* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Engineering - Mr. Kerins
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
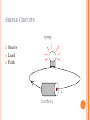
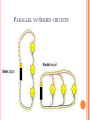
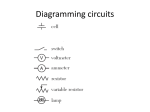
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Mr. Kerins ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Definition- is the design and construction of electrical and electronic components and devices 21% of all engineers are Electrical ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEGREE REQ’S Coursework: Electricity Electronics Chemistry Biology Physics High level Math Statistics IEEE Institute of Electrical and electronics Engineers 375,000 members 160 Countries Goal and Purpose; Dedicated to advancing technological innovation and excellence through their publications, conferences, standards, and activities ELECTRONIC BASICS Flow of Electrons Negative to Positive Moving At Speed of Light (24 x around earth in 1 second) Schematics are a must ELECTRONIC BASICS 3 Requirements for a complete circuit Source Load Path TYPES OF ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS Engineers must weigh unique benefits and drawbacks for each given circuit Circuits can be designed in three ways: Series Parallel Series in Parallel SIMPLE CIRCUITS Source Load Path SERIES CIRCUITS Has only ONE path for electrons/current to flow Runs through each load back to source Voltage drop is same among all loads If path or load is broken will not work PARALLEL CIRCUITS Have multiple paths and more than one load. Voltage across each path is equal to source voltage PARALLEL VS SERIES CIRCUITS SOLDERING A must for electronics A fusion of allows which have a low melting point Makes Connections Permanent and electrons flow Allow Combination of two or more metals SOLDER Definition:combination of lead and tin in various ratios 60/40 solder Avoid acid core solder Used in electronics and plumbing Low melting point among metals – 375degrees F(avg) SOLDER SAFETY Wear Safety Goggles Avoid contact with skin and eyes Conscience of soldering iron tip Avoid Fumesventilation Cold Solder Joint Don’t interrupt someone who is soldering SOLDERING – PROJECT Wire Strip 5 Wires and Solder them together safely OHMS LAW Relationship between resistance, current, and voltage in electrical circuits. Extremely important component in electrical engineering Discovered by German Physicist George Ohm OHMS LAW E – Electromotive Force Amount of pressure causing electrons to flow Greater the pressure of electrons higher the voltage Measured in Voltage Could See “E” or “V” E = I (R) OHMS LAW Resistance – Opposition of current flow. Measured in ohms Resistors are used to limit current flow and divide voltage Resistor- Color band codes Variable vs. Fixed Resistors R = E/I OHMS LAW Intensity- Measure of the flow of electrons per unit of time. Also known as Coulomb, current or intensity I or A can be used for symbols of intensity Measured in Amps I = E/R OHMS LAW Power- product of current and voltage Measured in watts One watt is equal to one volt moving one amp of electricity at one second P = I(E) ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PROJECT Line following mouse? Breadboard? Solder Project?