* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mesopotamia - MStew
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
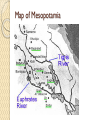
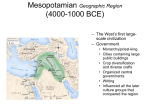
The Revolving Door of Mesopotamia Mesopotamia Mesopotamia means: Mesopotamia means: “land between two rivers” Civilization developed between The Euphrates and Tigris Rivers By 3000 B.C. a number of civilizations established by the Sumerians Map of Mesopotamia Role of the Environment Rivers provided the basics for exsistance • Water • Food • Sanitation Role of the Environment Problems with living hear a river valley? - Destroyed by frequent floods that ravaged entire cities - Communication amongst the various isolated cities was very difficult Invention of Writing Origins of Writing probably go back to te ninth millennium B.C. 4th millennium – realized that drawing tokens was easier than making tokens Result was the development of cuneiform: - “wedge-shaped” - Pictographic system Cuneiform Sumerian Inventions Wagon wheel Potter’s wheel (shape containers) Number system 12 month calendar Metal plow Sail Some of the earliest known maps New architecture Sumer, 3200-2350 B.C. Sumerian Society Sumer was different from all other earlier civilizations ◦ Advanced cities ◦ Specialized workers ◦ Complex institutions ◦ record keeping ◦ Advanced technology Developed city-states Food surplus > increased population > expanded trade > expansion of Sumerian society Sumer Society Polytheistic - believed in many gods Wrote myths (Epic of Gilgamesh) ◦ Priests and kings were at the top ◦ Slaves were at the bottom Women probably couldn’t attend school but had many other rights Advances in mathematics ◦ Number system based on 60 (60 seconds = 1 minute) From Sumerians to Babylonians The Sumerians city-states eventually fell to foreign invaders (2000 B.C.) The Akkadians: ◦ Semites – nomaidc people from the Arabian Peninsula that migrated to Mesopotamia ◦ Sargon I (2300-2200 B.C.E.) unites all Mesopotamia (created first empire) ◦ Under Sargon I Akkadians adopted Sumerian religion and farming Sargon’s Empire Babylonian Empire Located in modern day Syria Conquered many parts of old Sumer (including Babylon) Hammurabi –created a law code with harsh punishments Borrowed heavily from Sumerian culture After Hammurabi’s death Babylon declined Hammurabi of Babylon, 17921750 B.C.E Hittites A strong army with chariots Conquered Babylon in 1595 B.C.E. Borrowed from Mesopotamian and Egyptian culture Had a law code less harsh than Hammurabi’s Lasted until about 1200 B.C.E Assyrians Started to gain strength about 900 B.C.E Powerful army Treated conquered people cruelly Large empire with good roads Collapsed about 612 B.C.E Chaldeans Defeated the Assyrians in about 612 B.C.E Descended from Hammurabi’s Babylonians At its height during the rule of Nebuchadnezzar (605-562B.C.E) ◦ Spent a lot of money on Babylon ◦ Built Hanging Gardens Empire collapsed in 539B.C.Wafter being defeated by Persians Hanging Gardens of Babylon Persians Cyrus (conquered from the Nile to the Indus Darius I (son is Xerxes) ◦ Administered the empire using satrups (governors) ◦ Tolerant of those who were conquered ◦ Increased trade and build roads ◦ Lost to the Greeks in 480 B.C.E