* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20: Digestive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
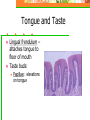
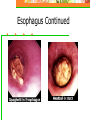
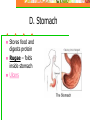
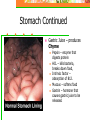
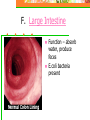
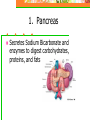
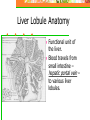
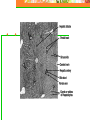
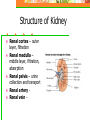
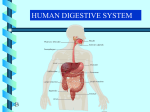
Chapter 20: Digestive System Chapter 21: Urinary System Functions of Digestion Ingest food Break down food in to small molecules: Mechanical digestionChemical digestion – Absorption Elimination Carbohydrates Include sugars and their polymers Monomer is the monosaccharide Include 3 – 7 carbons with the –OH group being present on each carbon except one, which is double bonded to an oxygen (carbonyl group) Lipids A group of polymers that have one characteristic in common, they do not mix with water. They are hydrophobic. Some important groups are fats, phospholipids, and steroids. Enzymes Increase speed of chemical reactions catalyst A protein Can change shape if conditions are not favorable. Alimentary Canal Hollow tube that begins at the mouth, ends at the anus Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Rectum A. Mouth • Forms a bolus Chemical digestion – mucous, amylase (break down carbs) Mechanical digestion: chewing Roof of mouth: Hard palate Soft palate Tongue and Taste Lingual frendulum – attaches tongue to floor of mouth Taste buds: Papillae: elevations on tongue Salivary Glands Saliva – water mucous, amalase Parotid – front of and below ears. (mumps) Sublingual submandibular B.Pharynx Region between mouth and esophagus “throat” Function – swallowing Epiglottis – blocks larynx Uvula – back of throat C. Esophagus 3. 4. 5. Lined by mucous membrane and smooth muscle Peristalsis – involuntary contraction of esophagus Heartburn – (acid reflux) Esophagus Continued D. Stomach Stores food and digests protein Rugae – folds inside stomach Ulcers Stomach Continued Gastric Juice – produces Chyme Pepsin – enzyme that digests protein HCL – kills bacteria, breaks down food, Intrinsic factor – absorption of B12. Mucous – softens food Gastrin – hormone that causes gastric juice to be released. E. Small Intestine Function- receives secretions from the liver, pancreas and absorption of nutrients. Lined with Villi – furry looking, absorption, increase surface area F. Large Intestine Function – absorb water, produce feces E.coli bacteria present Disorders of Large Intestine Diarrhea – Constipation – Appendicitis – Diverticuloisis – colon cancer Colonoscopy Part 2: Digestive System Accessory organs – food does not pass through 1. Pancreas Secretes Sodium Bicarbonate and enzymes to digest carbohydrates, proteins, and fats 2. Liver – Largest gland Storage of glucose as glycogen Destruction of old red blood cells – this creates bilirubin Production of bile Plasma proteins Detoxification of blood Storage of iron and other vitamins Liver Lobule Anatomy Functional unit of the liver. Blood travels from small intestine – hepatic portal vein – to various liver lobules. 3. Liver Disorders Hepatitis – inflammation of the liver due to contaminated drinking water, sexual transmission, or blood transfusion Cirrhosis of liver Cirrhosis – chronic disease due to excessive amount of alcohol. Liver becomes fatty tissue. Jaundice Jaundice – yellowish tint due to large amounts of bilirubin in blood. C. Gallbladder Storage of bile – emulsifies fats and neutralize acids Chapter 21 Excretory system Structures of Urinary System 1. 2 kidneys 2. 2 ureters – tube that leads to bladder 3. Bladder – stores urine 4. Urethra – tube for eliminating urine Structure of Kidney Renal cortex – outer layer, filtration Renal medulla – middle layer, filtration, absorption Renal pelvis – urine collection and transport Renal artery Renal vein - Functions of Kidney I. Kidney Function – filter blood that has collected wastes from cells. A. Excrete waste – urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium B. Maintain blood volume – regulating water excretion C. monitor electrolytes in blood D. monitor blood pH E. secrete Renin – enzyme to help maintain blood pressure F. stimulates red blood cell production Lipids A group of polymers that have one characteristic in common, they do not mix with water. They are hydrophobic. Some important groups are fats, phospholipids, and steroids.