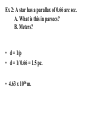* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astro 1 ppt - Red Hook Central Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
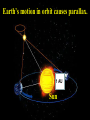
Astronomy Contents of the universe We live in the solar system. Earth orbits the sun every yr in elliptical orbit. Distance Earth to sun 1 AU Birth of the Solar System Solar system born ~4.5 BYA 2 min http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= qfdDWdZcpOw Our Solar System planets/moons/asteriods Asteroid Belt mars-Jupiter Icy Comets -All orbit the sun -very elliptical orbits Solar system is part of the milky way galaxy. Orion Arm. The galaxy revolves around black hole. Sun revolution ~ 250 million y. Galaxies –large aggregates of stars, gas, & dust containing ~ 100 billion (1011) stars ranging in diameter from 1,500 to 300,000 light-years across. Orbit central point. Av distance btw stars 10 ly. Stars can form stellar clusters w/i galaxies – smaller groups of stars held by gravity. ~ 1000’s of stars. Constellations – star groups not necessarily near each other. Galaxies form groups too. Galactic Clusters • Nearest cluster = Virgo cluster Open Cluster • also galactic cluster- a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. Contain gas and dust Globular Cluster - older • Generally outside Milky Way in Halo. Nebulae • Gas clouds – Star nurseries • Formed after Big Bang • from supernova It’s a long way btw stars. Use Light Years LY The d light travels in 1 yr. • 1 LY = 9.46 x 10 15 m. • 1 AU = 1.5 x 10 11m • 1 pc parsec = 3.09 x 1016 m Powers of 10 Film 6:30 min http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tnhken4_-A0 Earth’s Rotation makes stars appear to rotate on fixed sphere. Rotation is around Polaris on 24 h cycle. Sun/planets wander through stellar backdrop. From Earth Stars Appear to be embedded in sphere. Stars rotate around Polaris 24 hr cycle rise east set west Stars appear fixed on sphere relative to each other. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JCr_Pz4h2Bw Planetary Motion Wanderer & Retrograde • Know the planets in order, their relative sizes, the asteroids, Kuiper belt. • Clusters, galaxies, nebula Measuring Stellar Distances • Stellar Parallax few hundred pc • Absolute & Apparent Magnitudes • Spectroscopic Parallax • Cepheid variables distance Stellar Parallax • Hold up pencil • Blink eyes • Pencil moves against backdrop. • Look at post. • Blink eyes. Earth’s motion in orbit causes parallax. 1 AU Sun Measure Parallax Angle • Angles are very small – measured in arc seconds. Angular Measurements • expressed in degrees, arc-minutes or arc-seconds. • 360o in circle • 1° = 60 arc minutes. • 1 arcminute = 60 arc sec. • 1 pc= distance where an object has a parallax angle (p) of one arc second. Stellar Parallax d = 1/p p = 1/d d (dist) – #parsecs p (parallax angle) – #arc-seconds. Ex 1: The nearest star to Earth is Alpha Centauri, which is at a distance of 4.37 ly. Calculate the parallax angle that was measured to obtain that distance. • 4.37 LY / 3.26 = 1.34 pc. • p = 1/d • 0.746 arc-sec 1/1.34 pc Ex 2: A star has a parallax of 0.66 arc sec. A. What is this in parsecs? B. Meters? • d = 1/p • d = 1/ 0.66 = 1.5 pc. • 4.63 x 1016 m. Why can’t stellar parallax be used to measure very distant stars? • Angle gets too small. Few hundred pc upper limit. Parallax Method Clip 11 min • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XUQAI ldqPww