* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 231 Geometry Test 1 Review
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
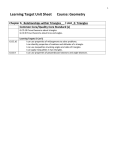
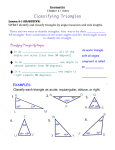
Math 231 Geometry Test 1 Review 2.1 axiomatic systems: undefined terms, definitions, postulates, theorems know the definitions and postulates given in this section, postulates 2.1 – 2.5 in particular know the notation for lines, segments, rays, angles 2.2 types of triangles: equilateral, isosceles, scalene, acute, right, obtuse polygons and number of sides: triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, octagon types of quadrilaterals: square, rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, kite circles: diameter, radius 2.3 Thm: the sum of measures in a triangle = 180º vertex angles in a polygon / diagonals Thm: the sum of measures of the vertex angles in any polygon is (n − 2)180 Thm: the measure of each vertex angle in a regular polygon is (n − 2)180 n given a diagram find the measures of the indicated angles 3.1 perimeter of a polygon, circumference of a circle areas of triangles and rectangles 3.2 areas of parallelograms, trapezoids, regular polygons, circles 3.3 Pythagorean Theorem: use to solve a missing side in a right triangle 30-60-90 triangles, 45-45-90 triangles: use to solve for missing sides applications of right triangles 4.1 conditional statements, biconditional statements, deductive reasoning converse, inverse, and contrapositive forms of conditional statements 4.2 definition of congruent triangles congruence postulates 4.3 proofs involving congruent triangles theorems: isoscles triangles, equilateral triangles, perpendicular bisectors Note: You do not have to memorize the definitions, postulates, and theorems word for word, although you can if it helps. You will not be required to write them out word for word on the test. However, you should understand what each one says (in your own words or the text’s) well enough to apply it in a proof or computation and well enough to answer true/false questions.