* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics and Pedigrees Bio I
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
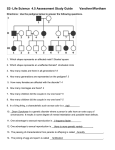
Genetics & Pedigrees Gregor Mendel Vocabulary Genetics-the study of inheritance or heredity Inheritance- the passing on of traits from one generation to the next Trait/Characteristic- any factor used to describe or distinguish Vocabulary Acquired trait- a trait that appears in your lifetime. You were not born with it. It cannot be passed onto offspring Inherited trait- a trait that you were born with. You can pass it onto offspring Gene- a segment of DNA that controls/influences our physical/ psychological/ intellectual/ emotional traits a segment of DNA that codes for the production of a protein Allele- a specific expression of a gene. You inherit one allele from each parent for a specific trait. You have 2 alleles for each gene 1 from your Mom 1 from your Dad Homozygous- both alleles for a specific trait are identical (purebred) -Homozygous dominant (Ex. BB) -Homozygous recessive (Ex. bb) Heterozygous- both alleles for a specific trait are different (hybrid) Ex. Bb Genotype- Combination of alleles; genetic make-up Homozygous BB, Heterozygous Bb Phenotype- Physical appearance; what that combination of alleles looks like Blue or Brown Dominant vs. Recessive Traits/Disorders Dominant Oval face shape Widow’s peak Separated eyebrows Dimples Free earlobe Almond eye shape Freckles Tongue roller Recessive Square face shape Straight hairline Unibrow No dimples Attached earlobe Round eye shape No freckles Non-roller Dominant Inability of tongue folding Mid-digit finger hair Straight thumb Dark skin Near-sidedness Far-sidedness Bent pinky finger Recessive Ability of tongue folding No hair Hitch-hiker thumb Fair skin Normal vision Normal vision Straight pinky finger Dominant trait/disorder If B= brown hair And b= blonde hair Then: BB= brown hair Bb= brown hair bb= blonde hair The heterozygous individual shows the trait Dominance- in the heterozygous genotype, the allele expressed in the phenotype is dominant; the allele that is not expressed is recessive. Dominance is NOT determined by how often the trait appears (frequency of occurrence) in the population! Recessive trait/disorder A carrier is heterozygous (Bb) But now, that recessive trait is “hidden” by the dominant allele Therefore, the heterozygous individual does not show that recessive trait They carry it and can pass that recessive allele on to children Pedigree a family tree that traces a trait through generations Recessive trait/disorder With recessive traits, carriers are represented in a pedigree as a ½-shaded circle/square… When drawing a pedigree, you must always know if the trait is dominant or recessive before shading individuals and determining genotypes and phenotypes