* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Programlama ve Nesneler
Software quality wikipedia , lookup
Scala (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Go (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Program optimization wikipedia , lookup
Functional programming wikipedia , lookup
Java (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Programming language wikipedia , lookup
Object-relational impedance mismatch wikipedia , lookup
One-pass compiler wikipedia , lookup
Software bug wikipedia , lookup
History of compiler construction wikipedia , lookup
Reactive programming wikipedia , lookup
Java ConcurrentMap wikipedia , lookup
Abstraction (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Java performance wikipedia , lookup
Structured programming wikipedia , lookup
Cross compiler wikipedia , lookup
Interpreter (computing) wikipedia , lookup
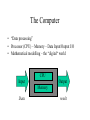
Object-Oriented Programming Week 1: Introduction Mustafa Emre İlal Course Objectives • Programming in Java • Object-Oriented Programming (Nesne Yönelimli Programlama) • Software development process • Computational design support tools • An awareness in Computation Evaluation • • • • Assignments (%20) Midterm (%30) Project (%20) Final Exam (%30) Mustafa Emre İlal [email protected] 1982 BASIC (Commodore PET) 1987 PASCAL (Apple IIe) 1993 B.Arch. - YTÜ 1994 C/C++/Lisp/Clips (UNIX) 1996 M.Sc. in Arch.– Acoustic Simulation 1997 Java (Distributed Systems) How about you? • Why programming? If you needed someone to develop software, who would you go to? Why be a programmer? • Software development is a field of specialization • Software – System Software – User Applications • Consultants are inadequate – “cook yourself – eat yourself” ;) • New fields for architects (the evolving profession) – Web Design (visualization) – Building Information Modeling – 5D tools (specialization) – Information Technology Consulting (perspective) Architects and Programming • Against the training of Architects – – – – Constrained: Mathematical models Strickt: No room for emotional decisions “Planned": Well defined train of thought Analytical: Every step is a calculated one • Our goal is to get over these obstacles Architects and Programming • Architects are very successful – Creativity – Ability to evaluate at various levels – Ability to see sub tasks within the main task • “Pogramming is an art.” Previous Experience in Programming • ++ Solving algorithms – Defining/solving a problem – Main task / sub tasks • -- Structural programming habits – Combining data and behaviour – Missing object – class relationship Computer Program • A sequence of instructions to perform a specified task • Need a common language between the instructors and the ones receiving the instructions • Examples: – Road directions – Cooking recipes The Computer • “Data processing” • Processor (CPU) – Memory – Data Input/Output I/O • Mathemetical modelling – the “digital“ world CPU Input Output Memory Data result Languages • Human natural languages: Turkish, English, Chinese, … • Computers: 00010101000101010111 – İntel x86, Alpha, PowerMac • Programming Languages: systems that convert English into “cumputerish” – “take the value of variable x, add it to the value of variable y and store the result in variable z" “Computerish" • A Compiler – Takes the source code (series of instructions) and converts them into machine code. – After the conversion is done once, the machine code can be run multiple times. – The machine code is platform specific – can only run on the type of computer (64 bit, x86, etc.) the conversion was targeting. • An Interpreter – The conversion is done on-the-fly as the program is run. – The interpreters are platform specific, not the programs themselves – Each run requires a conversion and therefore is slower Java • Has both a compiler and an interpreter • The compiler converts into a “byte code” that can turn into machine code easily • The interpreter interprets this byte-code Other languages • Machine Code • Assembly Language • High Level Languages – Fortran, COBOL, Pascal, C/C++ • Interpreted Languages – BASIC, Perl Software Engineering + Internet • An increasing complexity in systems – Simple programs • Ran on individual computers – Modular programming • Separate programs that were able to communicate within a computer (inter-process communication) – Client/Server architecture • Programs communicating across computers – Distributed systems • Networks of programs Object orientation • Common problems with growing complexity – Tracking of variables – Control mechanisms • The answer: Objects and encapsulation – Status - variables – Behavior - control • “Capsules” (independent agents) that larger systems can be built upon. – Code reuse! Objects • Objects can be seen as “agents” with well defined job descriptions • An abundance of fancy terms – no need for alarm: – – – – – Object, Instance Encapsulation, information hiding Inheritance, generalization Subclass, superclass Polymorphism • Easier if you have no programming background. Visual Elements • Java was developed for the internet – Byte-code is transferred and run on “virtual machines” • To turn web pages into an interactive media • Application – Applet • This course will not focus on windowing and visual elements Next Week • • • • • • Objects Classes Encapsulation Messaging Inheritance Your first Java program Assignment • Install the Java 2 Platform (J2 Standard Edition) – j2se 1.4.2_xx SDK (Software Developer Kit) – j2se 1.4.2 Documentation • java.sun.com – Tutorial -> Java Tutorial • First Cup of Java • Getting Started • www.mindview.net – Thinking in Java