* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Congenital heart diseases is a category of heart disease that
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
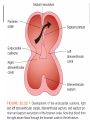
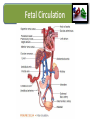
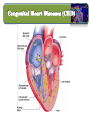
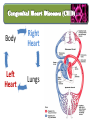
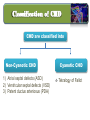
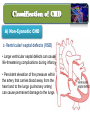
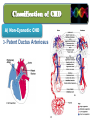
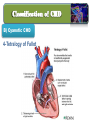
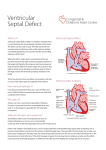
Lecture II Congenital Heart Diseases Dr. Aya M. Serry 2016 The Fetal Heart • The heart is the first functioning organ in the embryo. • Its first pulsatile movements begin during the third week after conception. • This early development of the heart is essential to the rapidly growing embryo as a means of circulating nutrients and removing waste products. • Most of the development of the heart and blood vessels occurs between the third and eighth weeks of embryonic life. Definition: • Congenital heart diseases is a category of heart disease that includes abnormalities in cardiovascular structures that occur before birth • Approximately 8 out of every 1,000 newborns have congenital heart defects, ranging from mild to severe • Congenital heart defects may produce symptoms at birth, during childhood, or not until adulthood. Other congenital defects may cause no symptoms Fetal Circulation Fetal Circulation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-IRkisEtzsk https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DC_wlkRPzw0 Congenital Heart Defects • Pathophysiology: • Abnormal Shunting of Blood • P. 833 (Chapter 32 from textbook) Symptoms: The symptoms of congenital heart disease in infants and children include: • Cyanosis (a bluish tint to the skin, fingernails, and lips) • Fast breathing and poor feeding • Poor weight gain • Recurrent lung infections • Inability to exercise In more severe cases, these problems may develop shortly after birth. However, symptoms sometimes don't develop until the teenage years or early adulthood. Diagnosis: Congenital heart disease is often first detected when your doctor hears an abnormal heart sound or heart murmur when listening to your heart Depending on the type of murmur your doctor hears, he or she may order further testing such as: •Echocardiogram •Cardiac catheterization •Chest X-ray •Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) Risk Factors In the majority of people, the cause of congenital heart disease is unknown. However, there are some factors that increase chance of having congenital heart disease. These risk factors include: • Genetic or chromosomal abnormalities in the child, such as Down Syndrome • Taking certain medications or alcohol or drug abuse during pregnancy Risk Factors Cont’d • Maternal viral infections, such as (German measels) in the first trimester of Pregnancy • The risk of having a child with congenital heart disease may double if a parent or a sibling has a congenital heart defect Body Right Heart Left Heart Lungs CHD are classified into Non-Cyanotic CHD 1) Atrial septal defects (ASD) 2) Ventricular septal defects (VSD) 3) Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Cyanotic CHD 4- Tetralogy of Fallot A) Non-Cyanotic CHD 1- Atrial septal defects (ASD) • Normally, a small opening between the two atria (foramen ovale) is present at child birth. • Shortly after birth, the atrial septum gradually grows and seals this opening •In infants with atrial septal defects, the atrial septum may not close properly or may be malformed during fetal development. • In these disorders, the opening between the atria persists long after it should be closed, resulting in an increase in the workload on the right side of the heart and excessive blood flow to the lungs A) Non-Cyanotic CHD 2- Ventricularl septal defects (VSD) • Ventricular septal defects can occur in any portion of the ventricular septum. •The size and location of the defect determine the severity of the symptoms. Small ventricular septal defects can close on their own (spontaneously) or become less significant as the child matures and grows • Moderately-sized defects can cause congestive Heart Failure, which is characterized by an abnormally rapid rate of breathing (tachypnea), wheezing, unusually fast heartbeat (tachycardia) A) Non-Cyanotic CHD 2- Ventricularl septal defects (VSD) • Large ventricular septal defects can cause life-threatening complications during infancy • Persistent elevation of the pressure within the artery that carries blood away from the heart and to the lungs (pulmonary artery) can cause permanent damage to the lungs A) Non-Cyanotic CHD 3- Patent Ductus Arteriosus A) Non-Cyanotic CHD 3- Patent Ductus Arteriosus • The ductus arteriosus is a normal fetal blood vessel that closes soon after birth. •In a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) the vessel does not close and remains "patent" resulting in irregular transmission of blood between two of the most important arteries close to the heart, the aorta and the pulmonary artery • A patent ductus arteriosus allows a portion of the oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs by flowing from the aorta (which has higher pressure) to the pulmonary artery B) Cyanotic CHD 4-Tetralogy of Fallot B) Cyanotic CHD Tetralogy of Fallot • Most common form of cyanotic heart disease • Cyanosis is the abnormal bluish discoloration of the skin that occurs because of low levels of circulating oxygen in the blood B) Cyanotic CHD Tetralogy of Fallot consists of the combination of four different heart defects: 1- a ventricular septal defect 2- obstructed outflow of blood from the right ventricle to the lungs (pulmonary stenosis) 3- a displaced aorta, which causes blood to flow into the aorta from both the right and left ventricles 4- abnormal enlargement of the right ventricle (right ventricular hypertrophy) THANK YOU…..