* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 371ch6S11
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
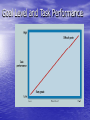
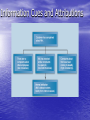
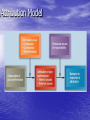
Learning a change in behavior acquired through experience Conditioning Classical Conditioning – Modifying behavior so that a conditioned stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stimulus and elicits an unconditioned response Operant Conditioning – Modifying behavior through the use of positive or negative consequences following specific behaviors Positive and Negative Consequences Positive Consequences Results of a behavior that a person finds attractive or pleasurable Negative Consequences Results of a behavior that a person finds unattractive or aversive Reinforcement, Punishment, and Extinction Reinforcement – cultivates desirable behavior by bestowing positive consequences or withholding negative ones. Punishment – discourages undesirable behavior through negative consequences, or withholding positive consequences. Extinction – weakens behavior by attaching no consequences to it. Bandura’s Social Learning Theory Prior experiences Persuasion from others Task-Specific Self-Efficacy – an individual’s internal expectancy to perform a specific task effectively. Assessment of physical and emotional capabilities Behavior models Learning and Personality Differences Goal Setting at Work the process of establishing desired results that guide and direct behavior Characteristics of Effective Goals Specific Measurable Attainable Realistic Time-bound Goal Level and Task Performance Goal-Setting Functions Increase work motivation and task performance Reduce role stress associated with conflicting or confusing situations Improve accuracy and validity of performance evaluation Increase Work Motivation and Task Performance • The higher the goal, the better the performance. • Need to ensure: – employee participation – supervisory commitment – useful performance feedback Reduce Role Stress • Goals clarify task-role expectations communicated to employees • Improves communication between managers and employees Improve Performance Evaluation Management by Objectives (MBO) – a goal-setting program based on interaction and negotiation between employees and managers Articulates what to do. Determines how to do it. Performance Management a process of defining, measuring, appraising, providing feedback on, and improving performance Performance Management Process Define performance in behavioral terms Measure and assess performance Feedback for goal setting and planning Improved Performance Performance Appraisal the evaluation of a person’s performance. Performance Appraisal • Provides feedback to employees • Identifies employees’ developmental needs • Decides promotions and rewards • Decides demotions and terminations • Develops information about the organization’s selection and placement decisions Actual and Measured Performance Communicating Performance Feedback • Refer to specific verbatim statements and observable behaviors • Focus on changeable behaviors • Both supervisor and employee should plan and organize before the session • Begin with something positive 360-Degree Feedback a process of self-evaluation and evaluations by a manager, peers, direct reports, and possibly customers o 360 Feedback Self Evaluation Customer Evaluation Manager Evaluation Feedback Peer Evaluation Reports Develop People and Enhance Careers [Supervisor should] • • • • • ] Coach and develop employees Be vulnerable and open to challenge Maintain a position of responsibility Listen empathetically Encourage employee to talk about hope and aspirations [Employee should] • Take responsibility for growth and development • Challenge supervisor about future development • Express individual preferences and goals Effective Appraisal Systems [Key Characteristics] • Validity • Reliability • Responsiveness • Flexibility • Equitableness Organizations get the performance they reward, not the performance they say they want. © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Individual or Team Rewards? Individual rewards • foster independent behavior • may lead to creative thinking and novel solutions • encourage competitive striving within a work team Team rewards • emphasize cooperation and joint efforts • emphasize sharing information, knowledge, and expertise Learning Outcome List several strategies for correcting poor performance. Correcting Poor Performance Identify primary cause or responsibility Determine problem’s source Develop corrective plan of action Kelley’s Attribution Theory Explains how individuals pinpoint the causes of their own and others’ behavior Consensus – the extent to which peers in the same situation behave the same way Distinctiveness – the degree to which the person behaves the same way in other situations Consistency – the frequency of a particular behavior over time Information Cues and Attributions Information Cues and Attributions Attribution Model