* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Constructive and Destructive Landforms
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Overdeepening wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
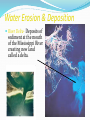
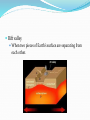
Two Types of Forces Destructive Forces: processes that destroy landforms. 2 types: Slow (weathering) and Fast (Erosion) Ex. landslides, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, floods Constructive forces: forces that build up an existing landform or create a new one. Caused by: water, gravity, wind and glaciers. Ex: deposition, landslides, volcanic eruptions, floods Weathering Weathering is the breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces. Rain, ice, and atmospheric gases cause this. Physical/ Mechanical weathering Rocks are broken into smaller pieces by physical agents. Ice wedging. Plant and animal actions. Water Chemical weathering Breaking down of rocks due to the chemical change in their composition. Air and water often cause this. Oxidation (rust) and acid rain. Erosion The process that moves rock material at Earth’s surface and caries it away. Movement of the rock particles. Causes of erosion… Gravity-landslides/rockslides. Running water-rivers form canyons Groundwater-underground water forms caves/caverns Glaciers-rocks are carried under a glacier. Wind-rock particles are blown Ocean currents-sand is moved along a beach by waves. Constructive Landform Processes Processes that build up Earth’s surface and cause the land surface to rise. Deposition The process by which eroded material is dropped off or deposited in a new area. Gravity Water Wind Glaciers Ocean currents Volcanic Eruptions Volcano: ??? an opening in the Earth’s crust through which steam, lava and ashes erupt. Cause both destructive and constructive changes to landforms. Volcanoes can be constructive, but also destructive… Folding and Faulting Forces in Earth’s surface caused by the movement of Earth’s plates squeezes and bends the surface of Earth. Folding occurs when the crust is bent upward or downward. Faulting occurs when the crust is actually broken. Volcanic Activity The movement of liquid rock underground and on earth’s surface. Magma is hot liquid rock beneath the Earth’s surface. Magma is less dense than solid rock so it rises to the surface. This forms a volcano. When volcano’s erupt, they release hot liquid rock called lava. Lava will harden forming new landforms. Mount St. Helens Saint Helen’s Before Saint Helen’s After Earthquakes Earthquakes: the shaking of Earth’s surface caused by the release of energy along a fault. San Andreas Fault, California Volcanoes & Earthquakes Tectonic Plates, Volcanoes & Earthquakes Landforms from Erosion Canyons/valleys Flowing water removes sediment. Sea cliffs Waves erode rock making steep cliffs. Sea caves, arches, and stacks. Landforms from Deposition Flood plains Sediments deposited when rivers overflow their banks. Deltas and Alluvial Fans When a stream flows into a large body of water (lake/ocean) or onto land, it deposits sediment in a fan shape. Delta-fan shaped pattern in a lake or ocean. Alluvial fan-fan shaped pattern on land. Water Erosion & Deposition River Delta- Deposits of sediment at the mouth of the Mississippi River creating new land called a delta. Beaches Area of shoreline made up of sediment deposited by ocean currents and waves. Landforms from Folding and Faulting Block mountains Large areas of Earth are forced upwards in a fault. Rift valley When two pieces of Earth’s surface are separating from each other. Folded mountains When the surface of Earth is bent upward making a mountain. Landforms from Volcanic Activity Volcanoes Dome mountain Magma forces the surface of Earth up into a dome shaped mountain. Plateau Primetime What are two examples of destructive forces? What are four examples of constructive forces? Give an example where constructive and destructive forces work together to create a landform.