants and animals can be preserved by this method of incomplete decay. Petrifaction – After death of the organism, the organic matter starts to decay. Water containing dissolved mineral soaks into every cavity and begins to recrystallize. These fossils can be made of silica, calcite, pyrite or limestone. Moulds and Casts – These are formed when the animal or plant dies, decays and leaves a cavity in the sediment. Sometimes this cavity is not filled and remains a mould. Usually, however, more mineral matter is moved in by water and fills the mould to form a cast. Trace Fossils – These are indirect evidence of behaviour of the organism. Trace fossils can include tracks, track ways, eggs and nests, tooth marks, imprints, trails, and burrows. Imprints are external moulds of very thin objects, such as leaves. Coprolites are fossilized feces. Metamorphic Rocks Made when heat, pressure, or fluids change one type of rock into another type of rock. Can be made from igneous and sedimentary rocks. Also from other metamorphic rocks. The formation is a long and slow process! Metamorphic rocks are always formed below the surface of the Earth where heat an pressure are always high. More Metamorphic Rocks Hot, watery fluids can flow into igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic rock and change the rock both physically and chemically. The original rock that is being changed is called the parent rock. Metamorphic rocks that have layers are said to be foliated – thin, leaf like layers When the mineral structure changes, the metamorphic rock does not have layers and is said to be non-foliated.