* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COURSE INFORMATION Course Code: ES 201 Course Name
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
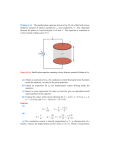
COURSE INFORMATION Course Code: ES 201 Course Name: Basic electrical and Electronics Engg.-II Contacts: 3L+1T=4 Credits: 4 COURSE OUTCOME At the end of this course, the incumbent will be able to: ES 201.1 Recall different laws of electrostatics and electromagnetisam and define various parameters related to electrostatics, electrical machines, FET, amplifiers. ES 201.2 Explain the working principle of DC machines, Induction motor, Transformer, FET and OPAmp. ES 201.3 Compute and solve practical oriented numerical problems dealing with 1Φ Transformers, DC machines, Induction motors and 3Φ system. ES 201.4 Draw phasor diagram of transformers and Induction motors and characteristic curves of different electrical and electronic devices mentioned earlier. ES 201.5 Compare among different types of Transformers, DC machines, Induction motors, 3Φ networks, FETs, Amplifiers. ES 201.6 Design and develop simple electronic circuits with FET, OPAmp and logic gates. PREREQUISITES To understand this course, the learner must have idea of: Elementary Physics, Mathematics Basic Electrical and Electronics Engg.-I SYLLABI Basic Electrical Electrostatics: Coulomb’s law, Electric Field Intensity, Electric field due to a group of charges, continuouscharge distribution, Electric flux, Flux density, Electric potential, potential difference, Gauss’s law, proof of gauss’s law, its applications to electric field and potential calculation, Capacitor, capacitance of parallel plate capacitor, spherical capacitor, isolated spheres, concentric conductors, parallel conductors. Energystored in a capacitor. DC Machines: Construction, Basic concepts of winding (Lap and wave). DC generator: Principle ofoperation, EMF equation, characteristics (open circuit, load) DC motors: Principle of operation, Speed - torque Characteristics (shunt and series machine), starting (by 3 point starter), speed control (armature voltage and field control) Single phase transformer: Core and shell type construction, EMF equation, no load and on loadoperation, phasor diagram and equivalent circuit, losses of a transformer, open and short circuit tests,regulation and efficiency calculation. 3 phase induction motor: Types, Construction, production of rotating field, principle of operation,equivalent circuit and phasor diagram, rating, torque-speed characteristics (qualitative only). Starter for squirrel cage and wound rotor induction motor. Brief introduction of speed control of 3 phase induction motor (voltage control, frequency control, resistance control) Three phase system: Voltages of three balanced phase system, delta and star connection, relationshipbetween line and phase quantities, phasor diagrams. Power measurement by two watt meters method. General structure of electrical power system: Power generation to distribution through overhead linesand under ground cables with single lone diagram. Basic Electronics Module – 1: Field Effect Transistors: Concept of Field Effect Transistors (channel width modulation), Gate isolation types, JFET Structure and characteristics, MOSFET Structure and characteristics, depletion and enhancement type; CS, CG, CDconfigurations; CMOS: Basic Principles. Module – 2: Feed Back Amplifier, Oscillators and Operational Amplifiers: Concept (Block diagram), properties, positive and negative feedback, loop gain, open loop gain, feedbackfactors; topologies of feedback amplifier; effect of feedback on gain, output impedance, input impedance,sensitivities (qualitative), bandwidth stability; effect of positive feedback: instability and oscillation, condition of oscillation, Barkhausencriteria. Introduction to integrated circuits, operational amplified and its terminal properties; Application of operational amplifier; inverting and non-inverting mode of operation, Adders, Subtractors, Constant-gainmultiplier, Voltage follower, Comparator, Integrator, Differentiator. Module – 3: Digital Electronics: Introduction to binary number; Basic Boolean algebra; Logic gates and function realization with OPAMPs. LECTURE PLAN Books/Study Materials Proposed Module Name. Sub Topics Electrostatics Coulomb’s law, Electric Field Intensity, Electric field due to a group of charges, Electric flux, Flux density, Electric potential, potential difference 1 Basic electrical,Thereja,D.P Kothari &Nagrath Gauss’s law, proof of gauss’s law, its applications to electric field and potential calculation 2 Basic electrical,Thereja,D.P Kothari &Nagrath 3 Basic electrical,Thereja,D.P Kothari &Nagrath Capacitor, capacitance of parallel plate capacitor, spherical capacitor, isolated spheres, concentric conductors, parallel conductors. Energy stored in a capacitor. D.C. Machines :Construction, Basic concepts of winding (Lap and wave). DC generator: Principle of operation, EMF equation, characteristics (open circuit, load) Required Lectures A TextBook of Electrical Technology, Vol. 2, B.L. Theraja, A.K. Theraja; 3 Principles of Electrical Machines, B.K. Meheta, RohitMeheta DC motors: Principle of operation, Speedtorque Characteristics (shunt and series machine), starting (by 3 point starter), speed control (armature voltage and field control) A TextBook of Electrical Technology, Vol. 2, B.L. Theraja, A.K. Theraja; 3 Principles of Electrical Machines, B.K. Meheta, RohitMeheta Single Phase Transformer Core and shell type construction, EMF equation, no load and on load operation 2 Phasor diagram and equivalent circuit, losses of a transformer 2 A TextBook of Electrical Technology, Vol. 2, B.L. Theraja, A.K. Theraja; A TextBook of Electrical Technology, Vol. 2, B.L. Theraja, A.K. Theraja; Open and short circuit tests, regulation and efficiency calculation. 3 Phase Induction Motor Three phase system: General structure of electrical power system: 2 Types, Construction, production of rotating field, 1 Principle of operation, equivalent circuit and phasor diagram, rating, torque-speed characteristics 2 Starter for squirrel cage and wound rotor induction motor 2 Introduction of speed control of 3 phase induction motor 1 Voltages of three balanced phase system, delta and star connection, 1 relationship between line and phase quantities, phasor diagrams 1 Power measurement by two watt meters method 1 Power generation to distribution through overhead lines and under ground cables with single lone diagram 1 Field Effect Transistors 1 Concept of Field Effect Transistors (channel width modulation), Gate isolation types, JFET Structure and characteristics Feed Back Amplifier, Oscillators and Operational MOSFET Structure and characteristics, depletion and enhancement type 2 CS, CG, CD configurations; CMOS: Basic Principles 2 Concept (Block diagram), properties, positive and negative feed back, loop gain, open loop 1 A TextBook of Electrical Technology, Vol. 2, B.L. Theraja, A.K. Theraja; A TextBook of Electrical Technology, Vol. 2, B.L. Theraja, A.K. Theraja; A TextBook of Electrical Technology, Vol. 1, B.L. Theraja, Electronics Devices and Circuits, J.B. Gupta Electronics Devices and Circuit theory, R.L. Boyelstad Electronics Devices and Amplifiers: gain, feed back factors; Digital Electronics Circuits, J.B. Gupta; Topologies of feed back amplifier; effect of feed back on gain, output impedance, input impedance, sensitivities, bandwidth stability; 2 Effect of positive feed back: instability and oscillation, condition of oscillation, Barkhausen criteria. 2 Introduction to integrated circuits, operational amplifier and its terminal properties; 1 Intigrated Electronics, Millman&Halkias; Application of operational amplifier; inverting and non-inverting mode of operation, Adders, Subtractors, Constant-gain multiplier, Voltage follower, Comparator, Integrator, Differentiator 4 Electronics Fundamentals and Applications, Rakshit, Chattopadhyay Introduction to binary number; Basic Boolean algebra 2 Logic gates and function realization with OPAMPs. 3 Electronics Fundamentals and Applications, Rakshit, Chattopadhyay RECOMMENDED READINGS TEXT 1. Basic electrical,Thereja,D.P Kothari &Nagrath 2. A TextBook of Electrical Technology, Vol. 2, B.L. Theraja, A.K. Theraja; 3. Principles of Electrical Machines, B.K. Meheta, RohitMeheta 4. Boyelstad&Nashelsky: Electronic Devices & Circuit Theory. REFERENCE 1. 2. Millman&Halkias: Integrated Electronics Schilling &Belove: Electronics Circuits Electronics Fundamentals and Applications, Rakshit, Chattopadhyay