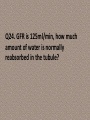* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download renal physiology tutorial discussion
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac output wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Circulatory system wikipedia , lookup
Biofluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hemodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
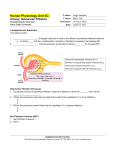
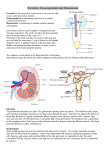
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY TUTORIAL DISCUSSION Dr. Zahoor TOPICS • • • • Nephron Glomerular Filtration Tubular Reabsorption (Lect 3 & 4) Tubular Secretion Q1. What are functions of kidney? Q2. What are components of nephron? Q3. Draw the nephron and label its parts. Q4. What are differences between cortical and juxta medullary nephron? Q5. What is vasa recta? Q6. What is juxta glomerular apparatus and what is its function? Q7. What is Glomerular Filtration? Q8. Define Glomerular Filtration Rate? Q9. Name the 3 layers of Glomerular membrane. Q10. Is the Glomerular membrane more permeable or less permeable than other capillaries. Give reason. Q11. Basement Membrane of Glomerular membrane has positive or negative charge. What is the importance? Q12. When blood passes through glomerulus, what blood substances are NOT filtered? Q13. Write the full word and value for - PGC - πGC - PBS Full word ________ ________ ________ Value ______ ______ ______ Q14. How much is the Net Filtration Pressure? Q15. What factors increase or decrease GFR? Give five factors. Q16. Kf (Filtration Coefficient) depends on what factors? Q17. Name two mechanisms responsible for Autoregulation in kidney. Q18. What is the range of mean arterial blood pressure, when kidney is doing Autoregulation? Q19. How much is - Renal Blood Flow _________ - Renal Plasma Flow _________ - GFR - _________ Q20. What is filtration fraction? How much is it? Q21. Name the two substances used to measure GFR. Q22. Name the blood constituents present in the glomerular filtrate. Q23. After filtration, how much percentage of the following substances is reabsorbed in the tubule Water ___ % Sodium ___ % Glucose ___ % Q24. GFR is 125ml/min, how much amount of water is normally reabsorbed in the tubule? Q.25. How much percentage of the following substances is reabsorbed in PCT Na+ _____ H2O _____ Q26. Na+ - K+ pump is operating where in the epithelial cell, for Na+ reabsorption? Q27. Name the hormone which helps in Na+ reabsorption in DCT and CT. Q28. What is JGA? Q29. Renin is secreted from where in the nephron? Q30. What is the function of principal cells? Where they are present? Q31. What is function of ANP? Q32. What is the function of ADH? Where does it act? Q33. Is Descending limb of LH permeable to Na+ Q34. Is Ascending limb of LH permeable to H2O? Q35. Name the receptors where ADH acts in the CT? Q36. Name the channels where ADH acts in CT. Q37. Where ADH is produced? Q38. Where ADH is stored? Q39. What causes increase ADH release? Q40. If ADH is not there, how much amount of urine person will pass? Q41. What is Diabetes Insipidus? What are two types of DI? Q42. What is Secretion? Q43. What is importance of Secretion? Q44. Name the substances secreted. Q45. Where K+ is secreted? Q46. Name the cells where K+ is secreted in DCT and CT. Q47. What is the control of K+ secretion in DCT and CT ? Q48. What is the action of Aldosterone on principal cells for K+ secretion? Q49. In Hyperaldosteronism, what happens to K+ secretion? Q50. In Acidosis, what happens to K+ secretion? Q51. Why K+ regulation is important? Thank you