* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parallax - mjeffries
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting instrument wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
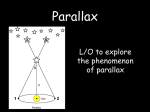
Parallax • How do we tell what is close and what is far? Triangles • A triangle is determined by the length of the base and the opposite angle. • If the base is fixed, the height is measured by the angle. base angle A angle B Measuring Triangles • How can the measurement of the triangle be improved? 1. Make the base larger. 2. Measure the angle more accurately. Apparent Shift • • • • A moving observer sees fixed objects move. Near objects appear to move more than far objects. Telephone poles whip by faster than distant trees. The effect is due to the change in observation point, and is used by our eyes for depth perception. angle A base angle B Apparent Shift • Earth’s orbit serves as our longest baseline. • From January… Apparent Shift • To July. • Notice the apparent change in position of the near star when compared to the distant stars in the background. Observing Parallax • Observe your thumb against the background below. • Hold your hand in front of your right eye and move your thumb so it appears to be in front of the number25. • Without moving your head, move your hand in front of your other eye. • Note the shift in numbers and direction. 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 Shifting Stars • If the orbit of Earth is used as the base,Near stars appear to move more than far stars. site A site B Stellar Parallax • A photo of the stars will show the shift. site A site B Observing Parallax • Repeat with your thumb against the background below, only this time, hold your hand closer to your right eye. • Now move your thumb so it again appears to be in front of the number25. • Without moving your head, move your hand in front of your other eye. • Note the greater shift in numbers. 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 Sources of Parallax • Heliocentric parallax uses the sun as a base. • Take a photo at two different seasons. • Geocentric parallax uses the earth as a base. • Take a photo two times in one night. Parsec • Distance is related to the shift in parallax. • A shift of one arc-second is about 3.3 ly. • This parallax-second is defined as one parsec. next